ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries
ACG 臨床指引: 肝功能異常的評估


♥ 評估肝功能異常應該再重覆檢驗。
♥ C 型肝炎應該驗anti-HCV 及HCV-RNA。
♥ 慢性 B 型肝炎應該驗 HBsAg,急性 B 型肝炎應該驗 HBsAg IgM anti-HBc。
♥ 急性 A 型肝炎應該驗 IgM HAV。急性E型肝炎應該驗 IgM HEV。
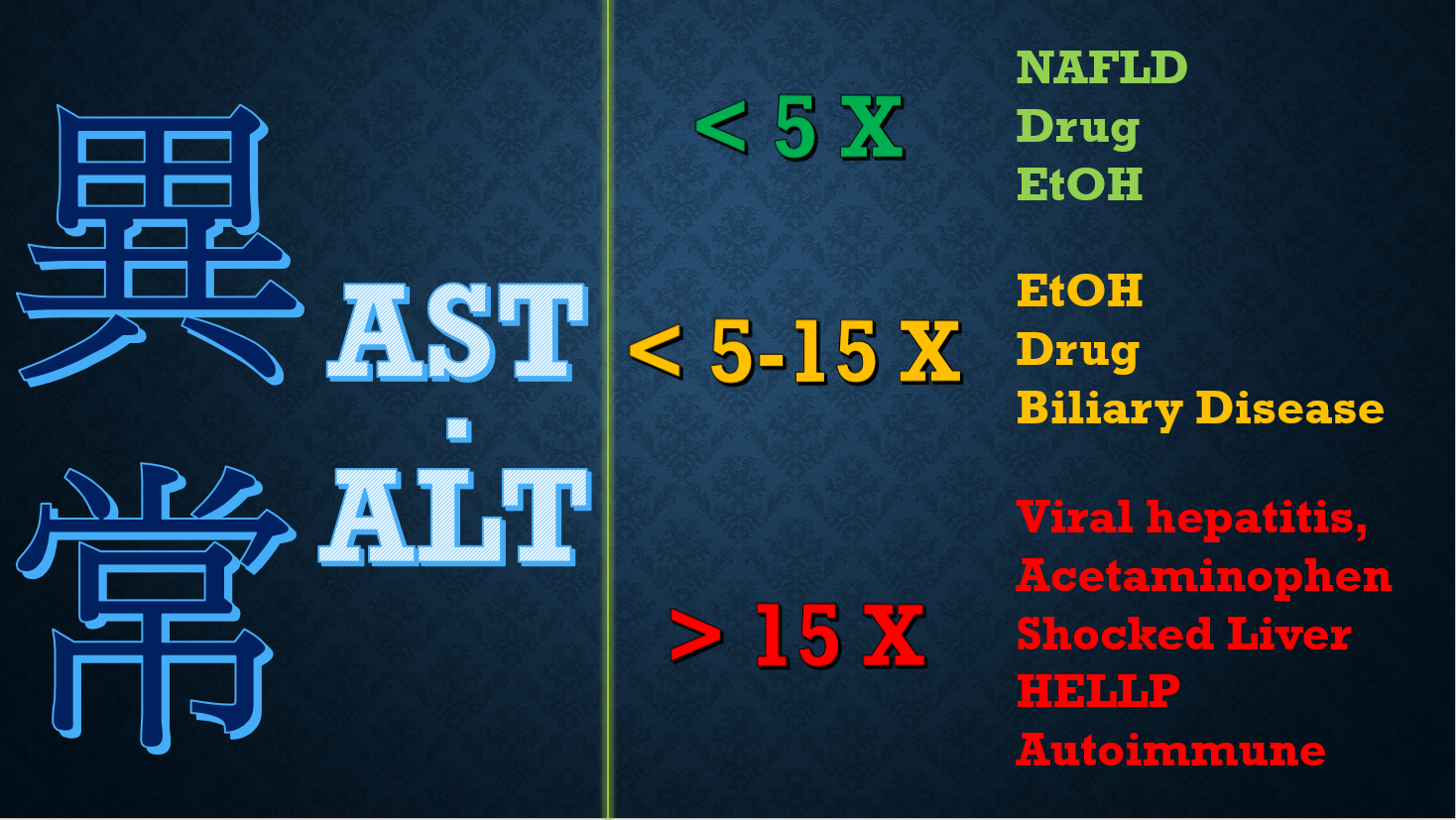
♥ 女性每週酒精攝取超過 140 g,男性每週酒精攝取超過 210 g,合併 AST>ALT 應該考慮酒精性肝病。

♥ 當病人肝功能異常但無病毒性肝炎應該考慮血鐵沉積症。
♥ 病人肝功能異常也應該考慮自體免疫疾病。
♥ Wilson’s disease 也應該考慮假如病人年紀小於55歲
♥ 肝臟切片是最後的方式來診斷肝功能異常原因。

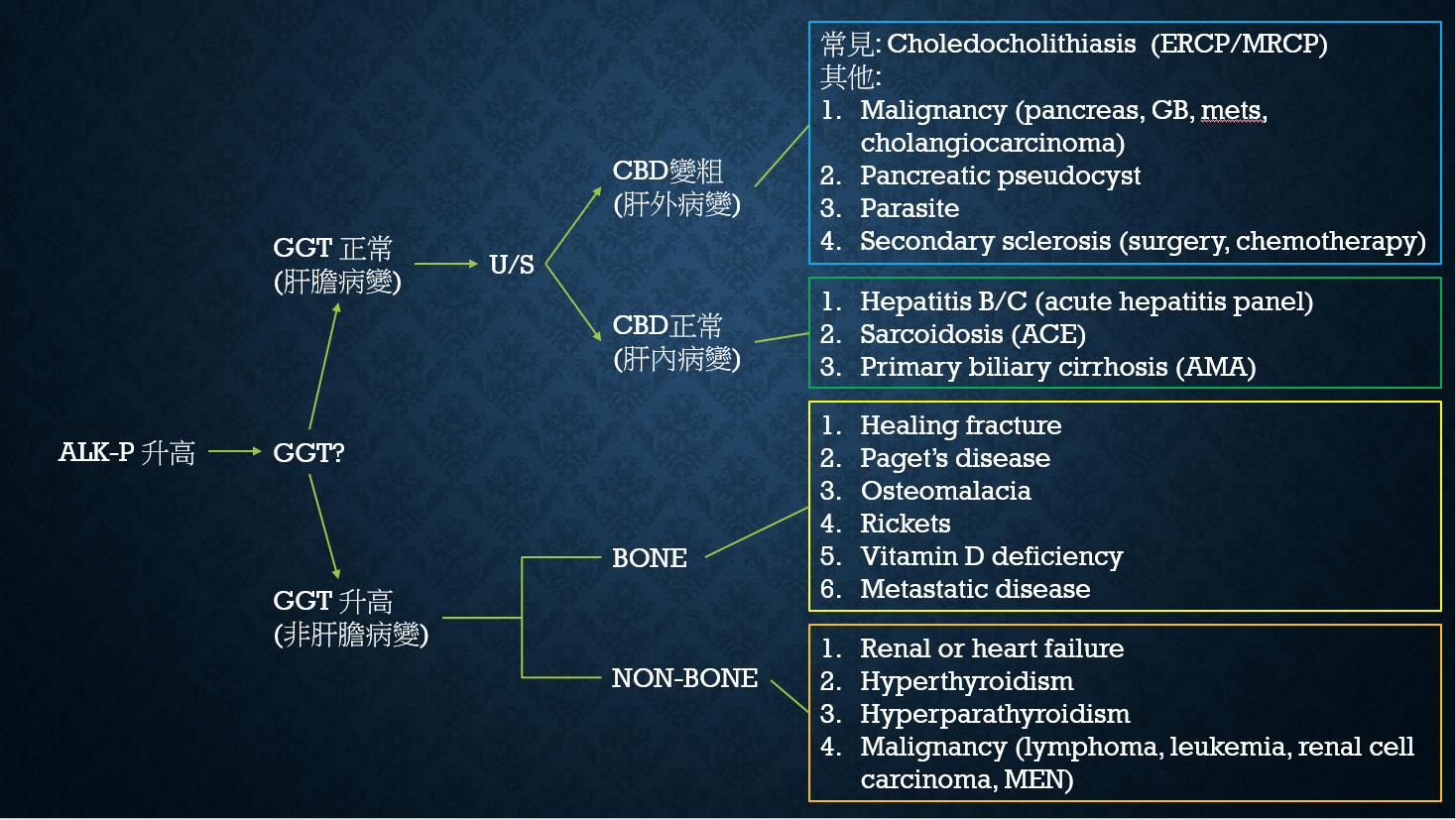
♥ Alk-P 跟 GGT 應該一同來評估肝功能異常,不可單獨來看。
♥ 病人 Alk-P 升高但無膽紅素升高應該考慮 PSC 應該要驗 anti-mitochondrial antibody。
♥ 病人呈現急性肝炎、PT 延長或肝性腦病變應該轉至肝臟專家。
造成AST及ALT升高的原因:
| Hepatic (generally AST>ALT) | Non-hepatic |
|---|---|
| Alcoholic liver disease | Skeletal muscle damage/rhabdomyolysis |
| Cirrhosis (of any etiology) | Cardiac muscle damage |
| Ischemic hepatitis | Thyroid disease |
| Congestive hepatopathy | Macro-AST |
| Acute Budd-Chiari syndrome | Strenous exercise |
| Hepatic artery damage/thrombosis/occlusion | Heat stroke |
| TPN | Hemolysis |
| Hepatic (generally ALT>AST) | Adrenal insufficiency |
| NAFLD | |
| Steatosis | |
| NASH | |
| Chronic viral hepatitis | |
| Acute viral hepatitis | |
| Medications and drug-induced liver injury | |
| Prescription medications | |
| Herbal products and supplements | |
| Over-the-counter agents | |
| Toxic hepatitis (amanita exposure) | |
| Hemochromatosis | |
| Autoimmune hepatitis | |
| Wilson’s disease | |
| Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency | |
| Celiac disease | |
| Acute bile duct obstruction | |
| Liver trauma | |
| Post-liver surgery | |
| Veno-occlusive disease/sinusoidal obstruction syndrome | |
| Diffuse infiltration of the liver with cancer | |
| HELLP syndrome | |
| Acute fatty liver of pregnancy | |
| Sepsis | |
| Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis |
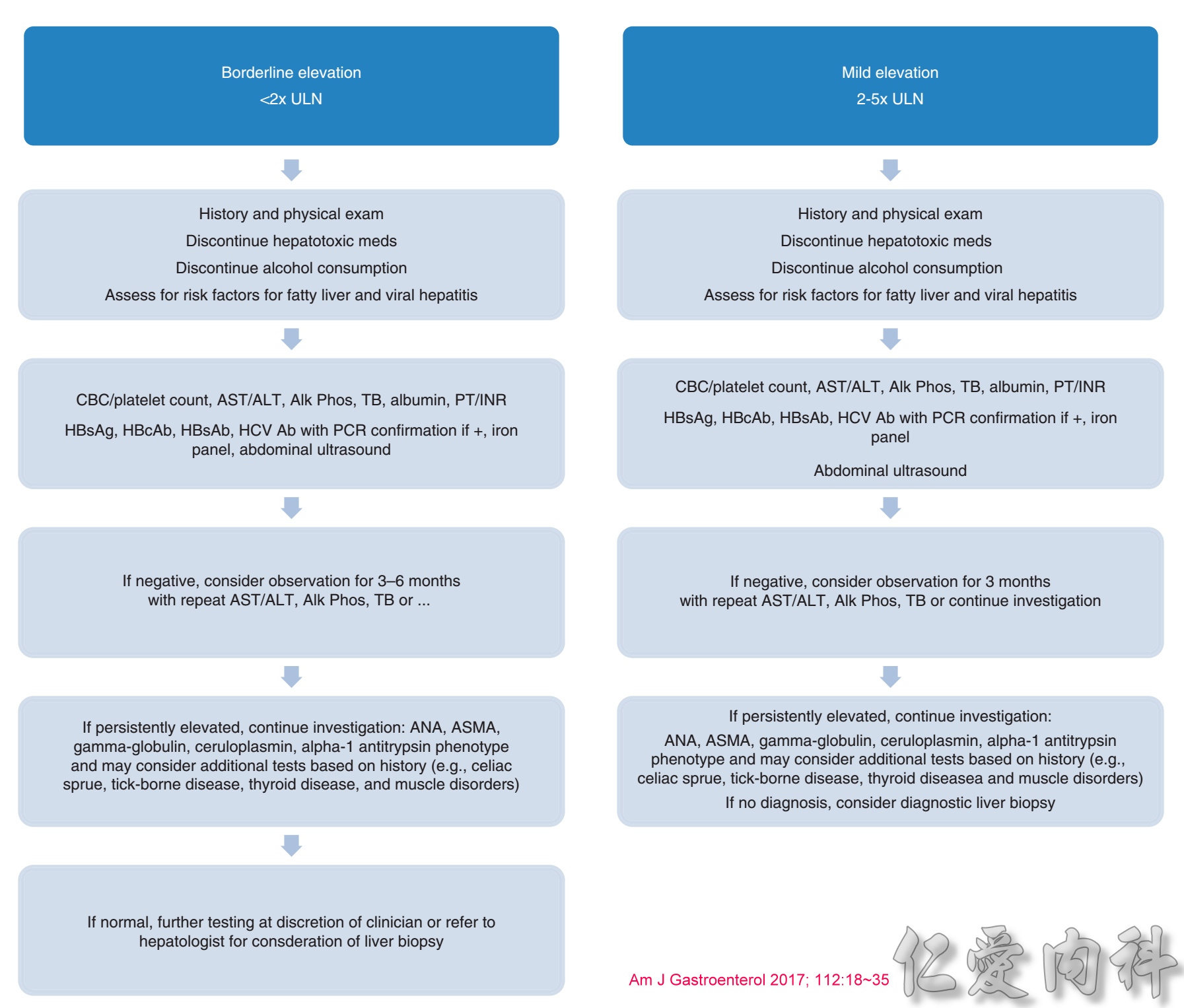
AST及ALT異常(小於兩倍上限值、二到五倍上限值)評估流程表 :
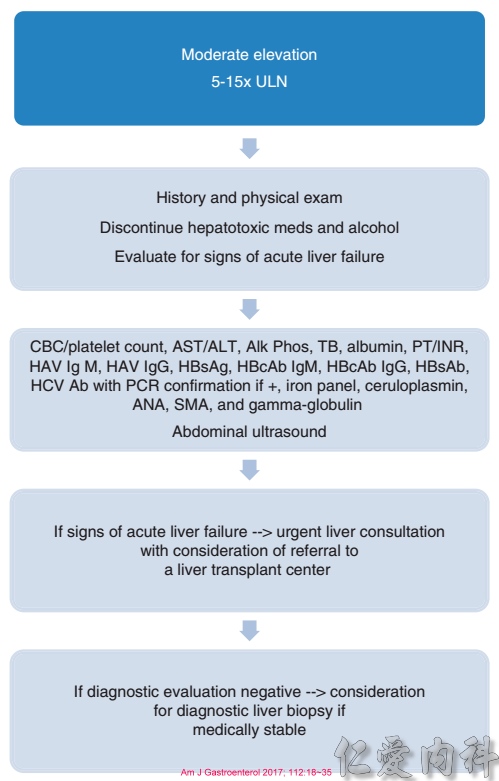
AST及ALT異常(五到十五倍上限值)評估流程表:
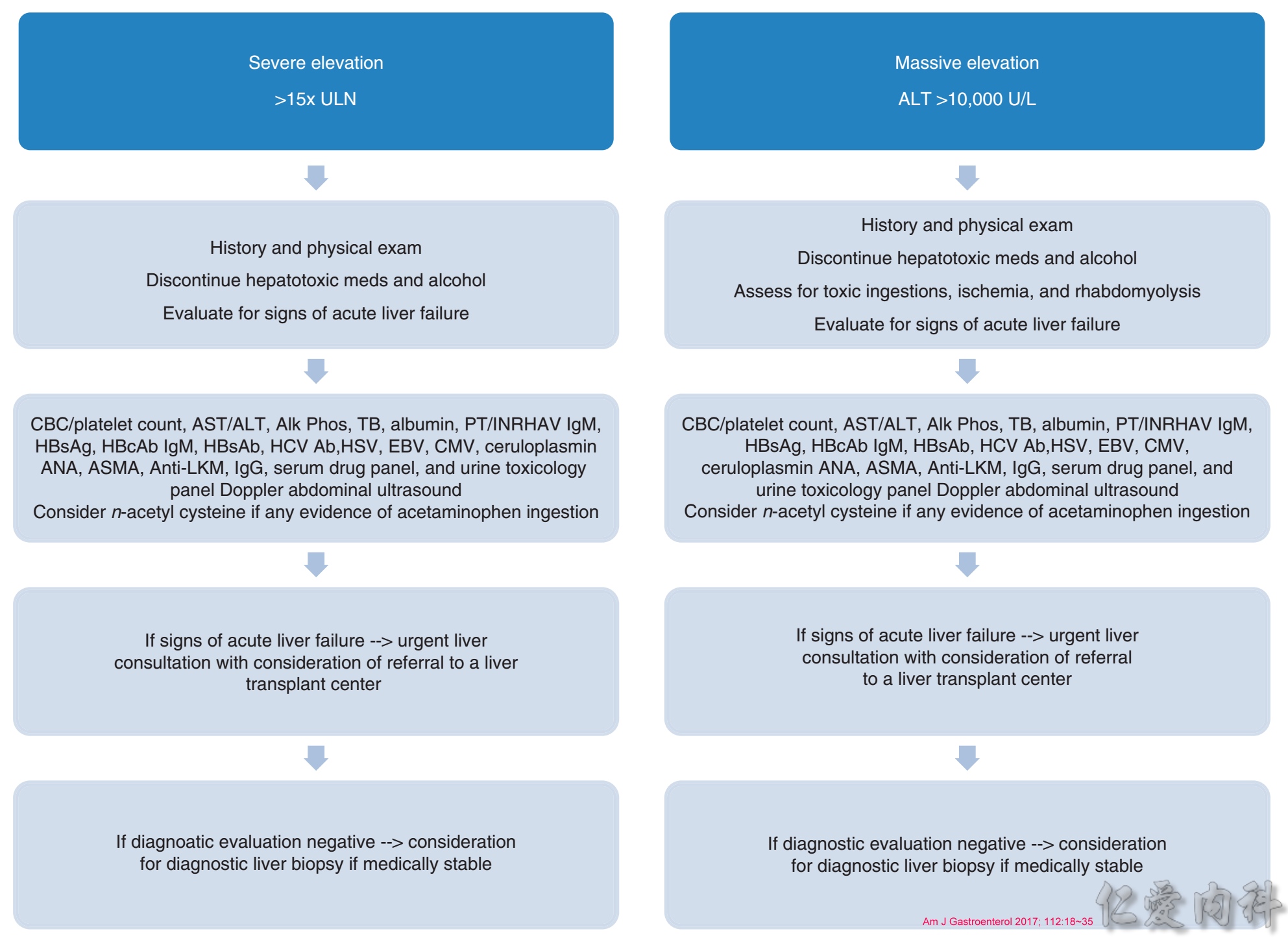
AST及ALT異常(超過十五倍上限值或ALT大於10000 U/L)評估流程表:
造成 Alk- P升高的原因 :
| Hepatobiliary | Non-hepatic |
|---|---|
| Bile duct obstruction | Bone disease |
| Choledocholithiasis | Osteomalacia |
| Malignant obstruction | Paget’s disease |
| Bile duct flukes | Primary bony malignancy |
| Bile duct stricture | Bony metastases |
| Ductopenia | Hyperthyroidism |
| AIDS cholangiopathy | Hyerparathyroidism |
| Cholestatic liver diseases | Pregnancy (third trimester) |
| Primary biliary cirrhosis | Chronic renal failure |
| PSC | Lymphoma |
| Medications and drug-induced liver injury | Extra-hepatic malignancy |
| Infiltrative diseases of the liver | Congestive heart failure |
| Sarcoid | Childhood growth |
| Granulomatous hepatitis | Infection |
| Tuberculosis | Inflammation |
| Amyloid | Influx of alkaline phosphatase after a fatty meal |
| Metastatic cancer | Blood type O and B |
| Lymphoma | Myeloid metaplasia |
| Hepatic abscess | Peritonitis |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | Diabetes mellitus |
| Viral hepatitis | Gastric ulcer |
| Cirrhosis | Increasing age, especially women |
| Vanishing bile duct syndrome | |
| Ischemic cholangiopathy | |
| Benign recurrent cholestasis | |
| Sarcoidosis | |
| Alcoholic liver disease | |
| Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy | |
| Benign post-operative jaundice | |
| ICU jaundice or multifactorial jaundice | |
| TPN | |
| Liver allograft rejection | |
| Acute alcoholic hepatitis | |
| Sickle cell liver crisis | |
| Sepsis | |
| Congestive heart failure | |
| Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis |
[註] PSC, primary sclerosing cholangitis; TPN, total parenteral nutrition
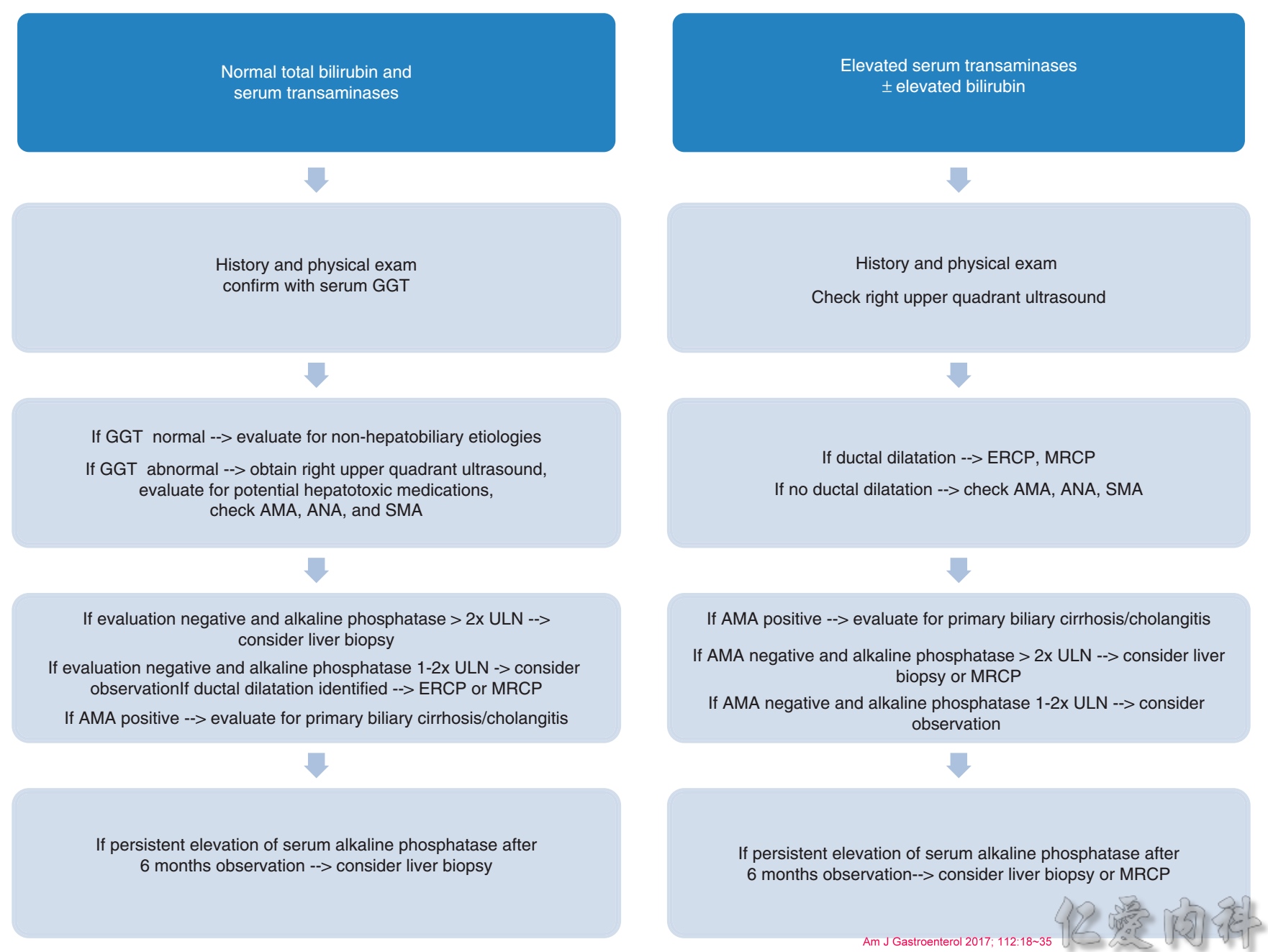
Alk-P升高的評估流程表:
造成膽紅素升高的原因 :
| Elevated conjugated hyperbilirubinemia | Elevated unconjugated bilirubin |
|---|---|
| Bile duct obstruction | Gilbert’s syndrome |
| Choledocholithiasis | Crigler-Najjar syndrome |
| Malignant obstruction | Hemolysis (intravascular and extravascular) |
| Bile duct flukes | Ineffective erythropoiesis |
| Bile duct stricture | Resorption of large hematomas |
| AIDS cholangiopathy | Neonatal jaundice |
| Viral hepatitis | Hyperthyroidism |
| Toxic hepatitis | Medications |
| Medications or drug-induced liver injury | Post-blood transfusion |
| Acute alcoholic hepatitis | |
| Ischemic hepatitis | |
| Cirrhosis | |
| Primary biliary cirrhosis | |
| PSC | |
| Infiltrative diseases of the liver | |
| Sarcoid | |
| Granulomatous hepatitis | |
| Tuberculosis | |
| Metastatic cancer | |
| Lymphoma | |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | |
| Wilson disease (especially fulminant Wilson’s disease) | |
| Autoimmune hepatitis | |
| Ischemic hepatitis | |
| Congestive hepatopathy | |
| Sepsis | |
| TPN | |
| Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy | |
| Benign post-operative jaundice | |
| ICU or multifactorial jaundice | |
| Benign recurrent cholestasis | |
| Vanishing bile duct syndrome | |
| Ductopenia | |
| Dubin-Johnson syndrome | |
| Rotor syndrome | |
| Sickle cell liver crisis | |
| Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis |
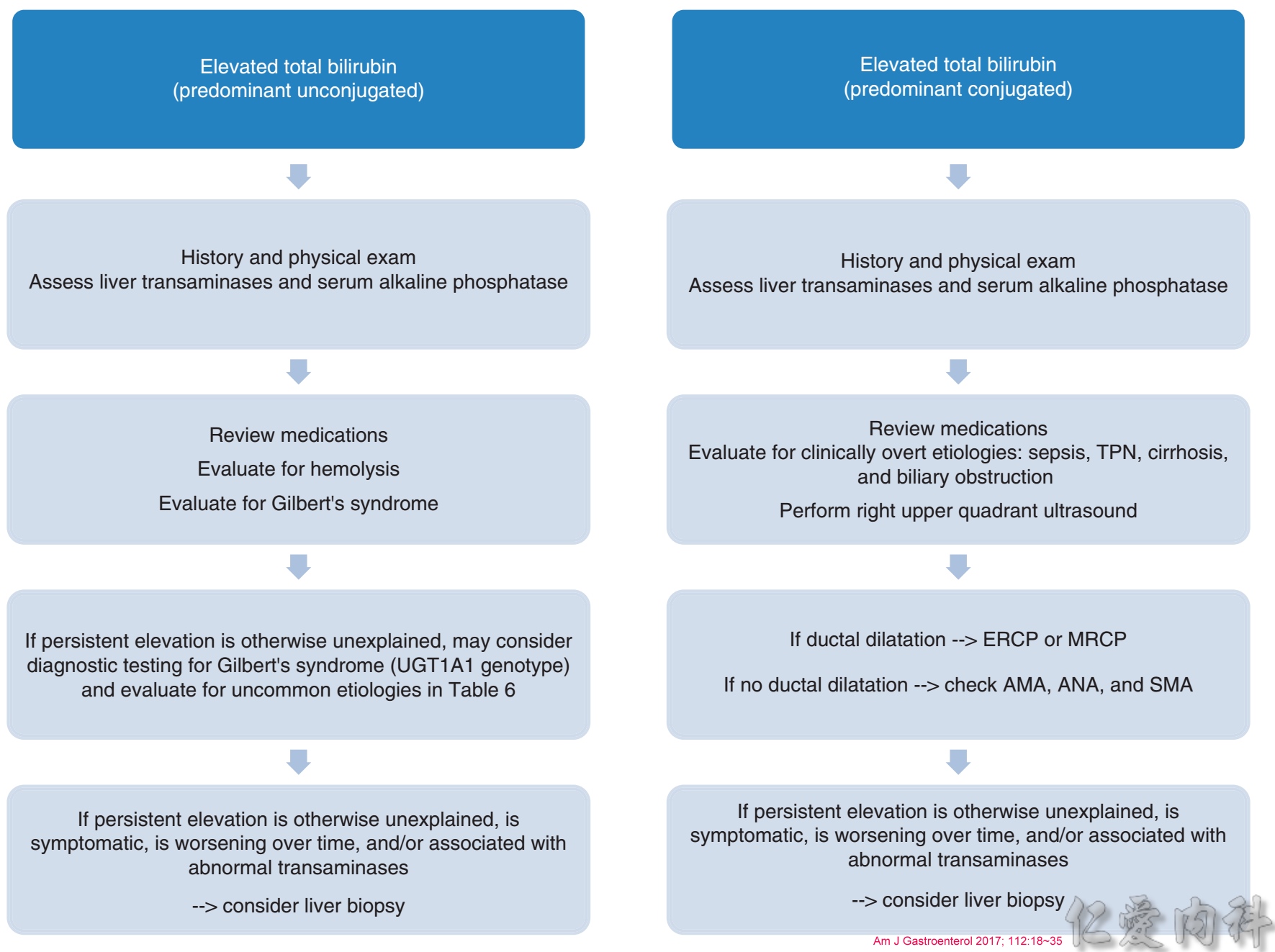
膽紅素升高的評估流程表:
整體而言, 造成異常的 hepatic panel (含AST, ALT, Alk-P, bilirubin, albumin) 的原因可以歸為三類:
- 肝細胞受傷 (hepatocellular damage)
- 膽汁鬱積 (cholestasis)
- 功能性受損 (functional impairment在 hepatic panel 中僅 albumin 可以真正反應肝臟工作的狀況)
關於 AST 與 ALT 升高時較為常見的幾個 differential diagnoses:
Alkaline Phosphatase升高的鑑別診斷流程:
[Latest revision by the Editorial Panel]