作者/講者: 李宜蓉 醫師
整理: Ian YC Chen, MD
校稿: Ian YC Chen, MD
上次校閱: 2018/07/22
本次內容是針對 AHA/ASA 所提出之 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke 進行介紹。內容分為 6 大部分:
第一部分為 Prehospital Stroke Management and Systems of Care,與我們醫院處置較無關係,因此不在本次討論。
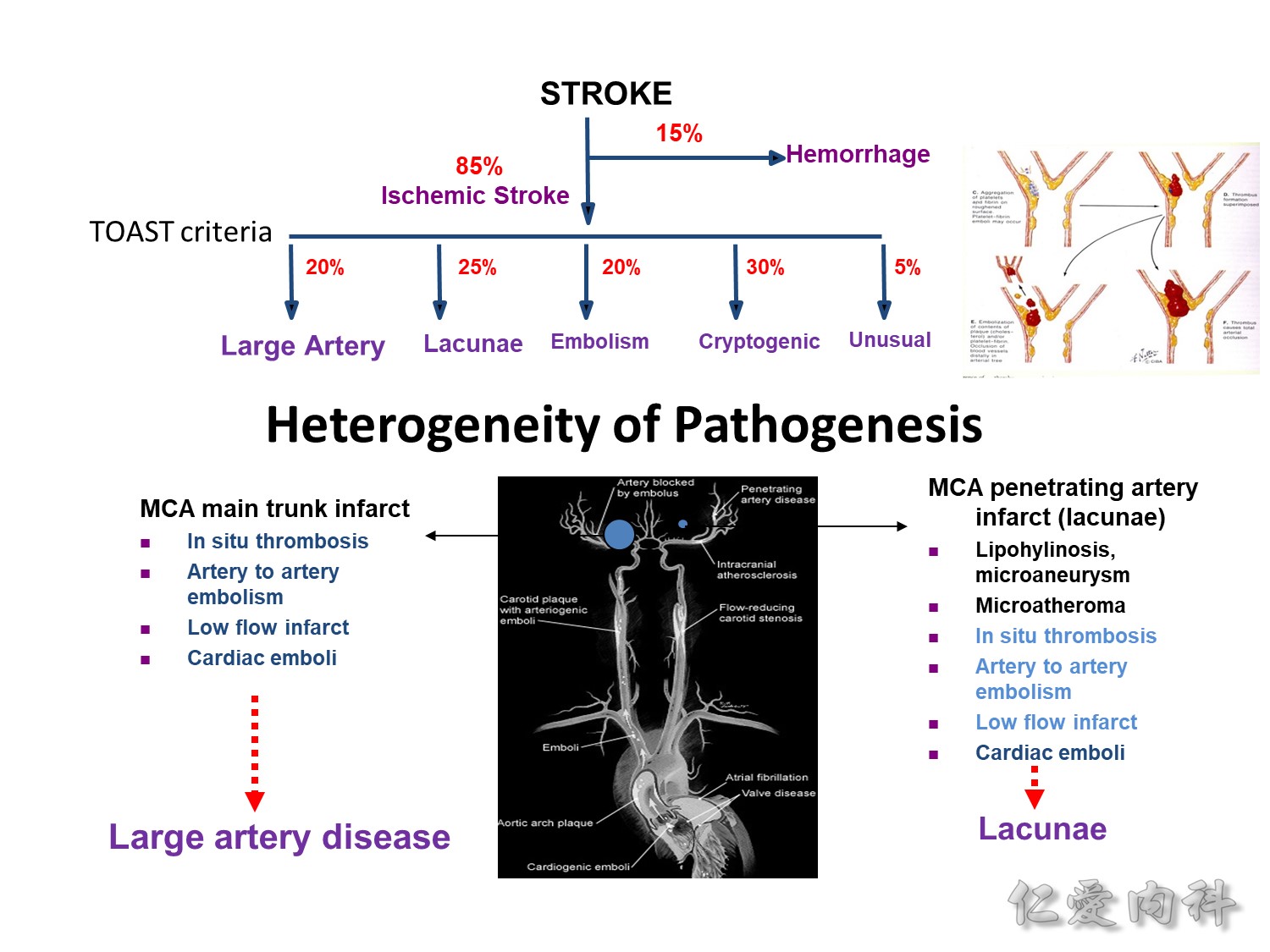
中風有 85% 是 ischemic stroke,15% 是 hemorrhage。
這個 TOAST criteria (trial of ORG 10172 in acute stroke treatment) 是 1993 年提出的分類方式,此後便都適用至今。但是 slide 裡這個比例會隨地域不同而有差異,譬如台灣人因為心臟造成 embolism而中風的比例是比西方人要高的。
中風最常見的分類是 large artery、lacunae 與 embolism;cryptogenic 是找不到原因的;unusual 是指一些特殊的異常 (例如 autoimmune diseases) 造成的中風。
Large artery 是指如 ICA 或 MCA 塞住;lacunae 是指中風範圍小於 1.5 公分;embolism 所看到的是散在性的、多發的中風。
這個 TOAST criteria 其實並沒有確實點出造成中風的原因,即便是 large artery disease,造成的原因便相當多,例如 in situ thrombosis、artery to artery embolism、low flow infarct、與 cardiac emboli 等皆可造成 large artery disease;而 lacunae (penetrating artery infarct) 最常造成的原因為 lipohylinosis/microaneurysm (Charcot–Bouchard aneurysms),但是其它如 microatheroma、in situ thrombosis、artery to artery embolism、low flow infarct、與 cardiac emboli 等也都會造成 lacunae infarction。
總之,ischemic stroke 的 pathogenesis 是非常的 heterogeneous。因此,有了這些分類與造成中風之原因的基礎知識,遇到病人時也才能知道該 survey 甚麼。
Approach 中風病人,history 是很重要的,譬如 embolism 塞到 large vessel 時,病人的表現可能是很 dramatic 的,前一秒都還好好的,下一秒就變很嚴重,病人也可能正在活動中發生中風;而如果是 thrombus 塞住大血管,病人的症狀多是漸進式的,或許先前會有些 TIA 的事件,病人可能早上就有些神經學症狀,到了下午又逐漸變嚴重。
接下來的 PE:heart murmur? irregular heart rates indicating atrial fibrillation? carotid bruits?
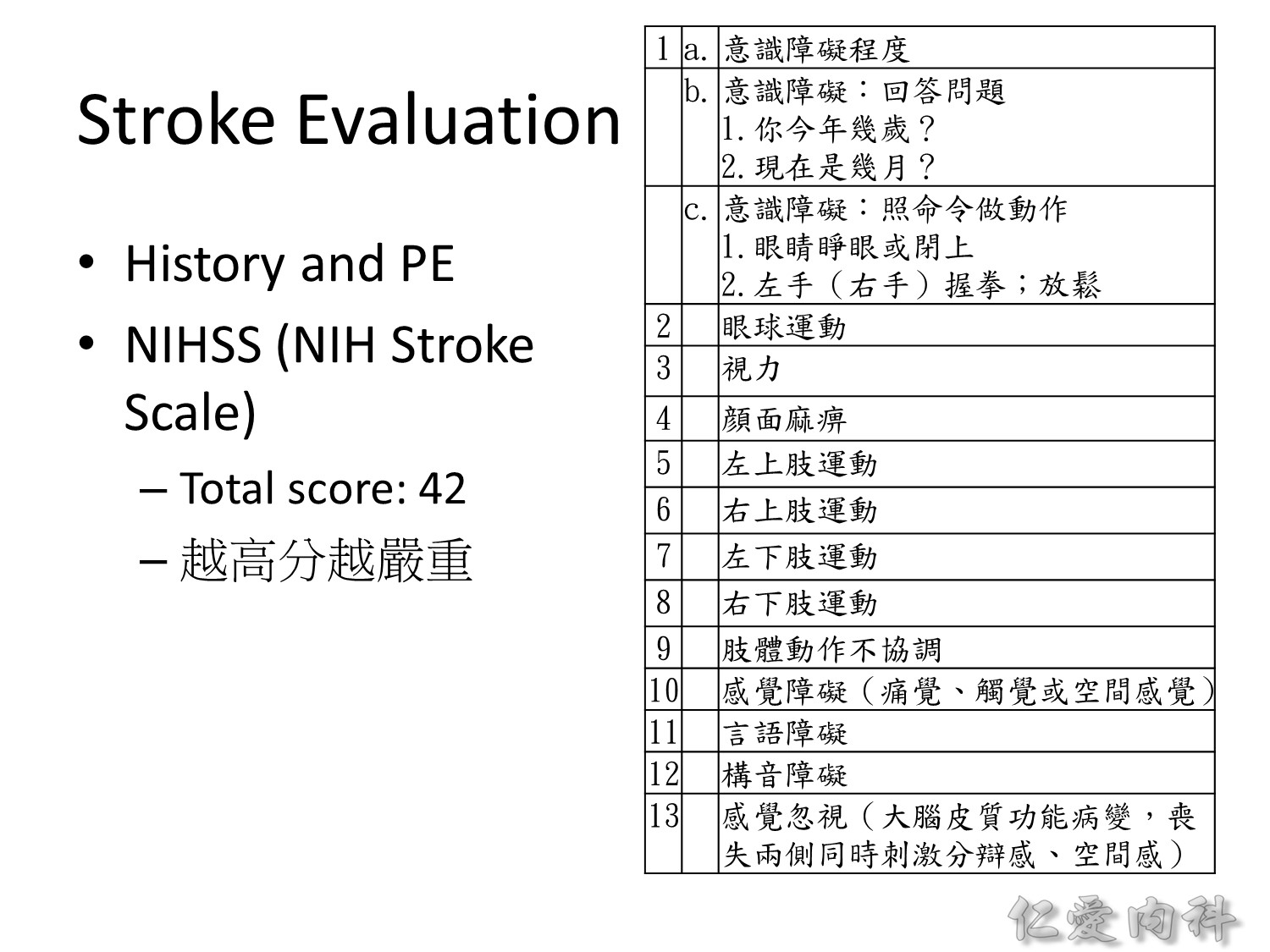
NE 的評估建議根據 NIH Stroke Scale 進行系統性評估。總分 42 分,越高分越嚴重。tPA 可以打的 range 就是 4-25 分。
ABC 一定要先做,病人意識可能很差或越來越差,bulbar function 如吞嚥或語言等功能變差,需給予 O2 維持 SPO2 > 94%,甚至應考慮 on oro-endotracheal tube with MV support。但若無 hypoxia (hypoxemia?),不用給 O2。
不建議使用高壓氧 (HBO)。
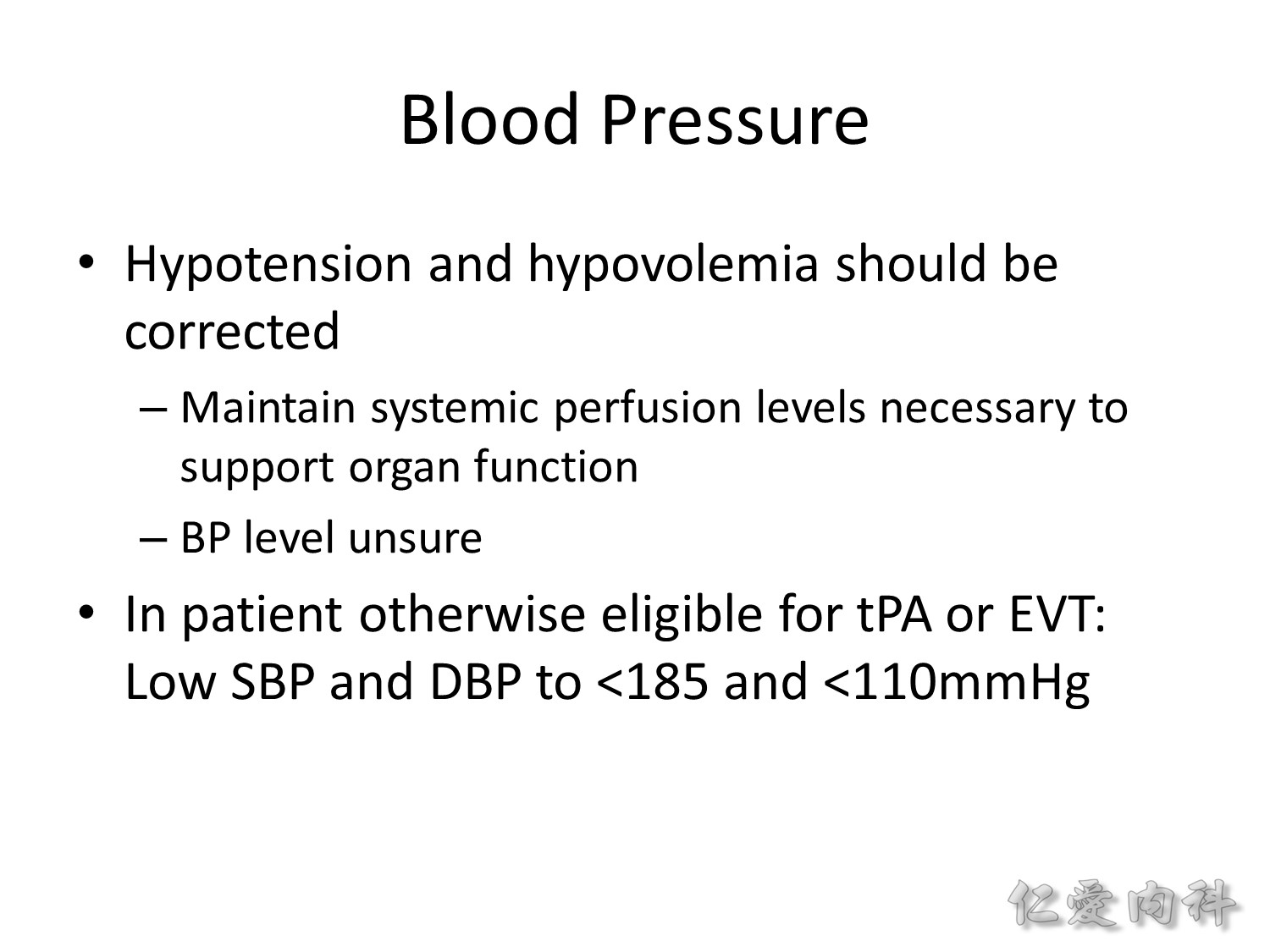
血壓若偏低,應矯正以維持 organ perfusion。
若是病人可接受 tPA 或是 EVT (endovascular thrombectomy):SBP < 185 mm Hg and DBP < 110 mm Hg
中風患者若有高血糖,會增加 mortality/morbidity,應控制在 140~180 mg/dL。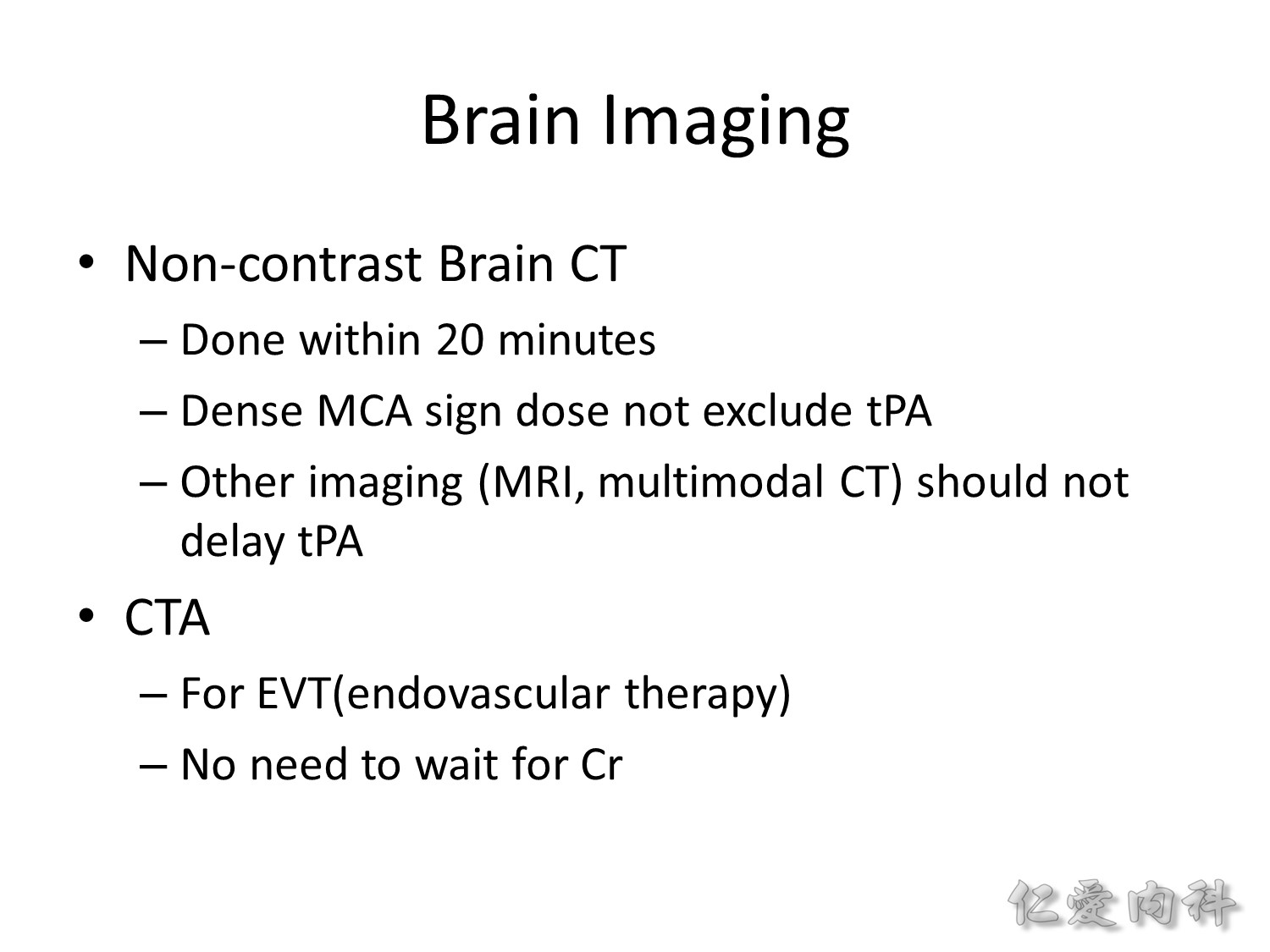
目標在 20 分鐘內做到 CT。
看到 dense MCA sign 不表示中風範圍很嚴重,不能排除使用 tPA 的可能。
其它的影像檢查都不可造成 tPA 的 delay。
若有進行 EVT (endovascular therapy) 的適應條件,CTA 不需要等 creatinine 的檢測結果 (除非患者的腎臟功能已知相當差)。
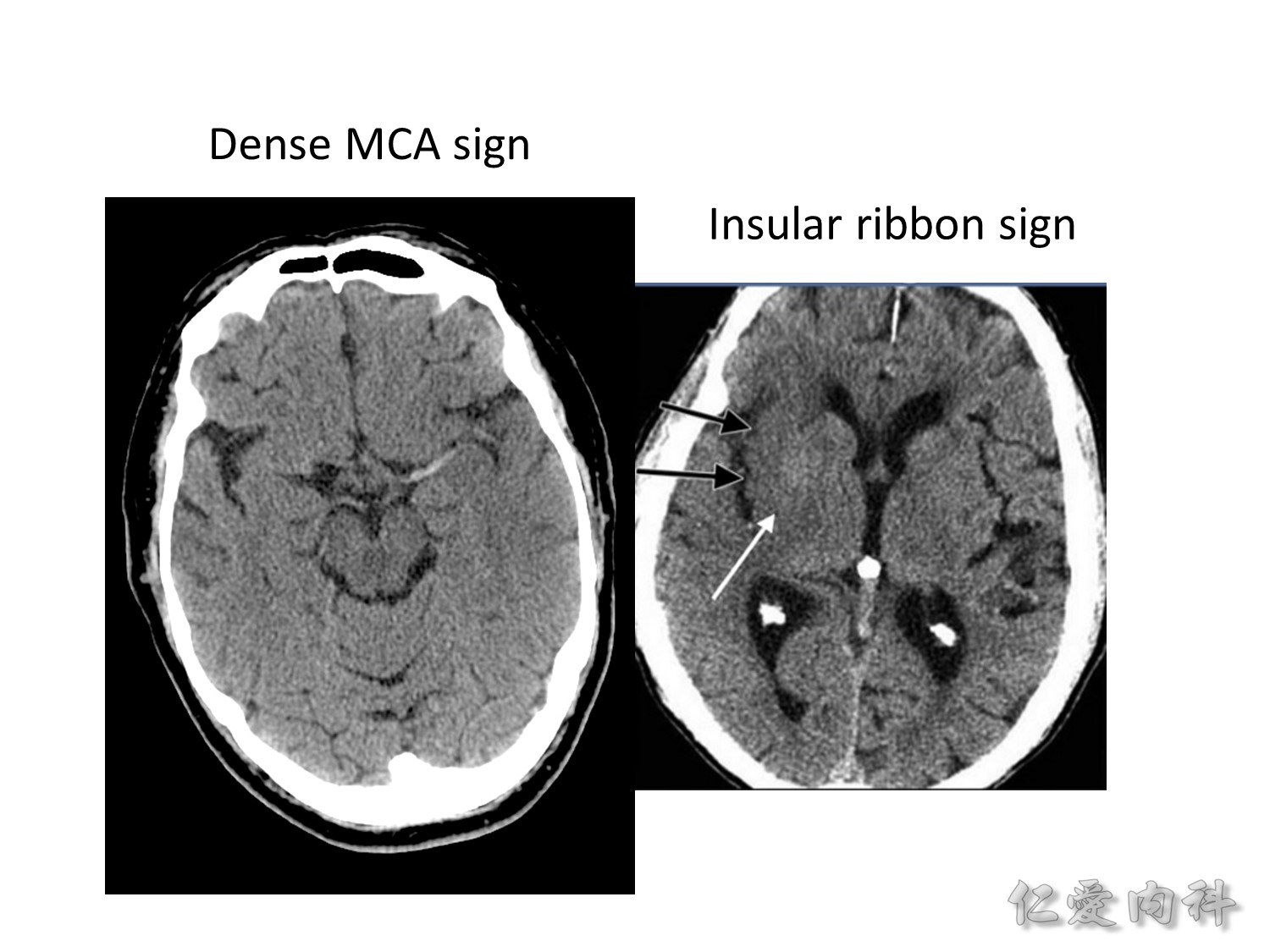
早期 MCA 中風的 CT image findings:
Dense MCA sign:(tip: 對照左右側)
focal increased density of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) on CT and is a direct visualisation of thromboembolic material within the lumen
Insular ribbon sign:(tip: 對照左右側)
a loss (effacement) of definition of the gray-white interface in the lateral margin of the insular cortex (“insular ribbon”) and is considered an early CT sign of MCA infarction
From Radiopaedia
一定要作的檢查是 blood sugar level,其它的檢查 (e.g., EKG, Troponin I, chest radiograph) 則建議在不 delay tPA 的條件下才檢查。
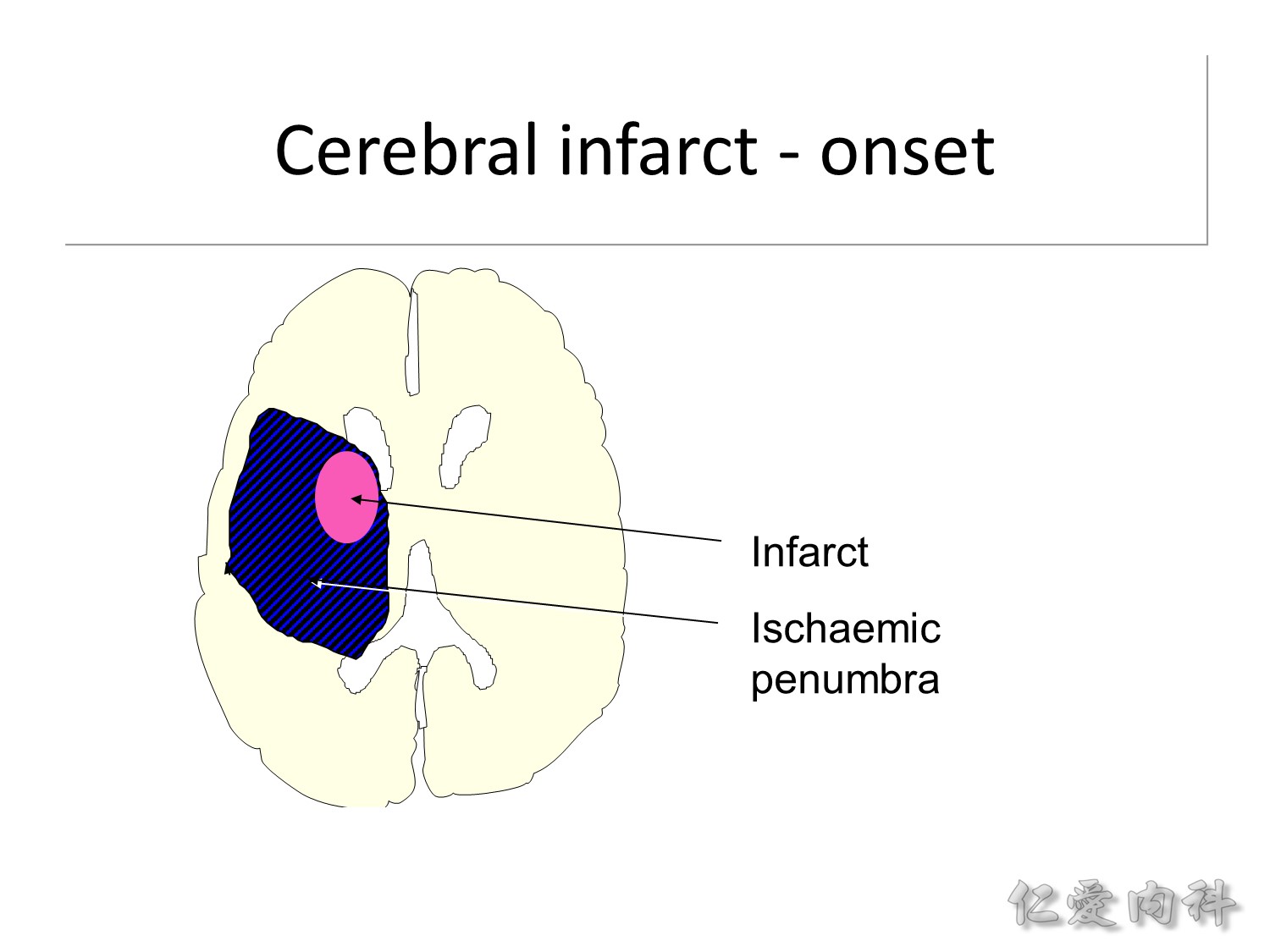
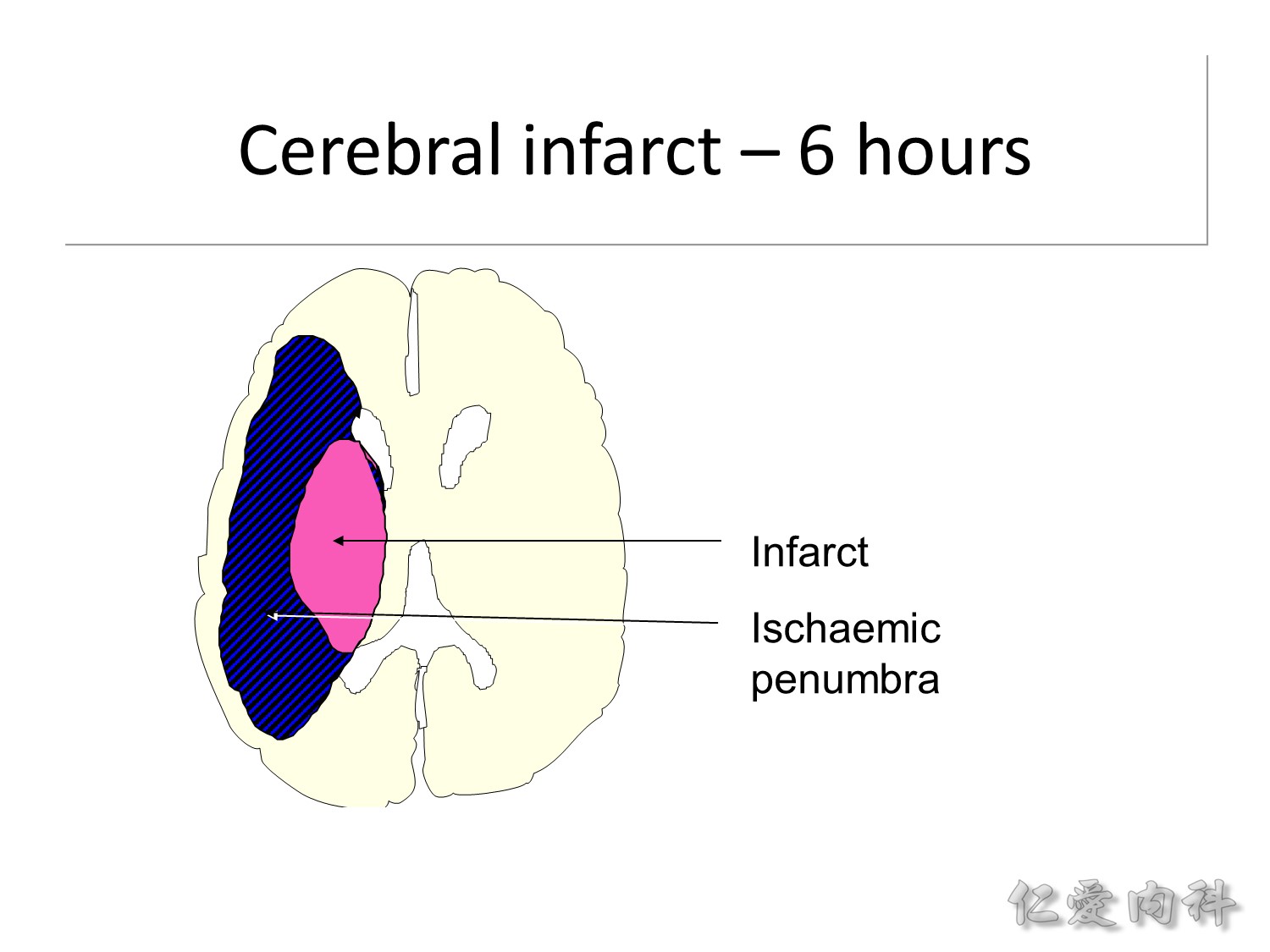
為什麼急性中風的 emergency treatment 很重要? 就是在中風發生時,真正直接沒有血流直接死亡的腦組織的範圍其實不大,事實上 slide 中的藍色區域都還是 viable brain tissue。
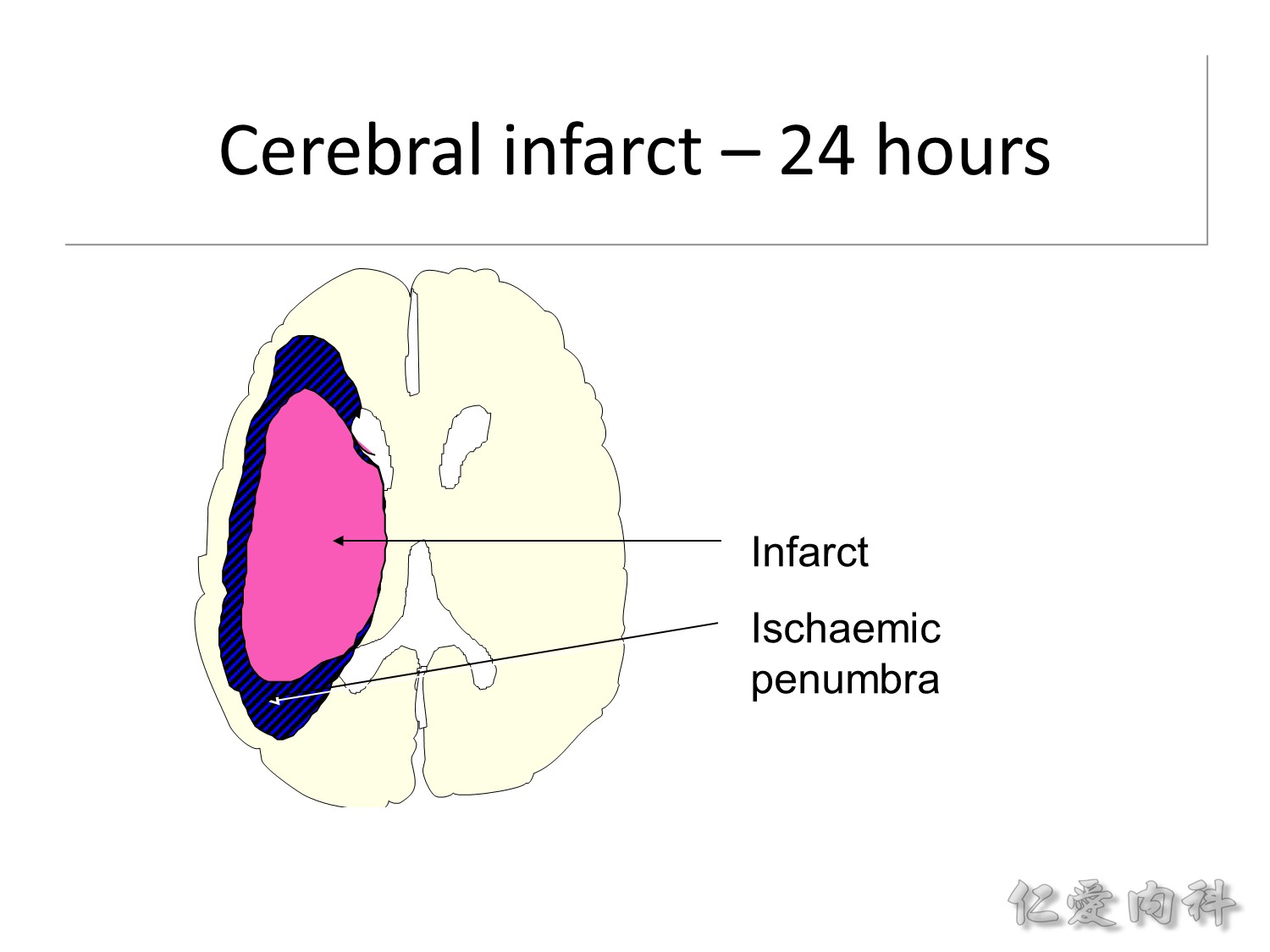
中風後的第 24 小時,大概可救的 ischaemic penumbra 都算是沒了。
這是 MCA territory 的 ischemic stroke,在中風 onset 的第 2 小時就可看到 insula ribbon sign 與 gray-white matter junction effacement。但是 24 小時候 ischemic penumbra 都沒了。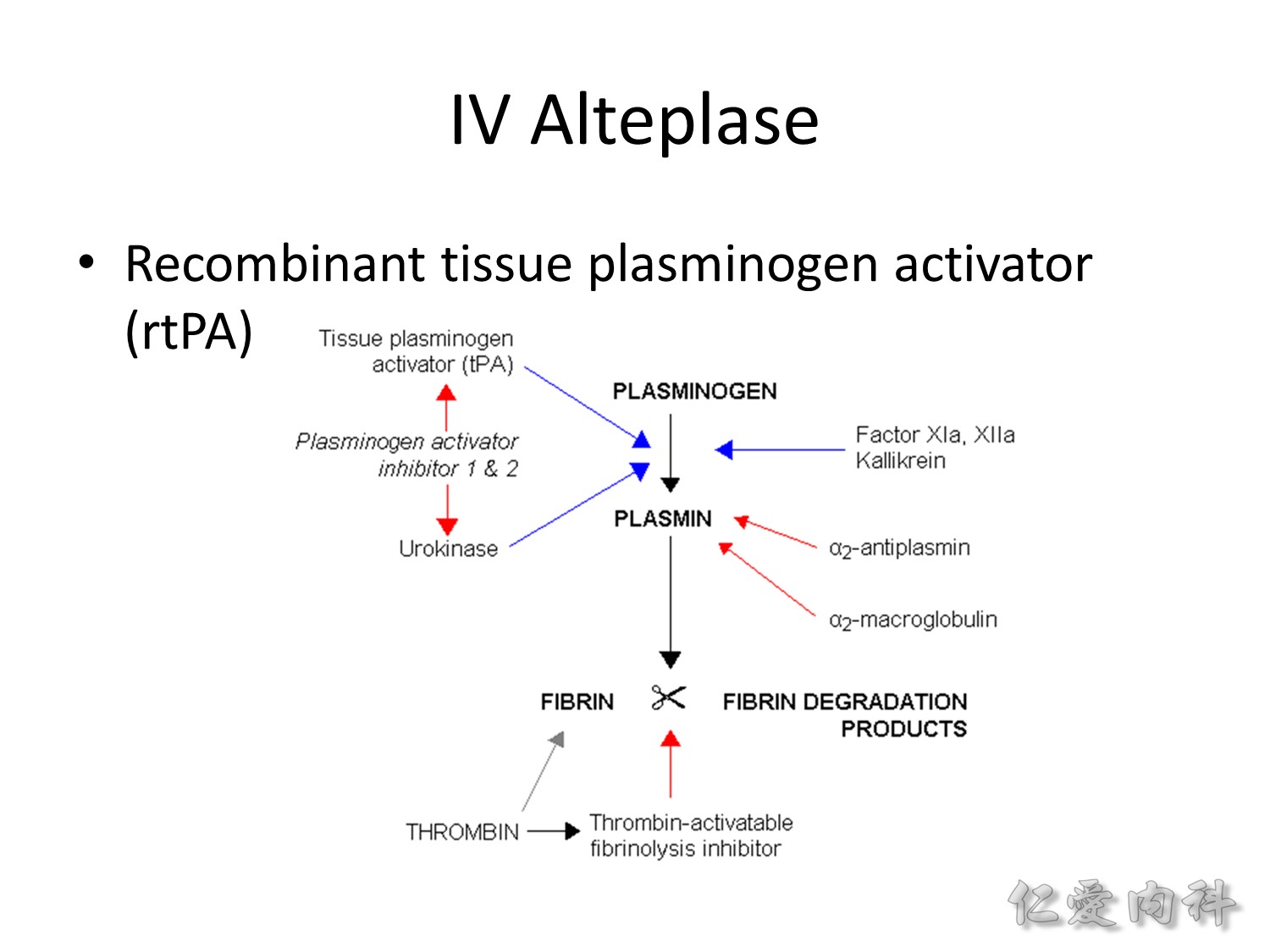
Recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rtPA) 的藥名是 alteplase,作用是讓 plasminogen 轉變成 plasmin,plasmin 可以切掉會形成 thrombus 的 fibrin,產生 fibrin degradation products。
這張 slide 還有列出一些以前曾經嘗試過的治療方式,但是都失敗了,所以就不提了。
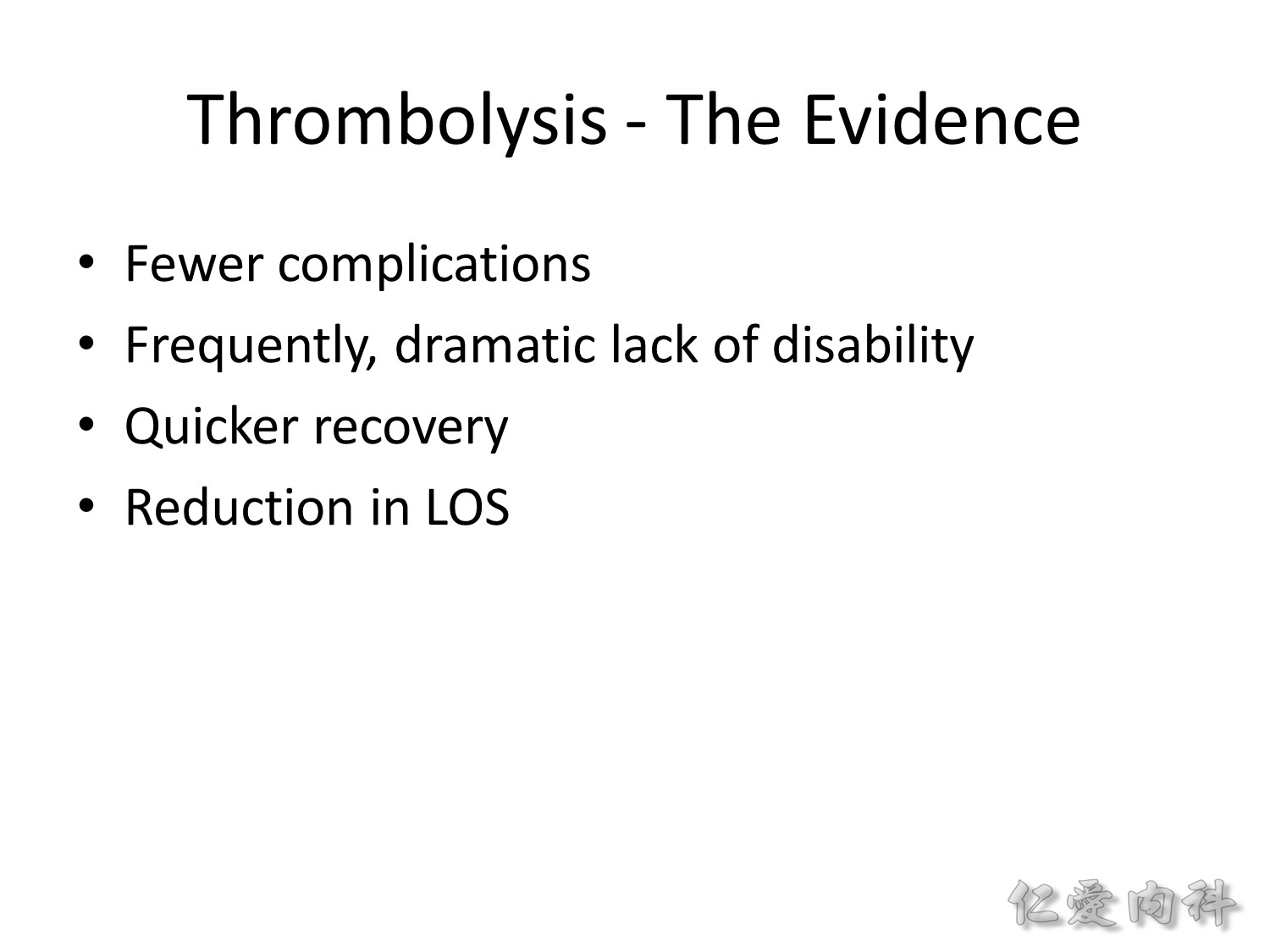
Thrombolysis 的證據是可以 decrease complications、lower the severity of disability (使 modified Rankin Scale [mRS] < 2 的比例很好,”< 2″ 表示能自己走來走去)、facilitate recovery、與 shorten length of stay。
關於 3 小時內…
(1) 假設病人 9 點睡覺,12 點起來上廁所發現症狀,護理師 1 點通知你,你認為這算是和 onset 的?
(2) 假設病人 6 點起床上廁所時確定無異狀,又回去睡,睡到 7 點發現症狀,7:30送到醫院,你認為這算是和 onset 的?
要從他最後最好的時間算起。
所以第一題是 nine o’clock 而不是 twelve o’clock。第二題是 six o’clock。
18-80 歲是健保的規定,國外是 18 歲以上即可。台灣 80 歲以上必須自費,打起來約是 20k-30k。
以下為排除條件…
(Ian’s comment: 時在是超級多項目,記幾個重要的就好吧? 有遇到沒有記憶中的排除條件的病人,再來這裡查查?)
關於 alteplase (Actilyse: Boehringer ingelheim pharma, Biberach, Germany) 造成的 angioedema (過敏反應)…
這裡需要稍微修正一下上課講的內容,也就是…
有一說是不可在曾經因為使用 ACE inhibitor 而發生 angioedema 的患者身上使用 alteplase,否則也容易發生 angioedema;但是 (Ian’s comment)…
Angioedema is a rare but potentially life-threatening complication induced by alteplase treatment. The mechanisms underlying the development of angioedema are hydrolyzes of plasminogen to plasmin that activates the kinin system with occurrence of potent vasodilator bradykinin and activation of the complement system resulting in mast cell degranulation and histamine release. The incidence of angioedema after alteplase treatment was up to 5%, and concurrent use of ACE inhibitors and signs of ischemia on initial CT were the major risk factors for the development of angioedema. ACE inhibitors may have an additional effect on the development of angioedema by inhibiting plasma kininases which are responsible for bradykinin degradation.
World J Emerg Med. 2015; 6(1): 74–76.
可見兩者發生 angioedema 的機轉不同 (alteplase 是刺激 bradykinin 生成,ACEI 是減少 bradykinin degradation),不應該有這種 concern。
不過,要小心兩者併用會增加 angioedema 的風險,且要知道 angioedema 的緊急處理 (H1 [and/or with H2] blockade antihistamine、給 epinephrine 若是有 airway obstruction、必要時須插管、shock 時須 fluid replacement)。
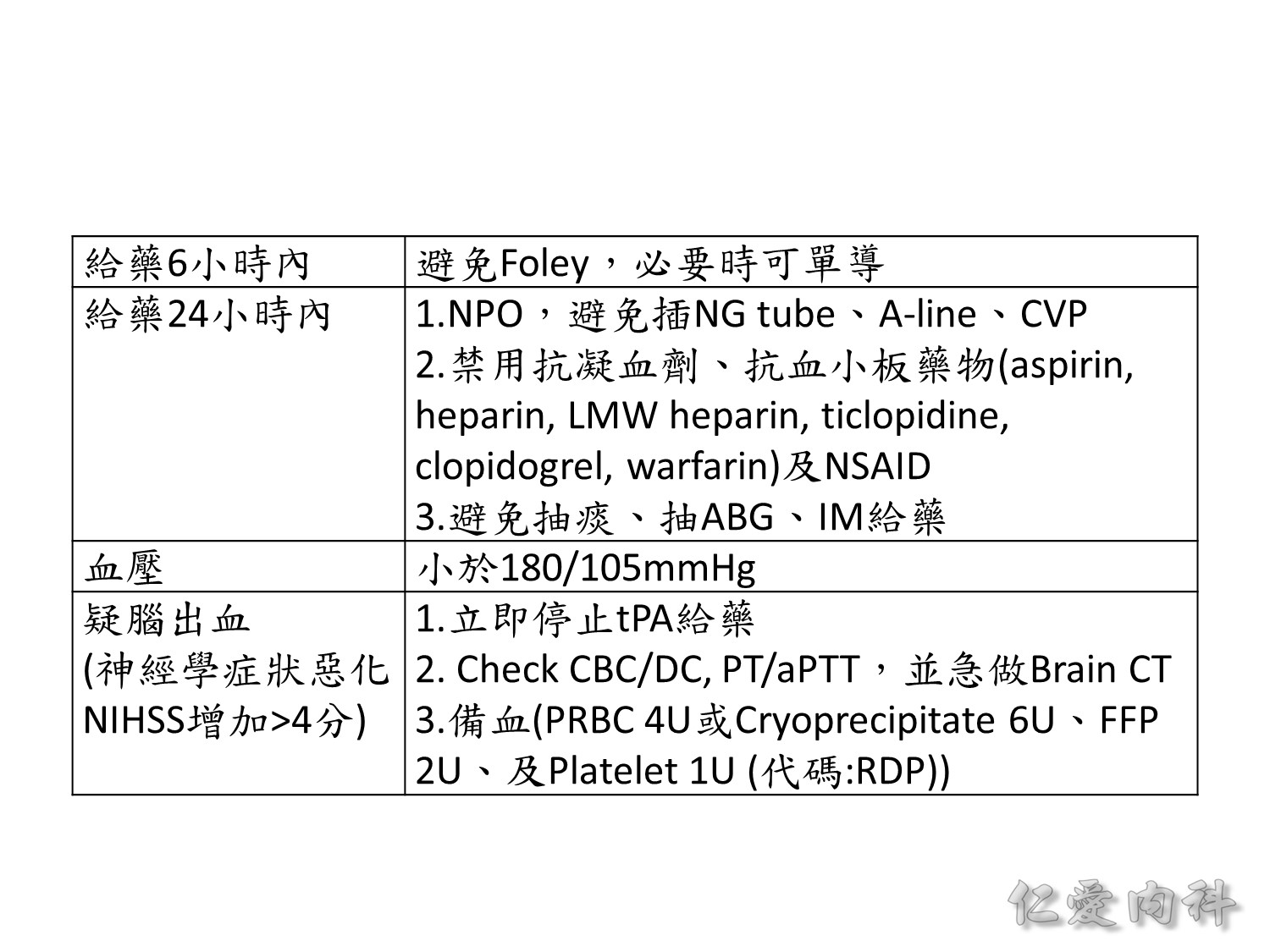
另外,打了 rtPA 後變成腦出血的風險有多高? 不打藥時,hemorrhagic transformation 的比例有 0.6%;打藥之後會提高到 6%。
alteplase 劑量不要超過 90 mg。
Nicardipine 可以泡 pump,泡法是 50 mg (5支共 50 ml) in 200 ml normal saline,從 5 ml/hr (1 mg/hr) 開始,每15分鐘評估一次,逐步往上調劑量。
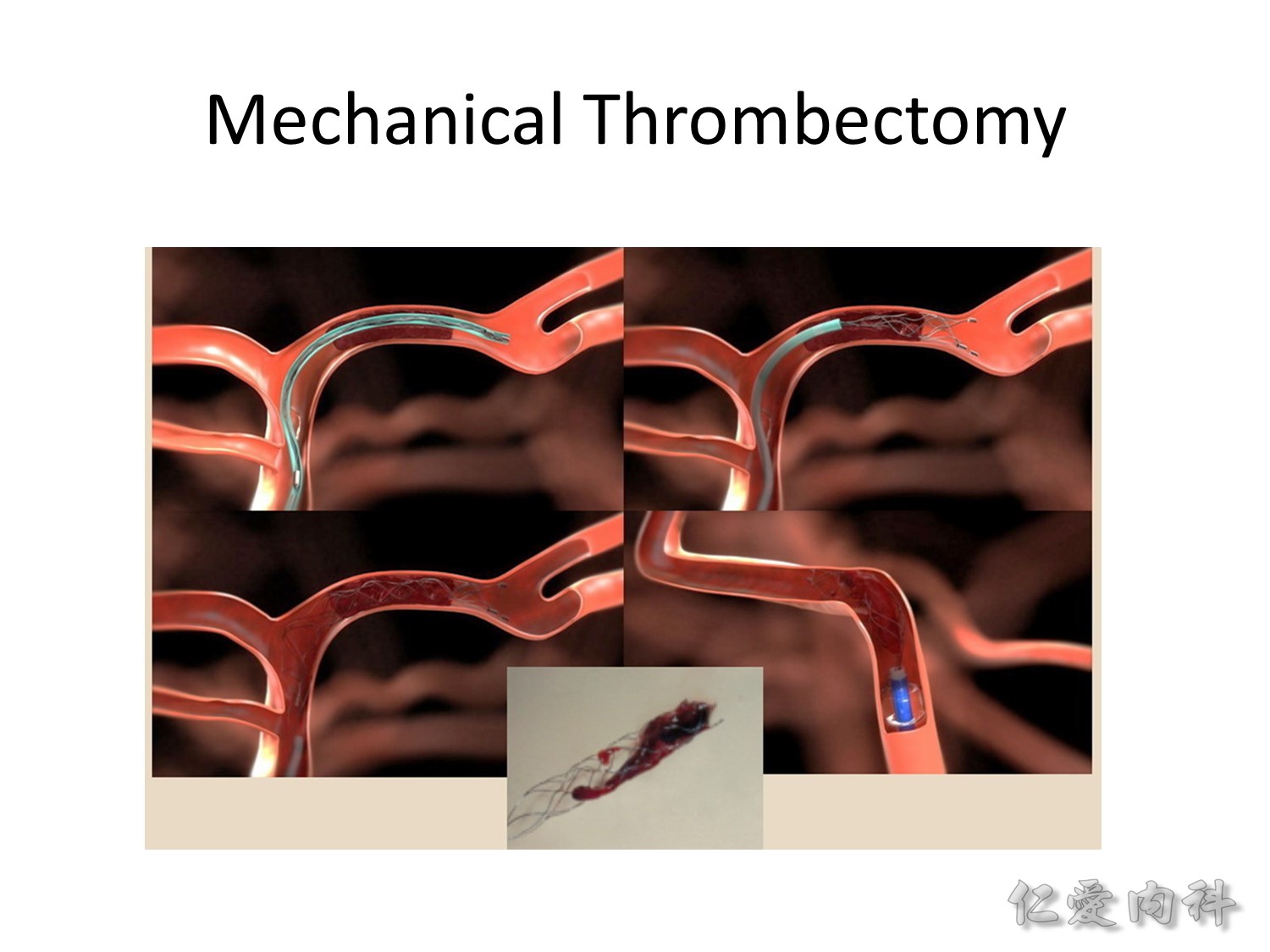
塞到比較大條的血管 (e.g., internal carotid artery [ICA] 或是 MCA 的 main trunk) 用 tPA 常常打不通。於是發展出 endovascular therapy,那麼哪些人是適合這種療法的?
要看是哪裡塞住,要作 CTA。最適合的是 internal carotid artery 或是 MCA segment 1 (M1)。
ASPECTS 是 CT 上的評分標準。可參考 MDCalc。
需要在症狀 onset 內的 6 hours 開始 procedure。(tPA 打完還是可以進行 endovascular therapy [EVT; mechanical thrombectomy])
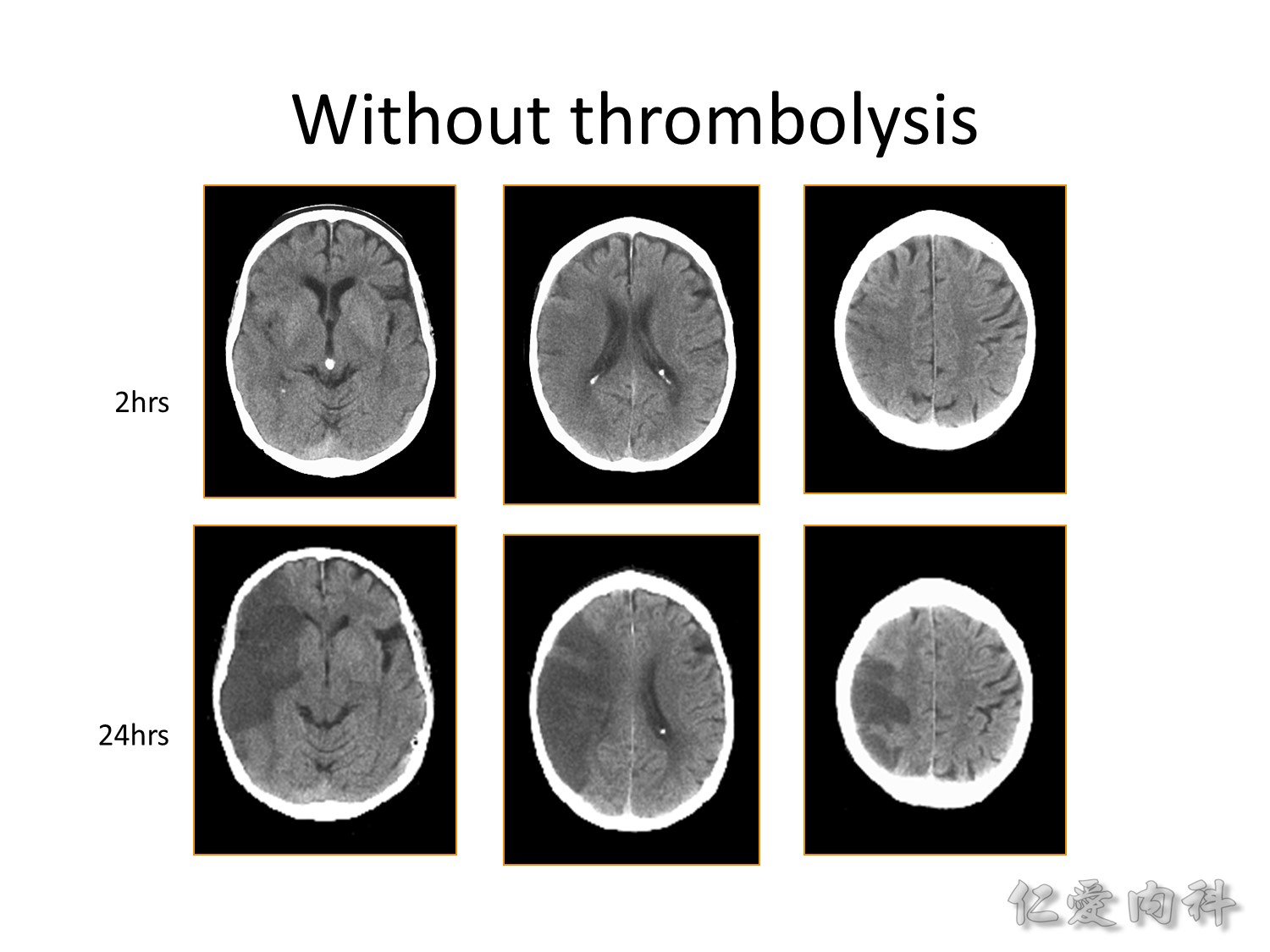
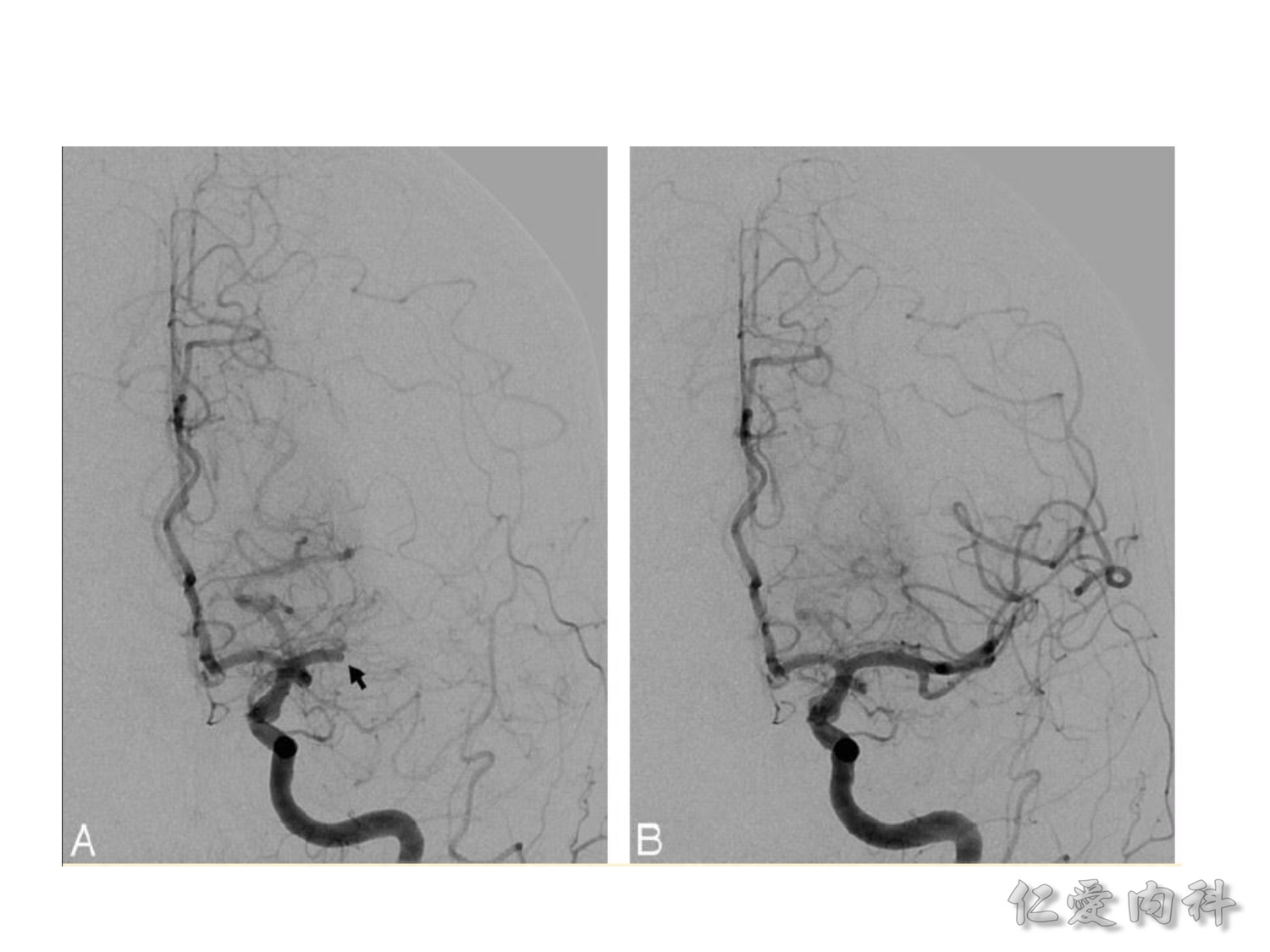
這 slide 是實際病人被打通後的影像變化。
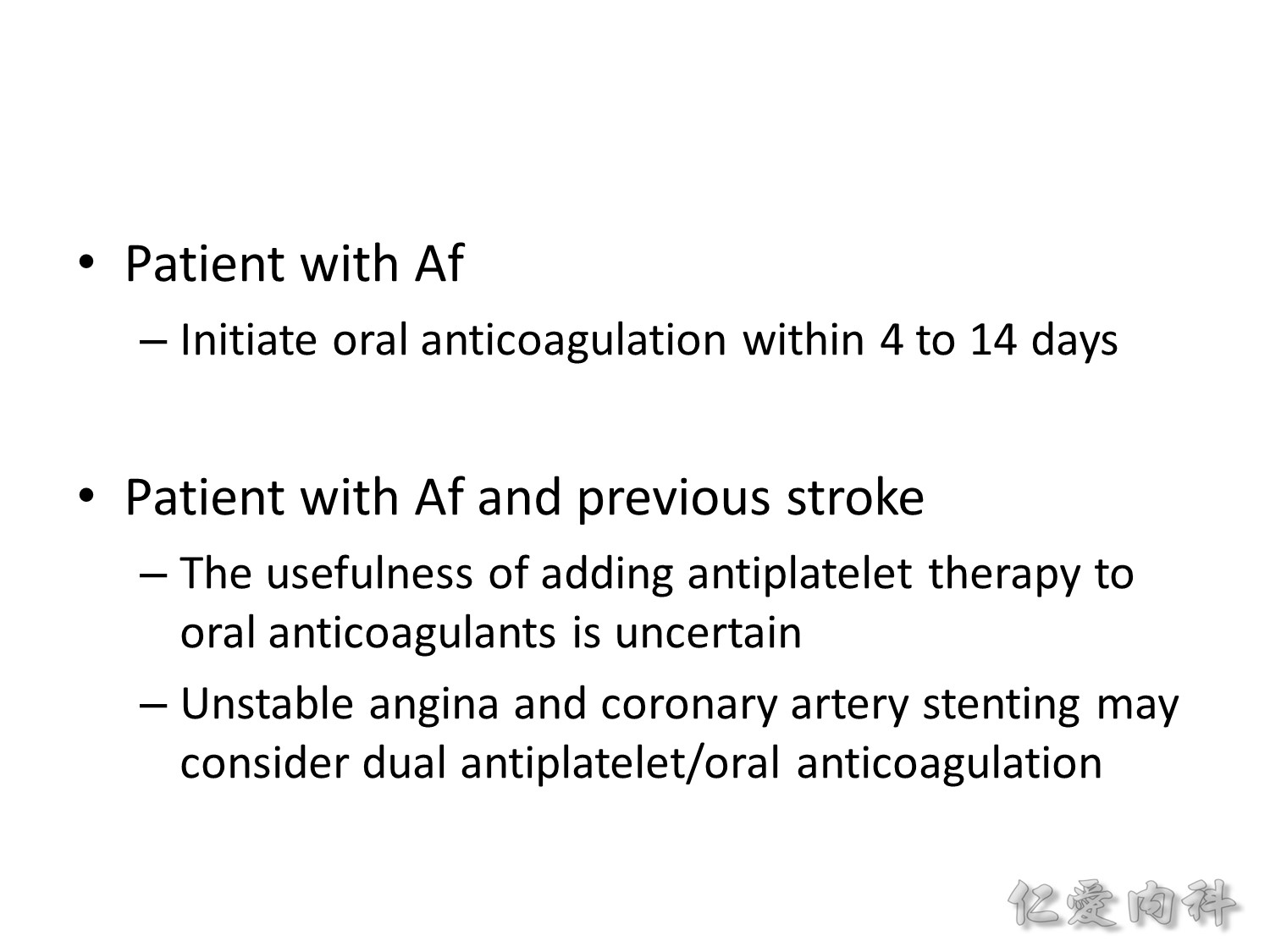
病人若要接受 tPA 或 EVT,不要給 aspirin;若沒有,48 小時內給 160-300 mg aspirin。
TIA 或是小中風,前 21 天每天都給 dual antiplatelet,可以有效降低 90 天內 early secondary stroke,但是吃久一點並不會更好。
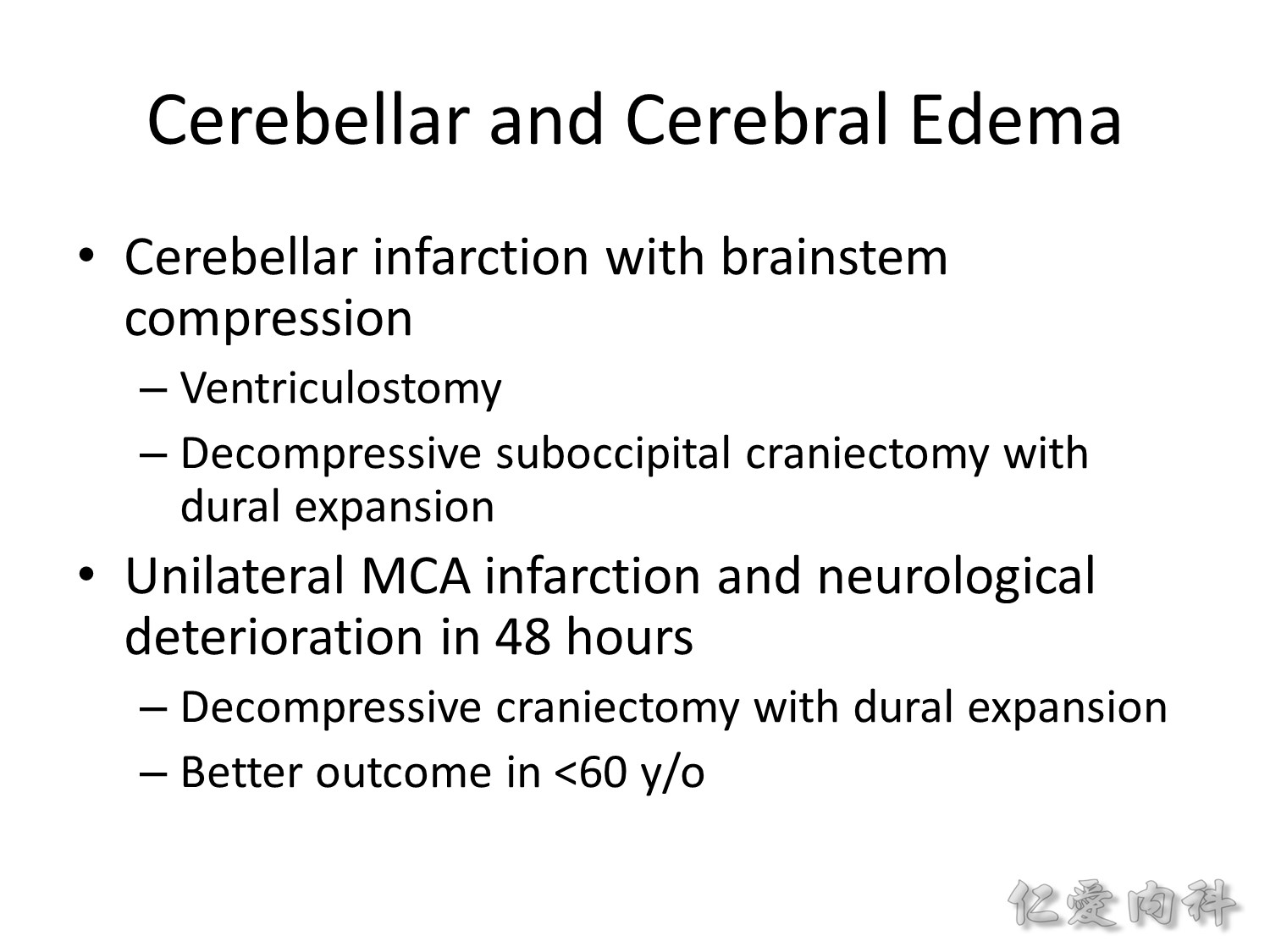
Brain edema 時,可給短時間的 hyperventilation,但是給 corticosteroids 是有害的。
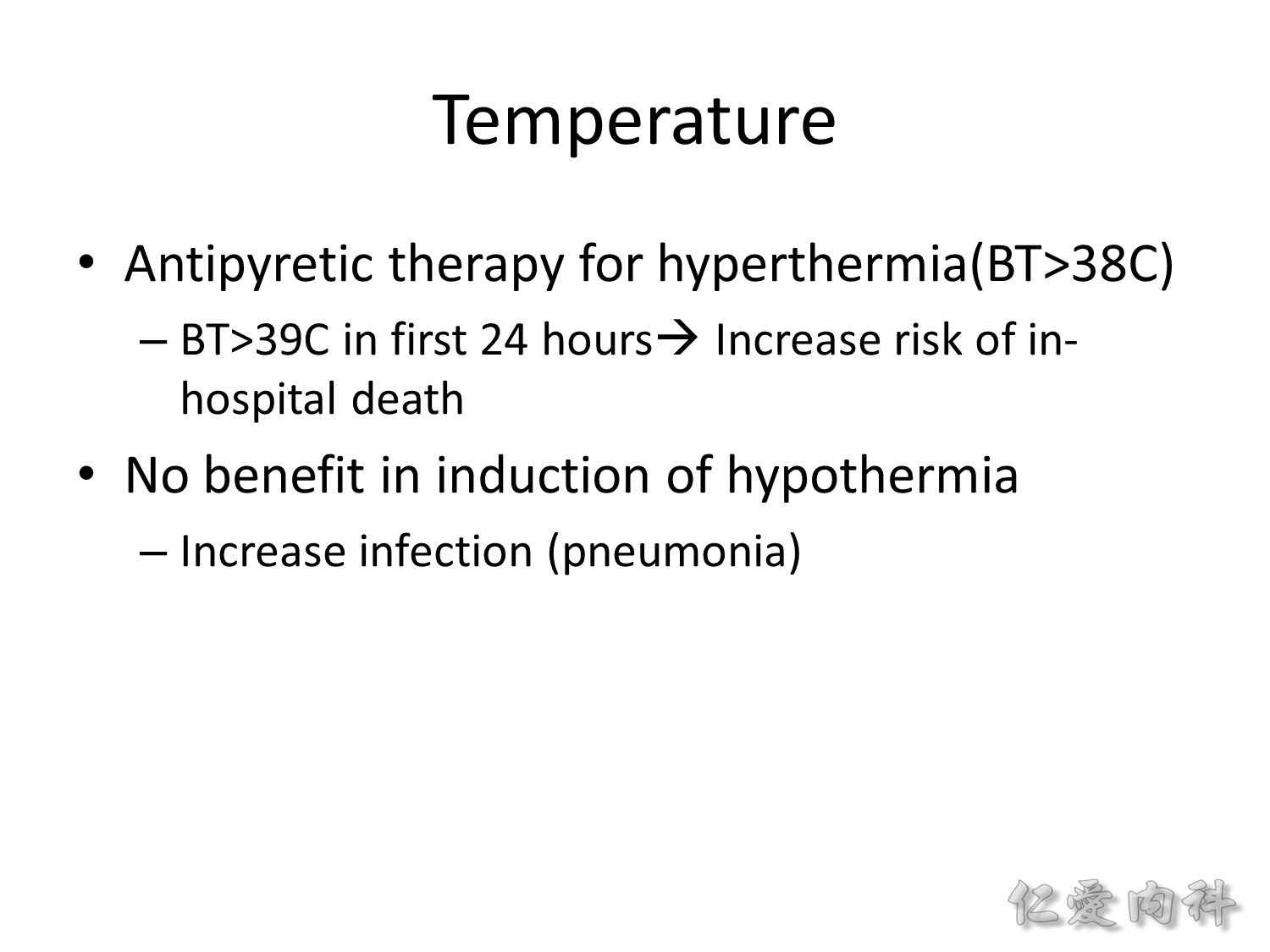
前 24 小時,發燒會增加 in-hospital death 的風險,應給 antipyretic therapy。但是不需要 hypothermia therapy。


早期復健有幫助,但不應急於中風的 24 小時內開始,中風後 6 個月內積極復健是有幫助的。出院前要評估 ADL (activity of daily livings) 與 IADL (instrumental activities of daily living scale) 的能力。
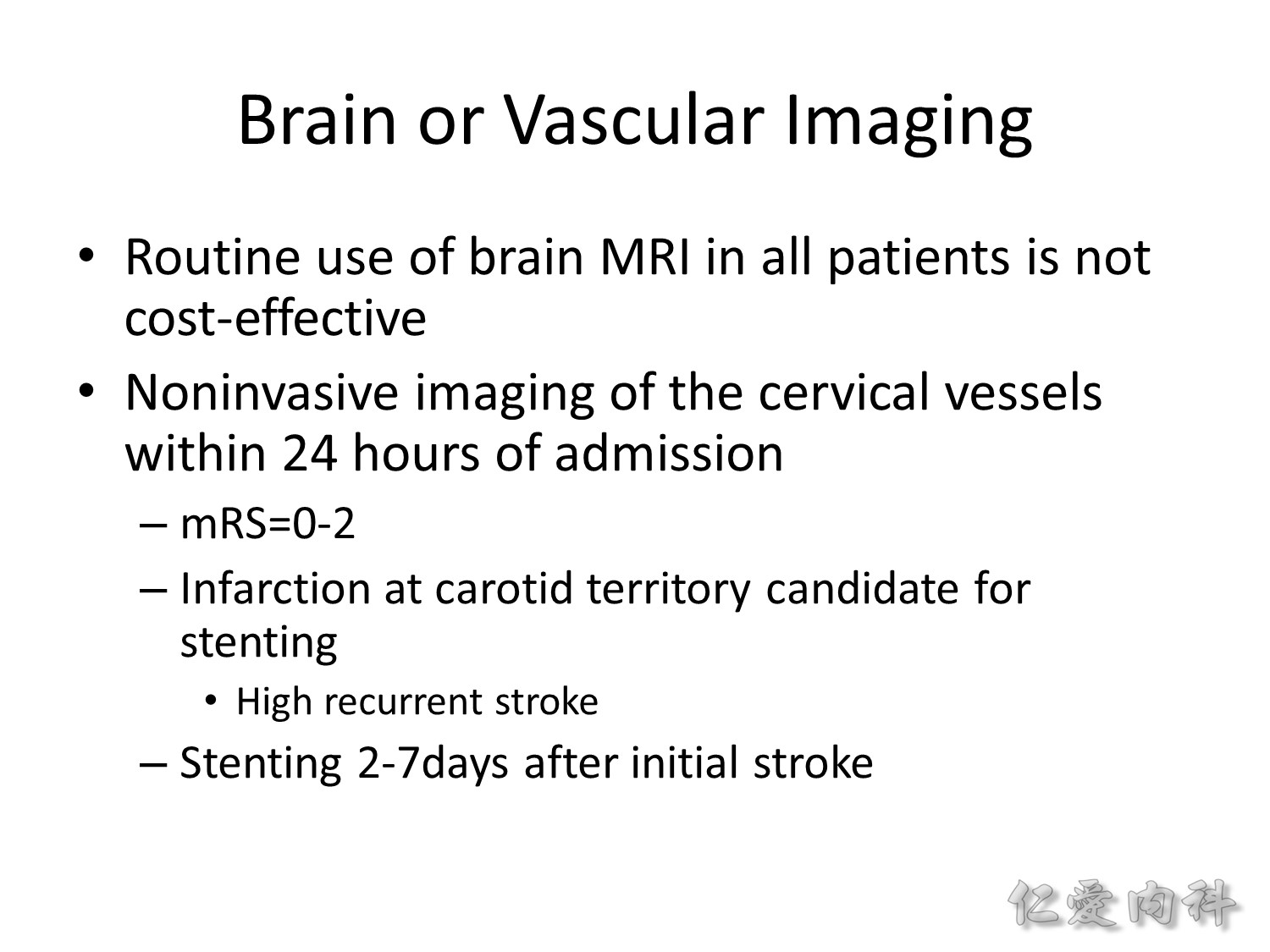
這裡的 noninvasive imaging 是指 MRA or CTA (主要是評估是否需要 stenting)。
查 HbA1C 會比 AC sugar level 準,因為 stress 會使 blood sugar levels 升高。
ASCVD (atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease) is caused by plaque buildup in arterial wall. This includes:
- Coronary heart disease (CHD), such as myocardial infarction (MI), angina, and coronary artery stenosis > 50%
- Cerebrovascular disease, such as transient ischemic attack, ischemic stroke, and carotid artery stenosis > 50%
- Peripheral artery disease, such as claudication
- Aortic atherosclerotic disease, such as abdominal aortic aneurysm and descending thoracic aneurysm
健保規定要大於 14 天才能吃 anticoagulant (NOACs/DOACs),所以 4-14 天內可以請病人自費吃。
不需要 routine 去篩檢 hyperhomocysteinemia, thrombophilic states, antiphospholipid antibodies, or OSA。