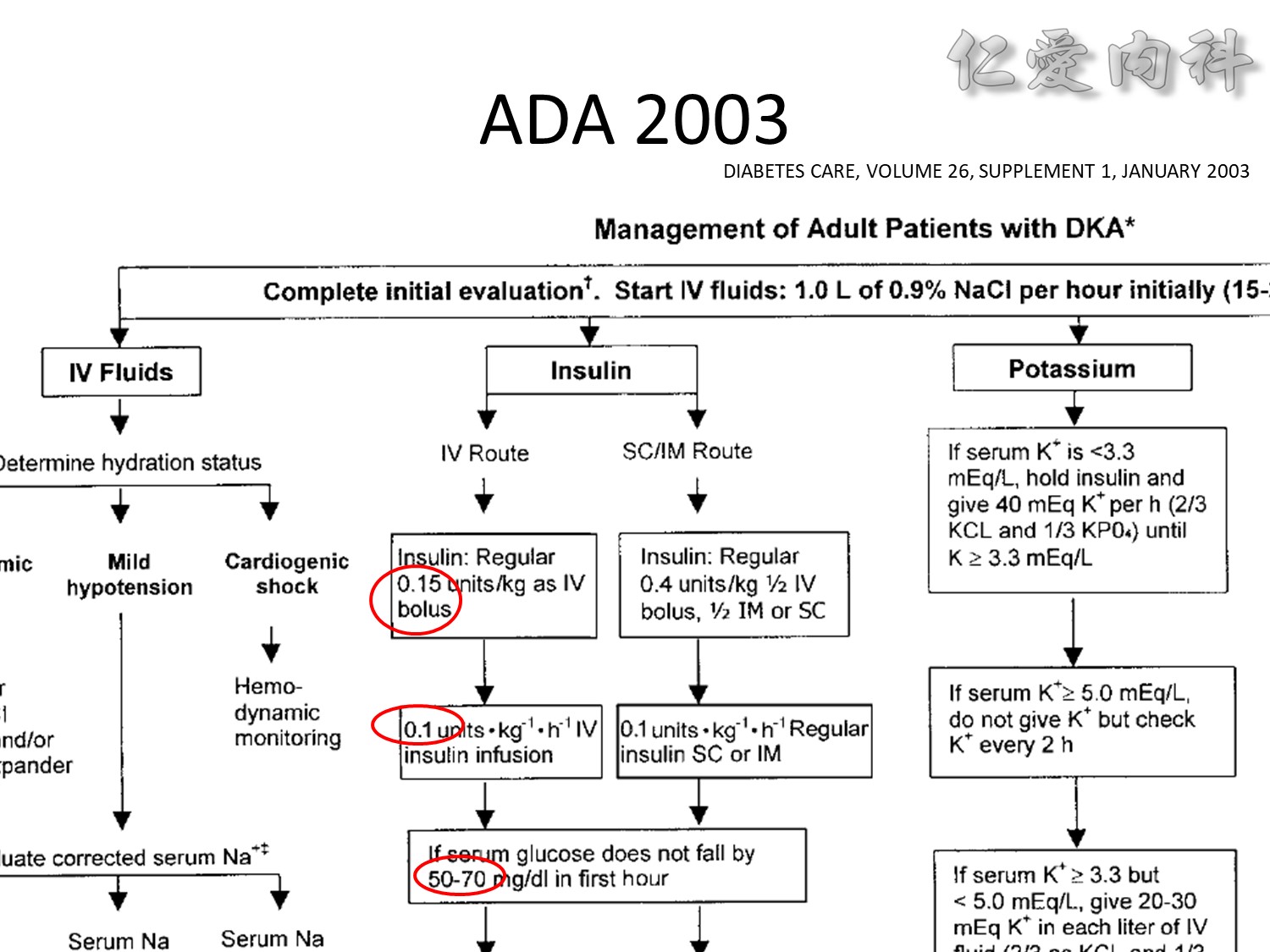
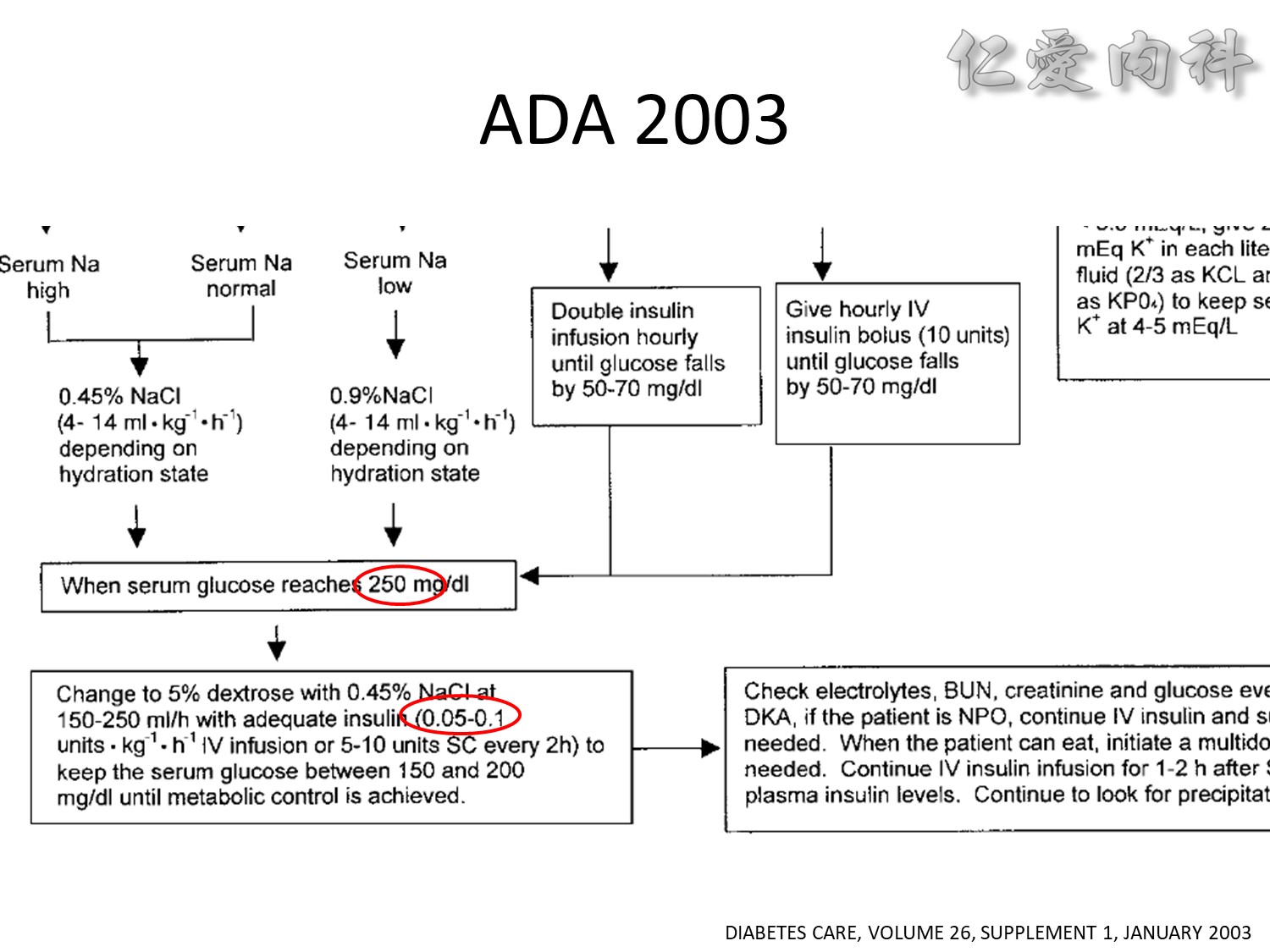
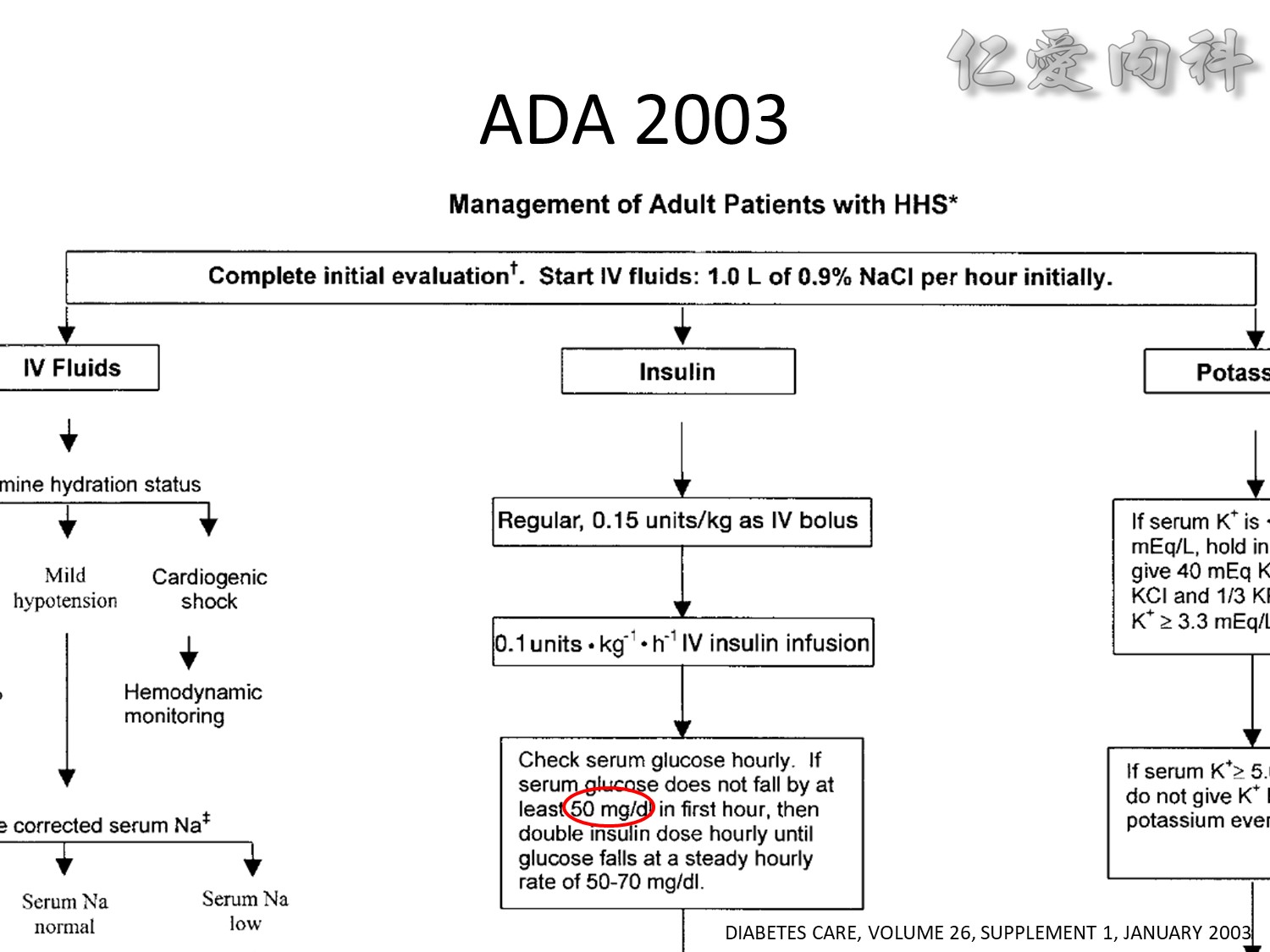
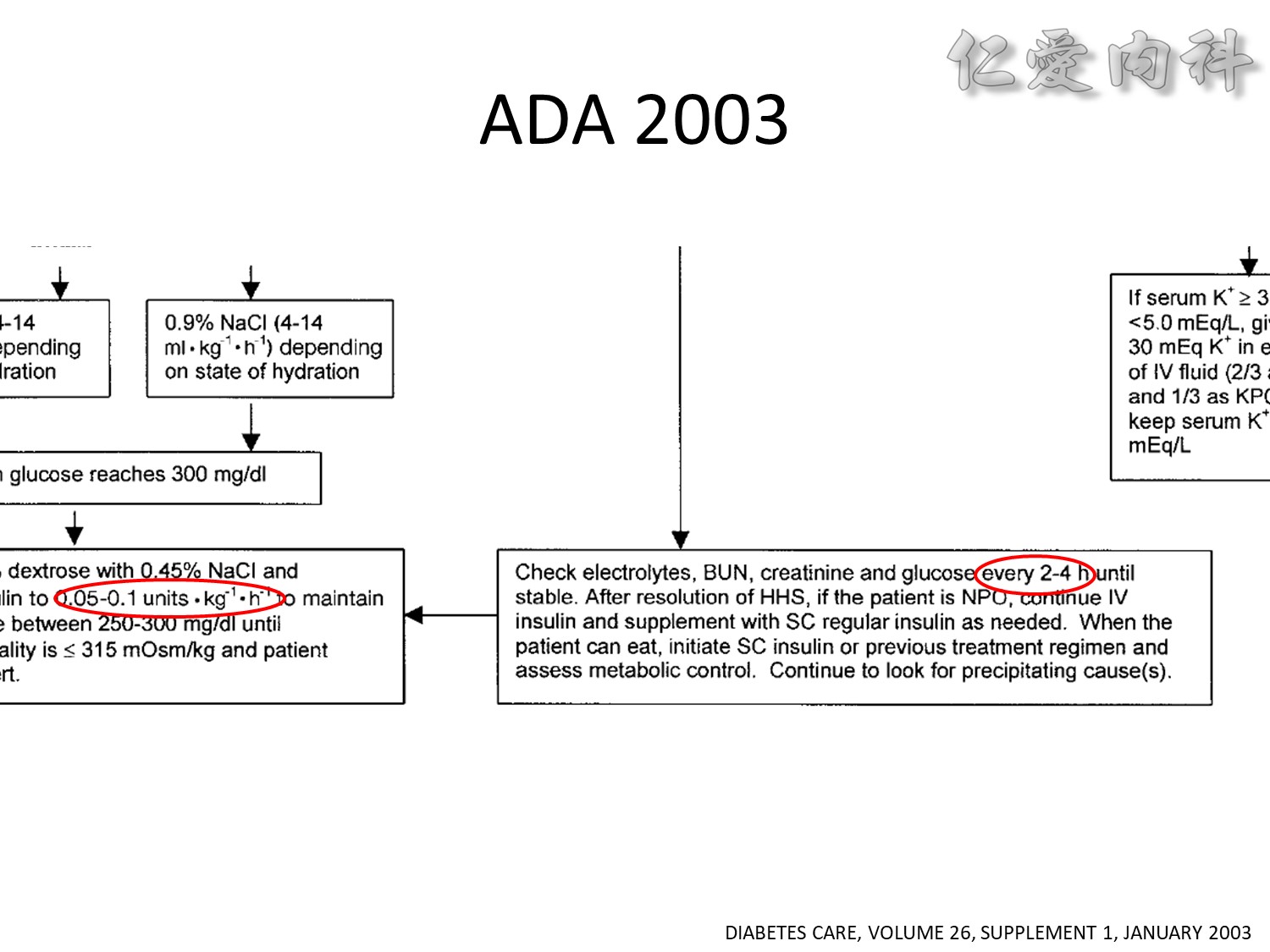
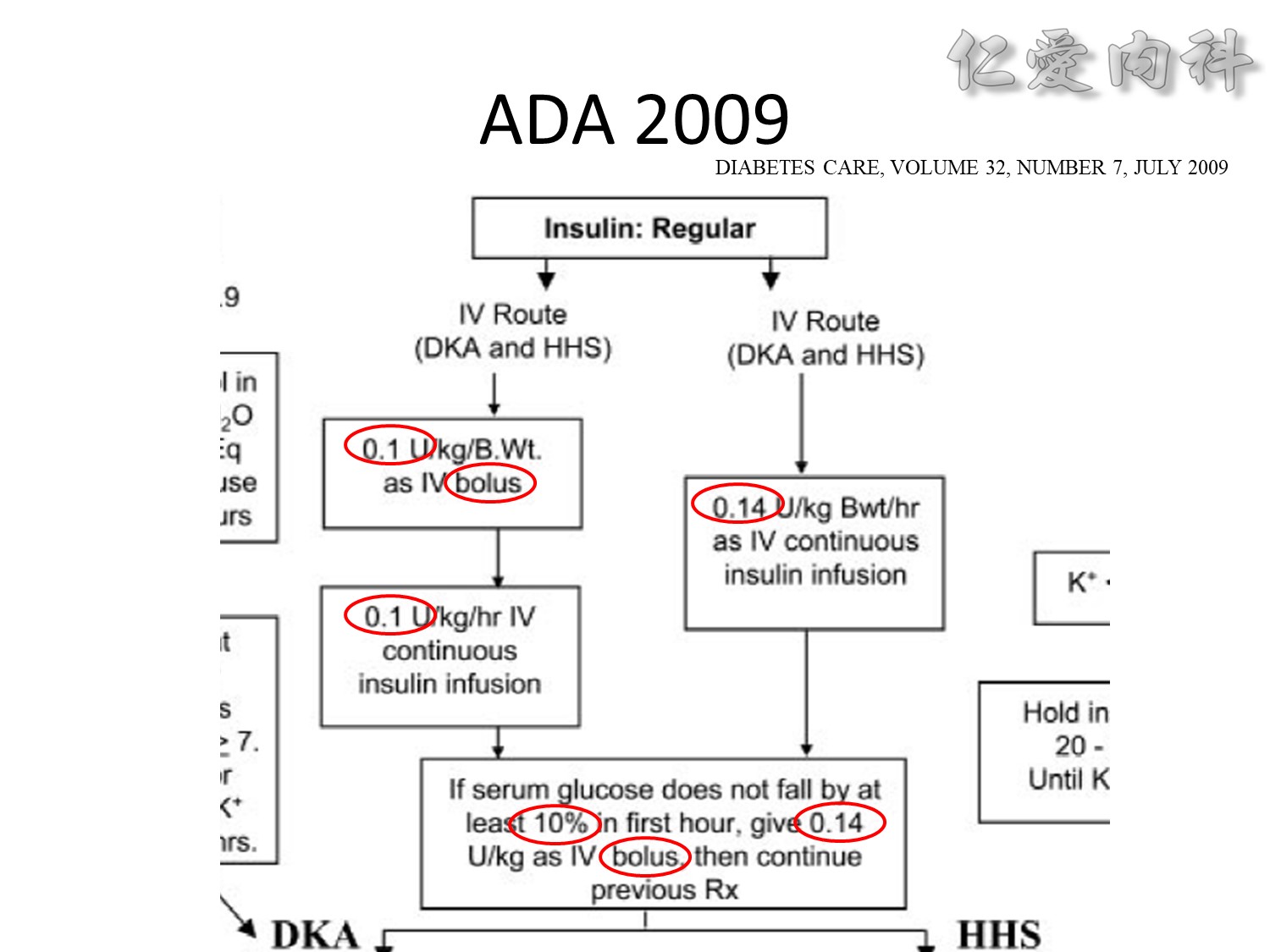
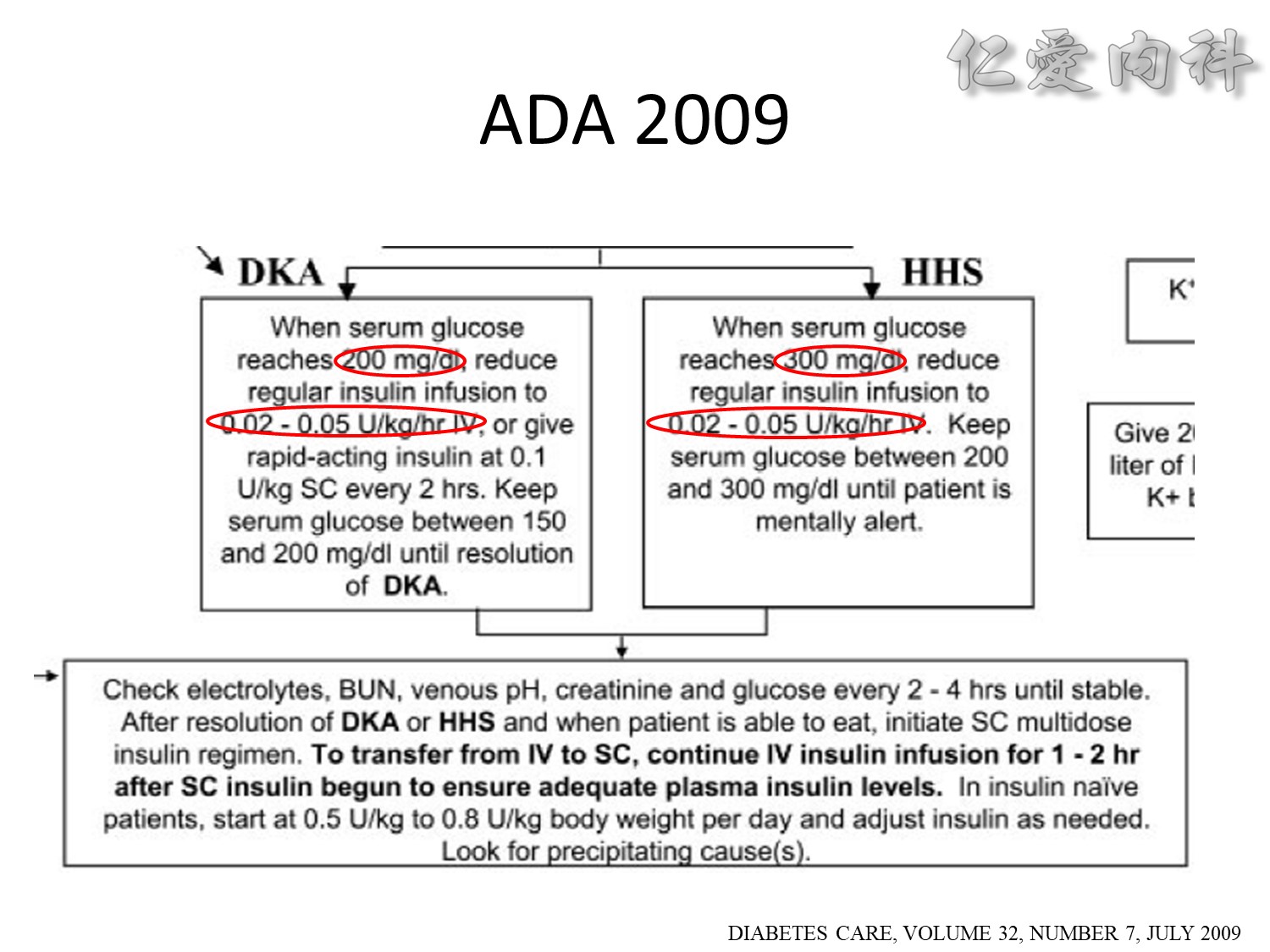
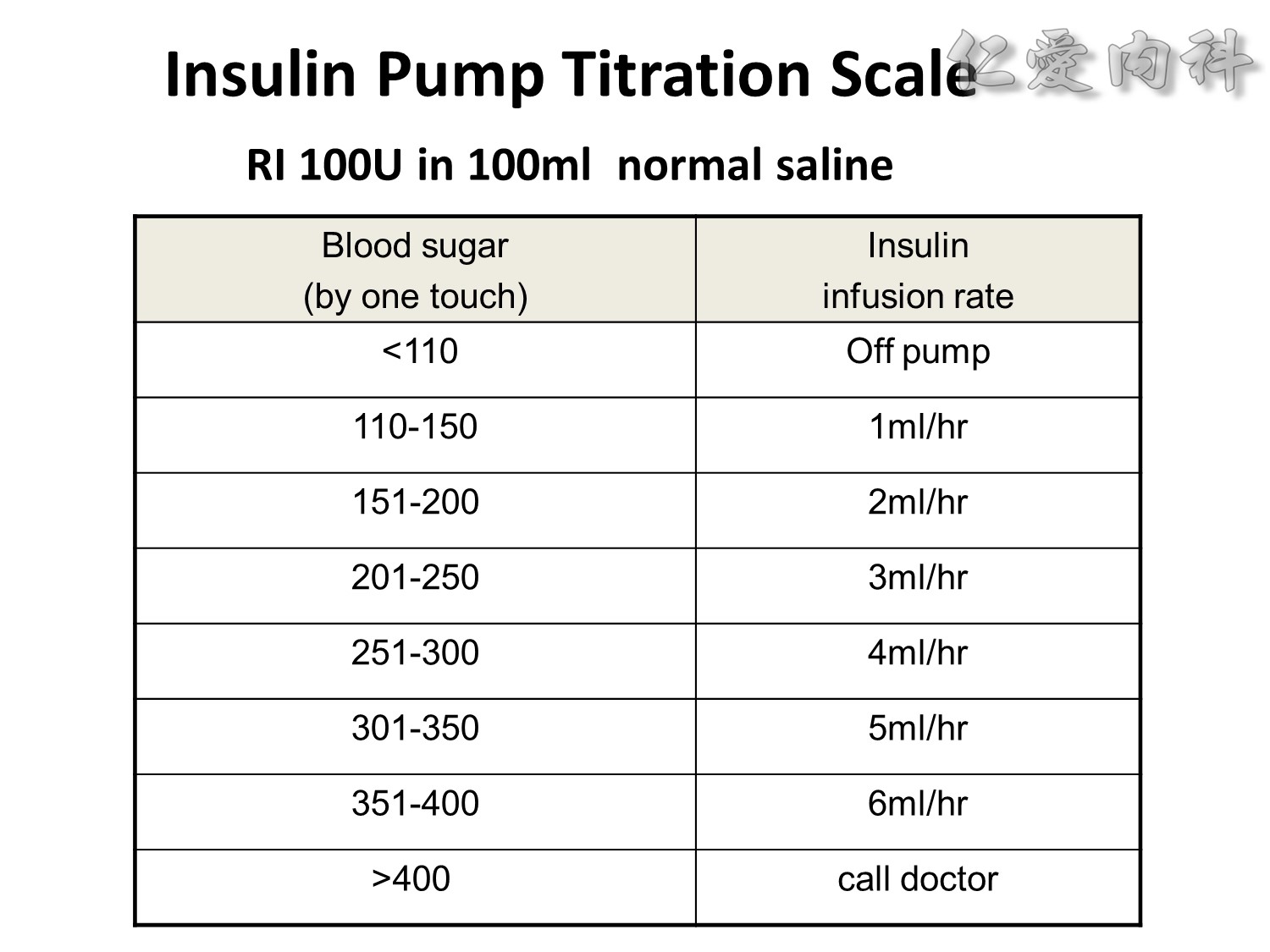
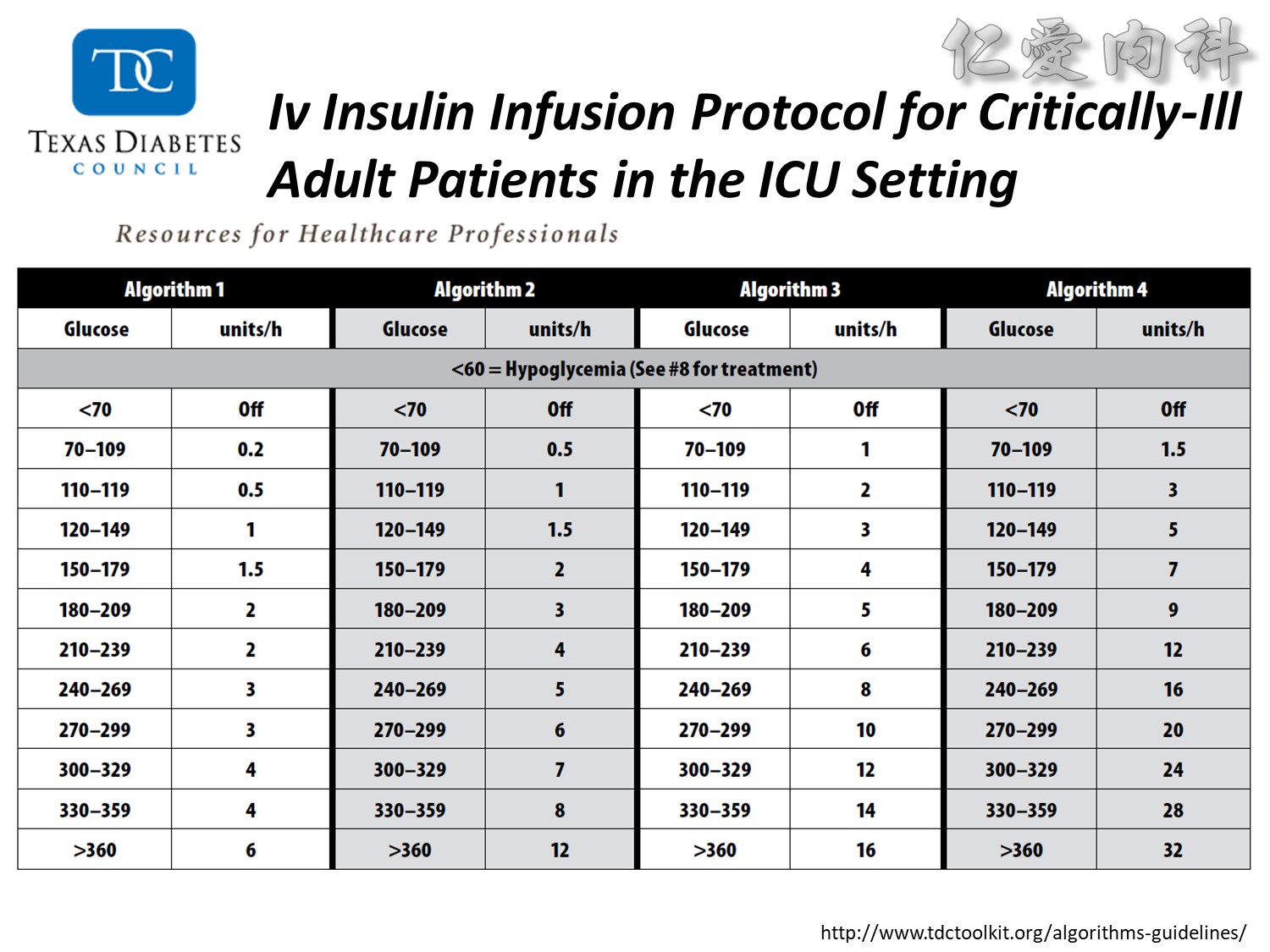
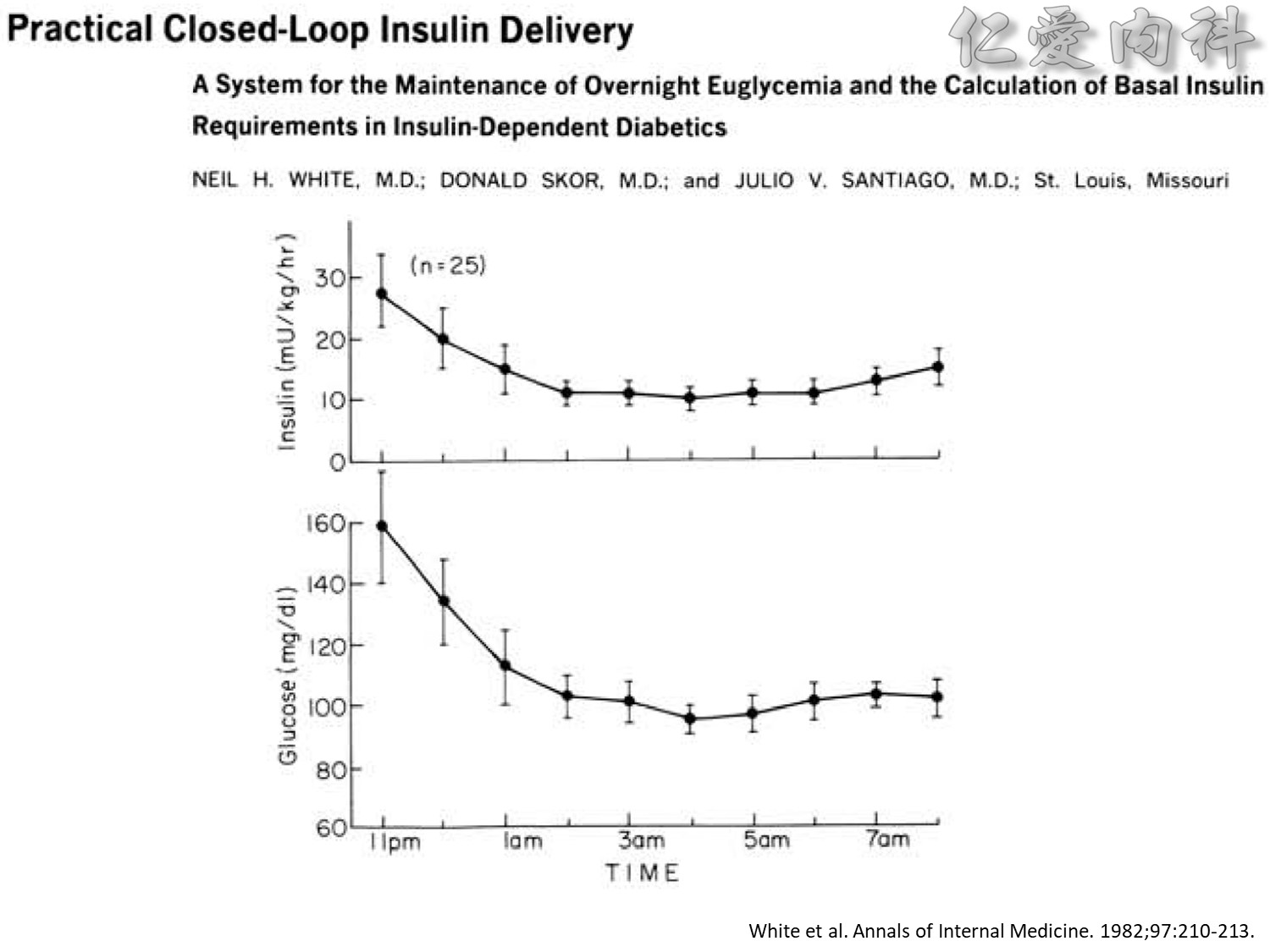
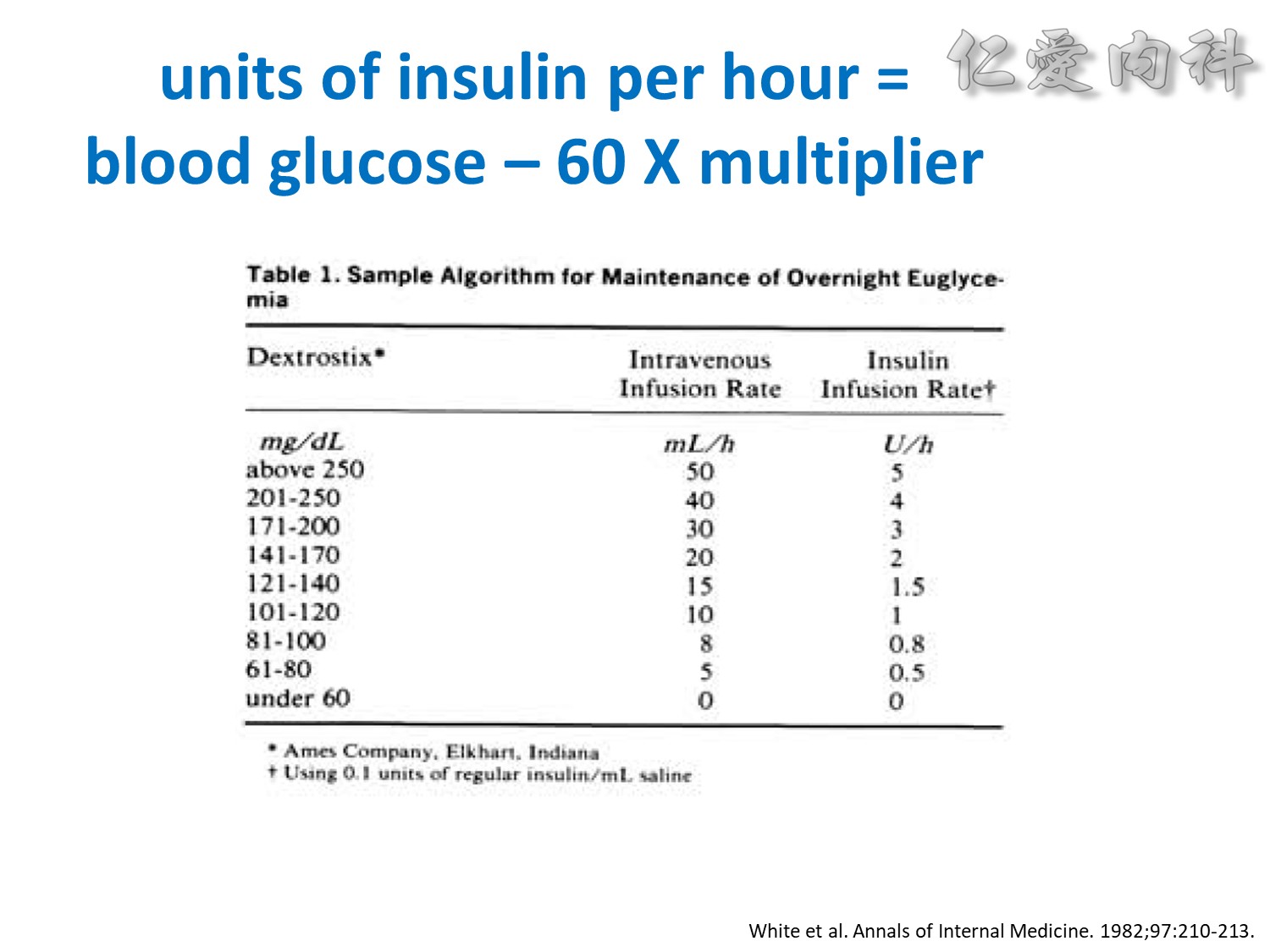
We evaluated a practical closed-loop system of insulin delivery consisting of hourly blood glucose determinations using glucose oxidase reagent strips and an intravenous infusion of insulin controlled by a commonly available controller. In 25 insulin-dependent diabetic subjects, this system was successful in achieving and maintaining near euglycemia (blood glucose, 101 +/- 2 mg/dL, mean +/- SE) in the fasting state between 0200 and 0800 hours. This system may be useful in the management of insulin-dependent diabetic patients in various hospital settings. Also, in 10 subjects treated subsequently using a continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion, the mean hourly insulin infusion rate using the described system correlated well (r = 0.92) with the optimal overnight basal rate needed during continous subcutaneous insulin infusion therapy.