作者/講者: 王喬弘 醫師
校稿: Ian YC Chen, MD
上次校閱: 2018/05/06


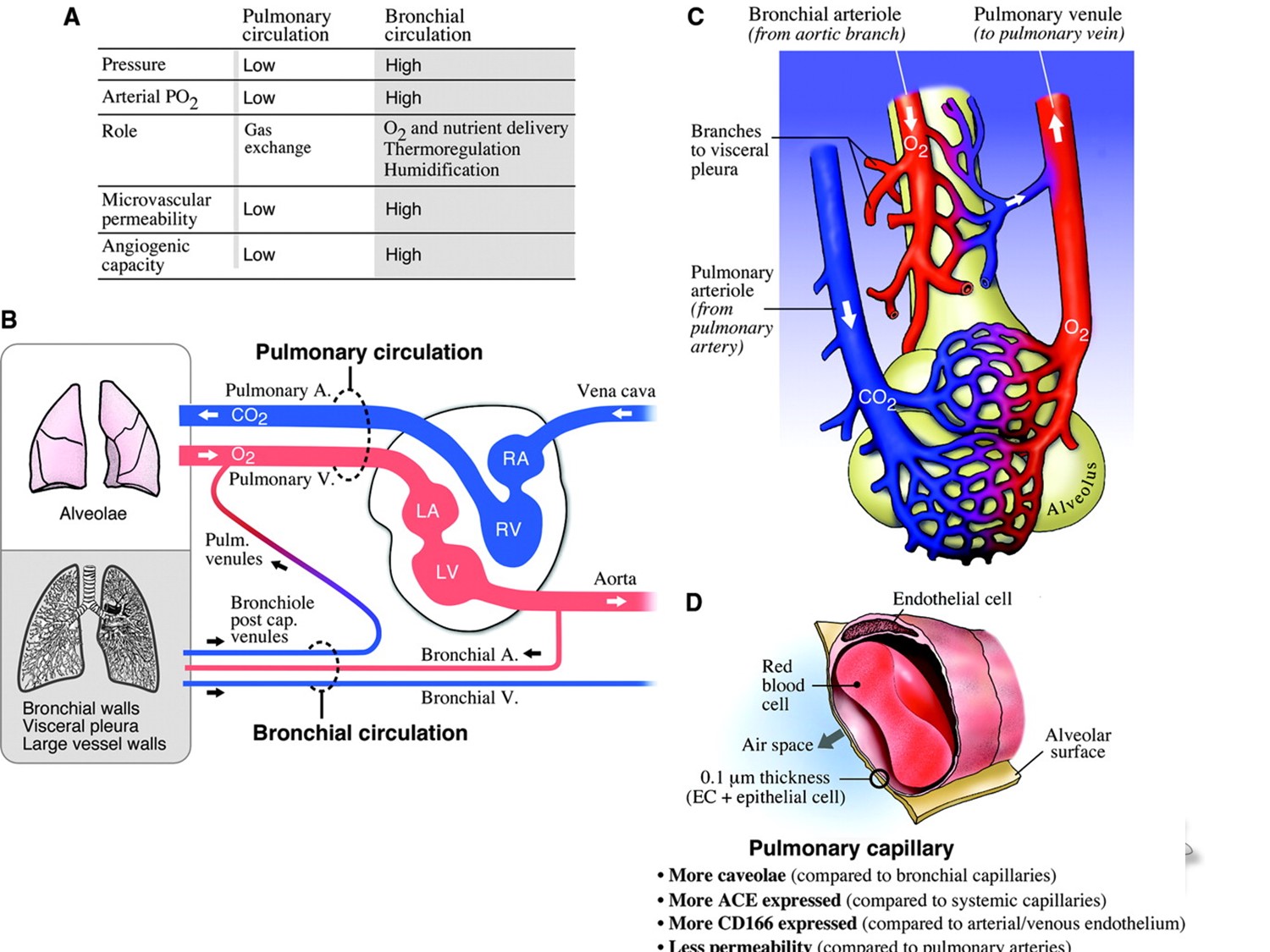
Acute respiratory failure can defined as a state in which the pulmonary system is no longer able to meet the metabolic demands of the body.
It can be divided into hypoxaemic respiratory failure and hypercapnic respiratory failure.
Hypoxaemic respiratory failure is defined as an arterial partial pressure of oxygen of less than or equal to 6.7 kPa when breathing room air and hypercapnic respiratory failure is defined as an arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide of more than or equal to 6.7 kPa.

Hypoxia 是組織缺氧; Hypoxaemia 是血中氧分壓低。
Hypoxaemia 一定會造成 Hypoxia; 但 Hypoxia 不一定會造成 Hypoxaemia。

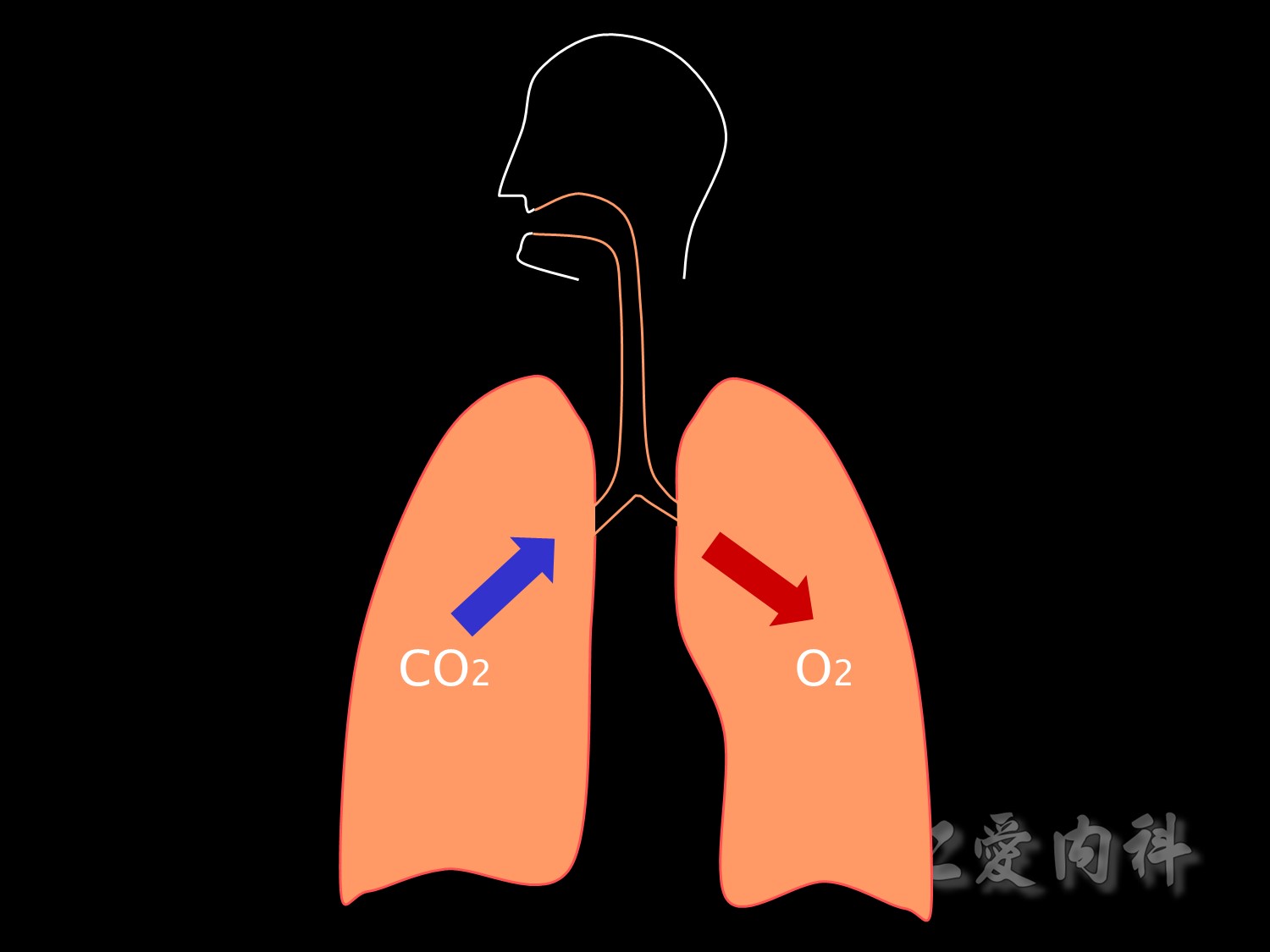
The major function of the lung is to get oxygen into the body and carbon dioxide outㄡ

Getting oxygen into the body depends on the partial pressure of oxygen in the alveoli, the diffusing capacity of the alveolar membrane, ventilation, perfusion and the relationship between the two.
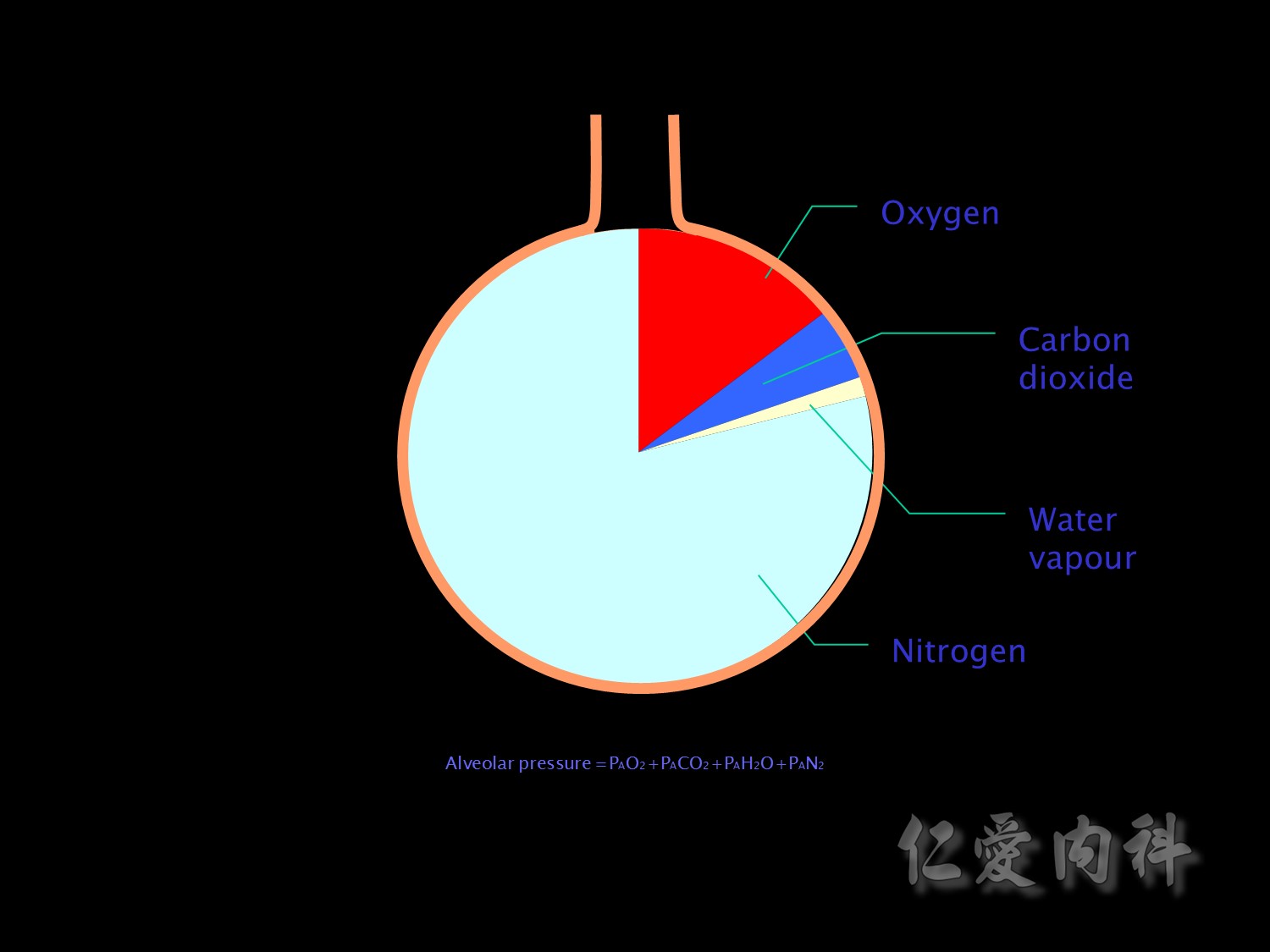
The partial pressure of each gas in a mixture of a gases is directly related to the proportions in which they are present. The sum of the partial pressures is equal to the total pressure inside the container. Thus the partial pressure of a particular gas can be increased by increasing the total pressure or by increasing the proportion of that gas in the mixture. Therefore increasing the alveolar pressure or the proportion of the alveolar gas that consists of oxygen increasing will increase alveolar PO2
Increasing the inspired concentration of oxygen increases the proportion of alveolar gas that is oxygen while reducing the proportion that consists of nitrogen.
The proportion of alveolar gas that is water vapour remains constant and therefore water vapour has no effect on changes in alveolar PO2. On the other hand the proportion of alveolar gas that is CO2 does change and so alveolar PCO2 does affect alveolar PO2
Finally as oxygen diffuses out of the alveolus and carbon dioxide diffuses in the alveolar PO2 falls and PCO2 rises. Ventilation with fresh gas is necessary to restore these to their initial values

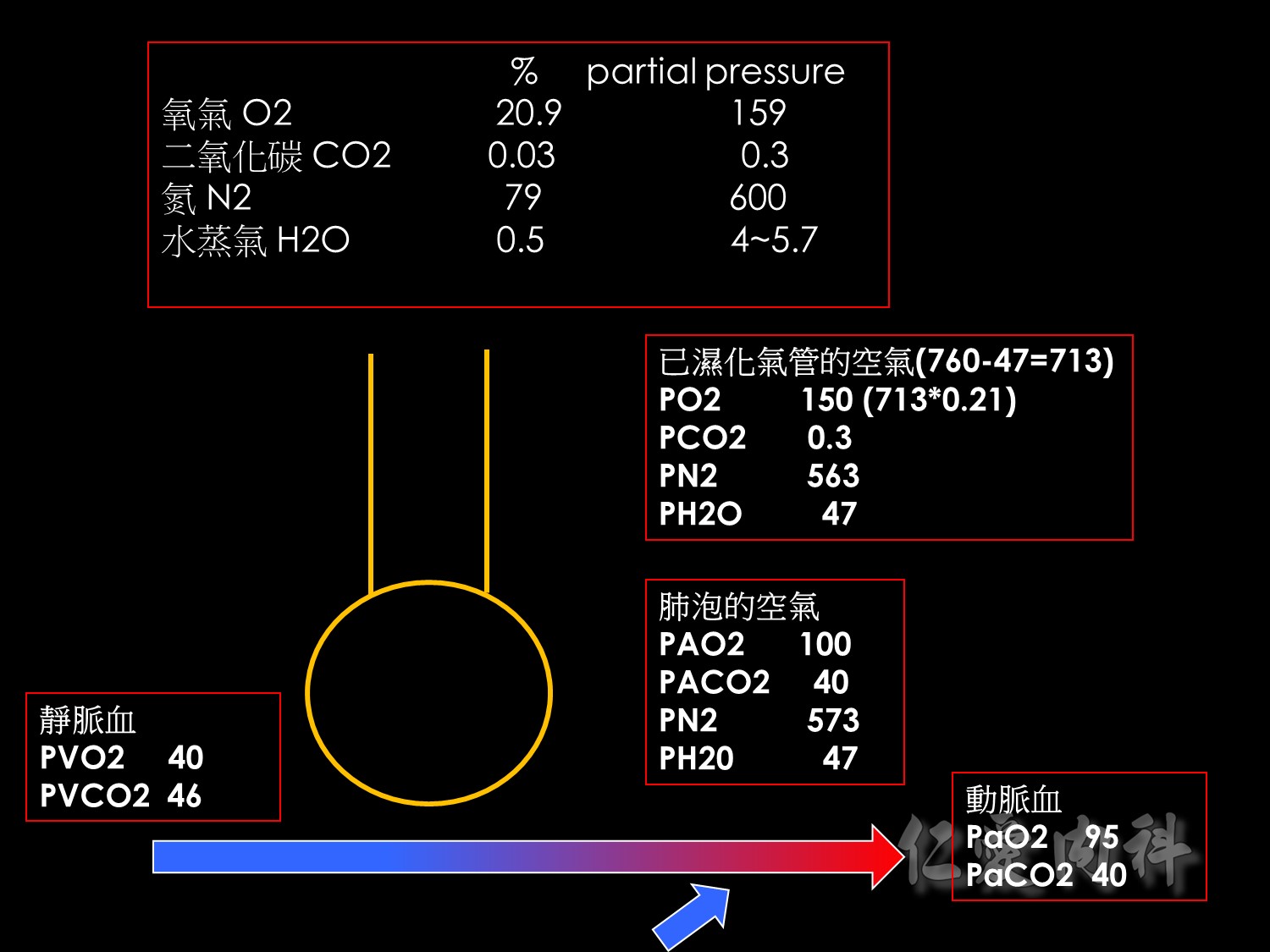
這是用來估計PAO2(濾泡氧分壓)的公式,因為沒辦法直接測得,原因下張ppt會解釋。
另外,PAO2-PaO2的值,也就是A-a gradient,正常大約是10 mmHg左右。
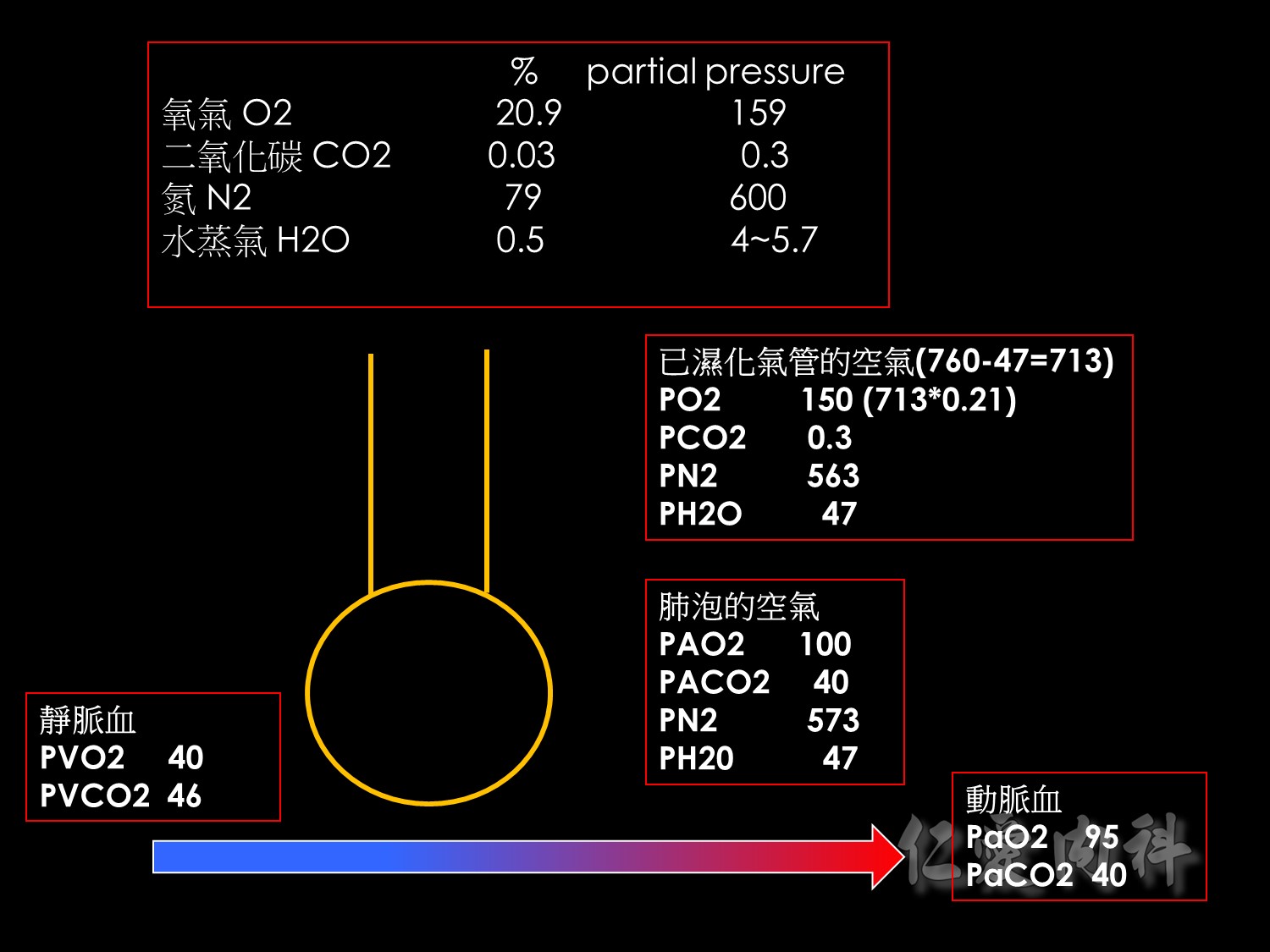
當空氣進入已濕化的氣管時,此時的氧氣壓力是由大氣壓力扣除水蒸氣壓力後的值,在乘上FiO2。
公式後半部的PaCO2/0.8,0.8為呼吸商,是概算當產生0.8mmHg的CO2時,必須消耗1mmHg的O2。又因為PACO2大約等於PaCO2,所以可以算出消耗的氧氣壓力。最後就能估算出肺泡的氧氣壓力 (PAO2)了。

如需估算年紀較大病人的A-a gradient,大約是Age/4+4
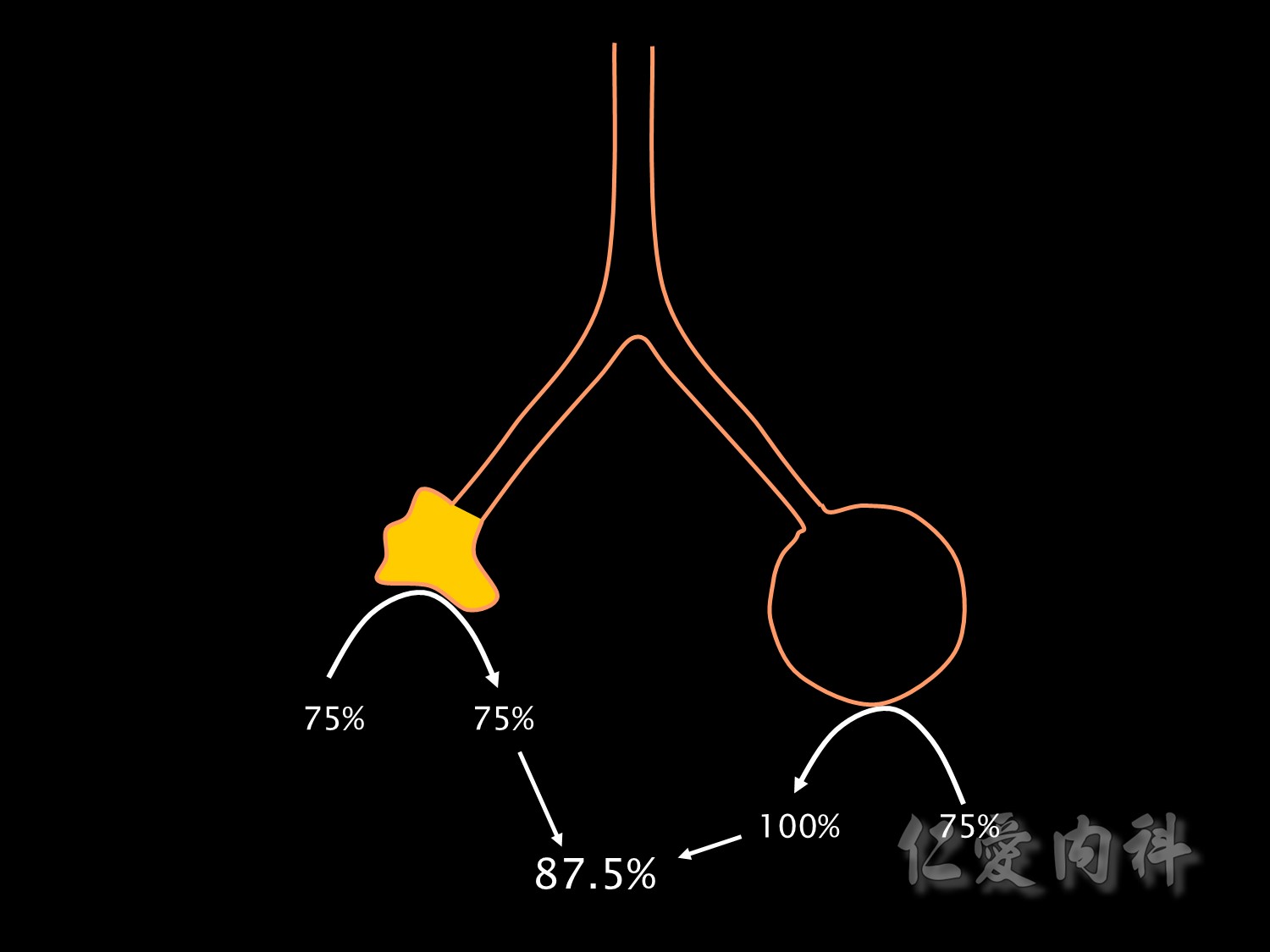
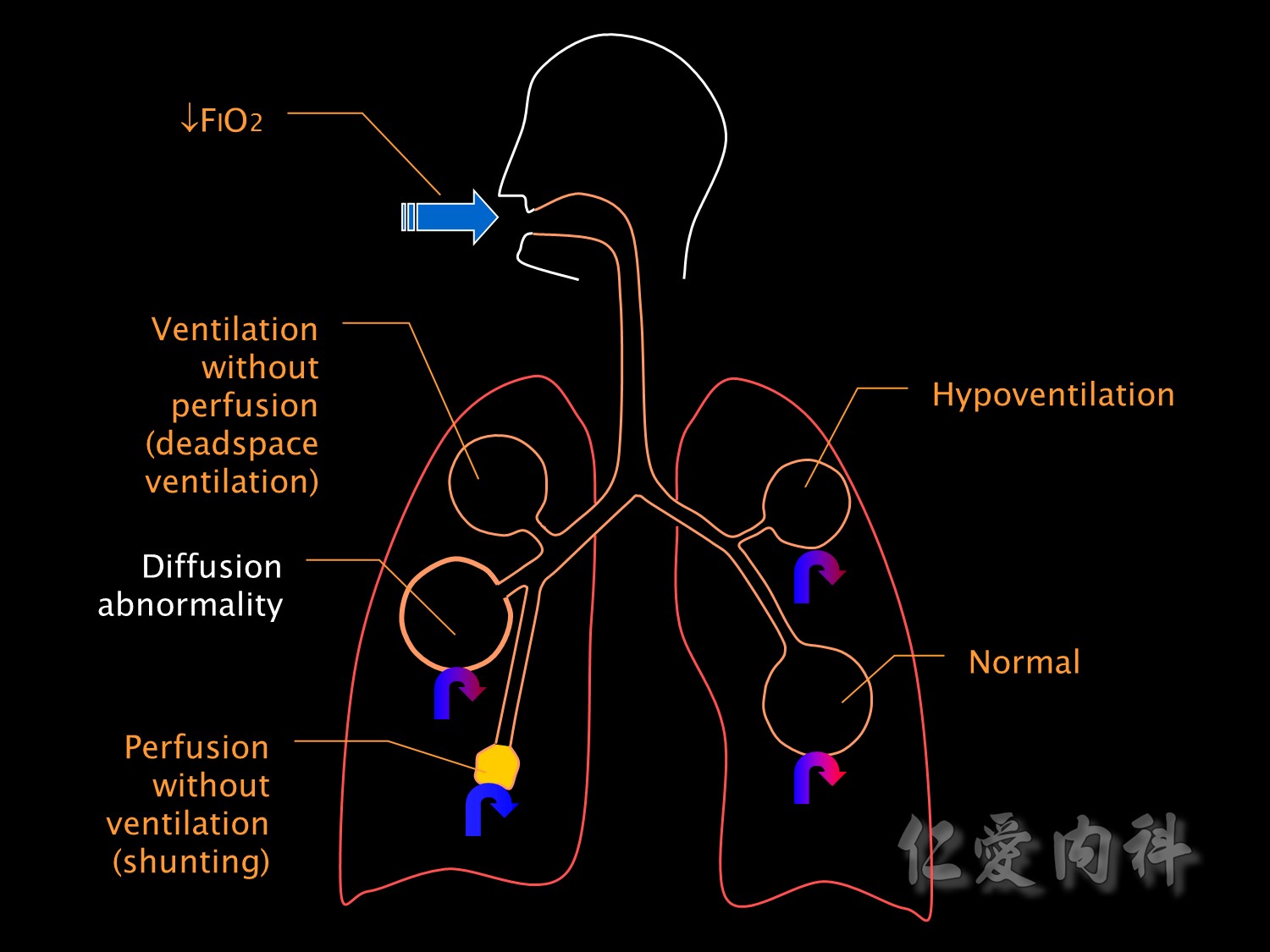
這張圖主要提醒大家有部分的肺血管沒有經過氧氣交換的過程,因此當流回血管時,會減少血管O2的分壓。
下方的箭頭即是代表著未經氣體交換的靜脈。

The effectiveness of carbon dioxide elimination is largely dependent on alveolar ventilation. This in turn is dependent on the respiratory rate, the tidal volume and the volume of dead space. Physiological deadspace but not anatomical deadspace is variable and dependent on ventilation-perfusion matching. Ventilation of non-perfused alveoli increases phsyiological deadspace.

Thus carbon dioxide elimination is dependent on the respiratory rate, tidal volume and ventilation perfusion matching.

接下來是病理性的低血氧的成因。
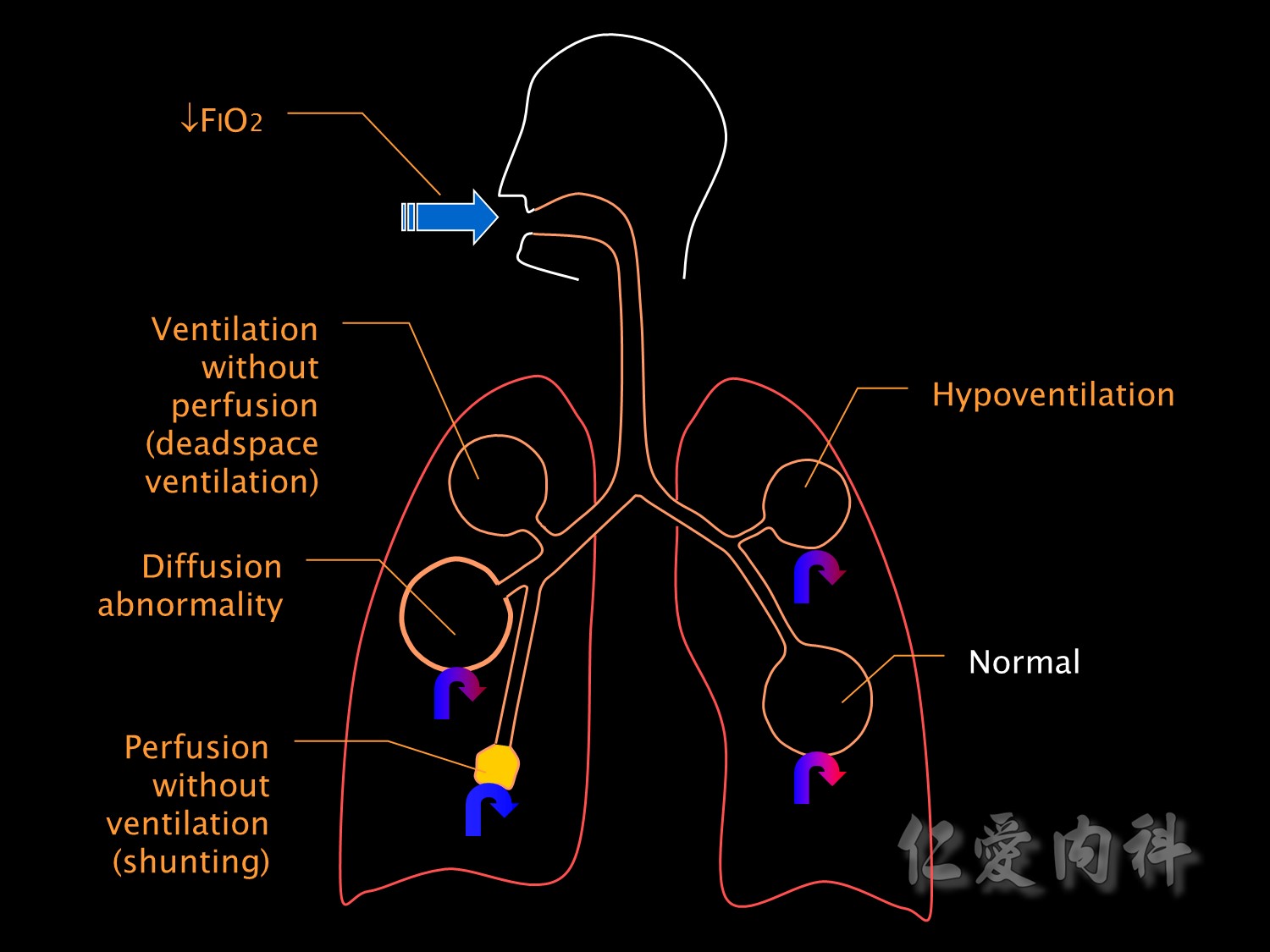
This slide illustrates the various pathophysiological mechanisms which cause respiratory failure.
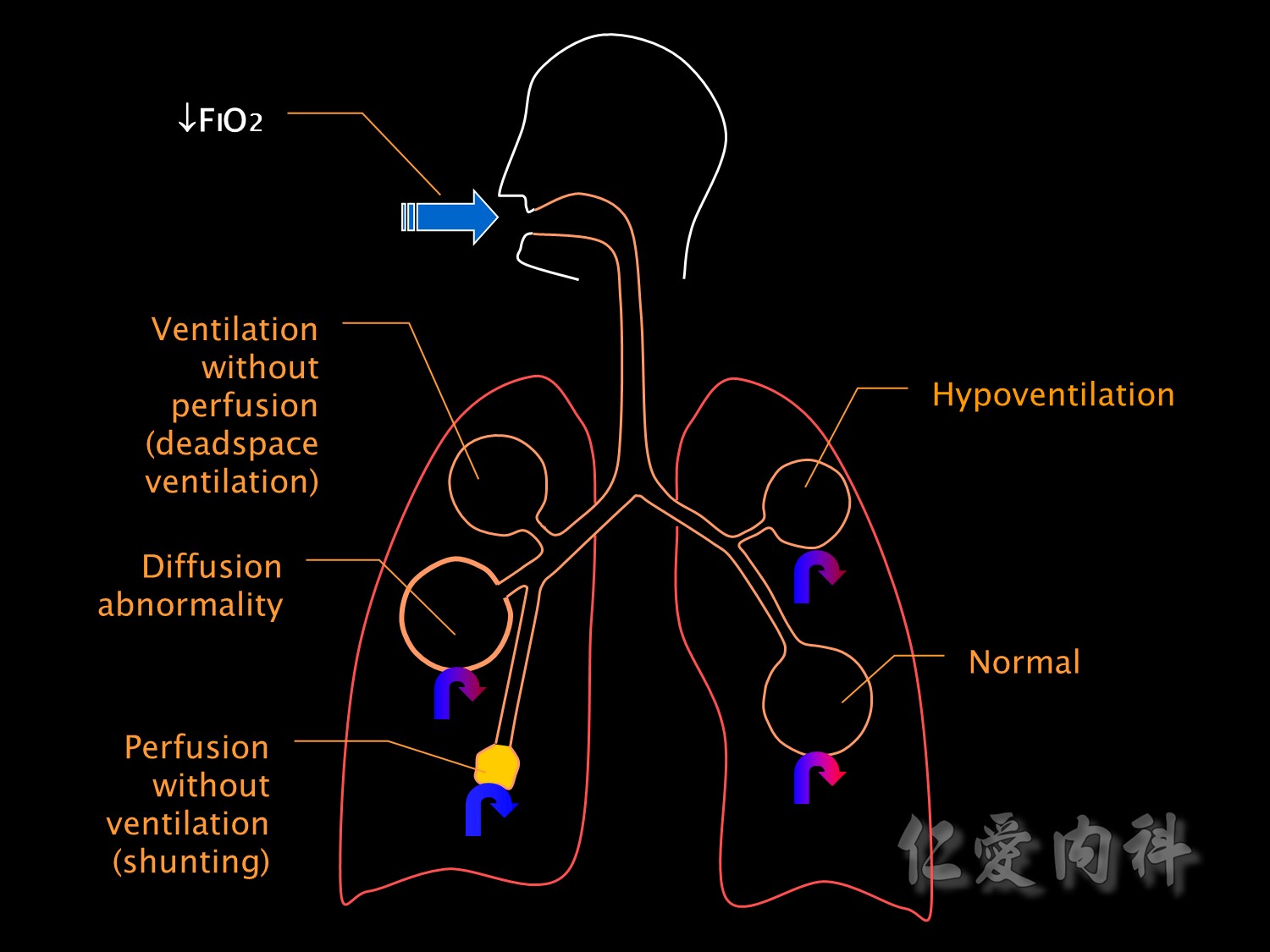
FiO2低會造成低血氧。
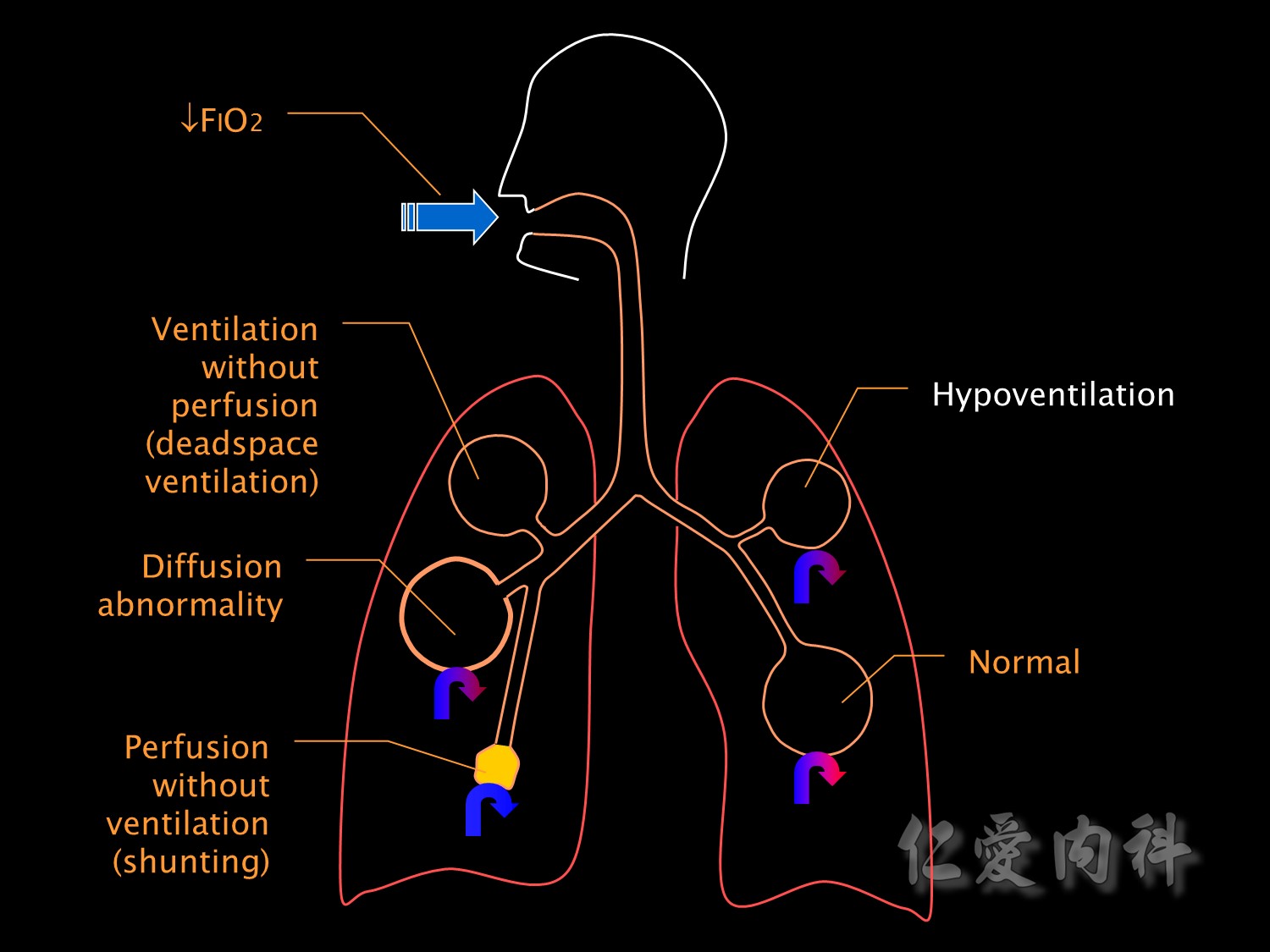
Hypoventilation也會造成低血氧。
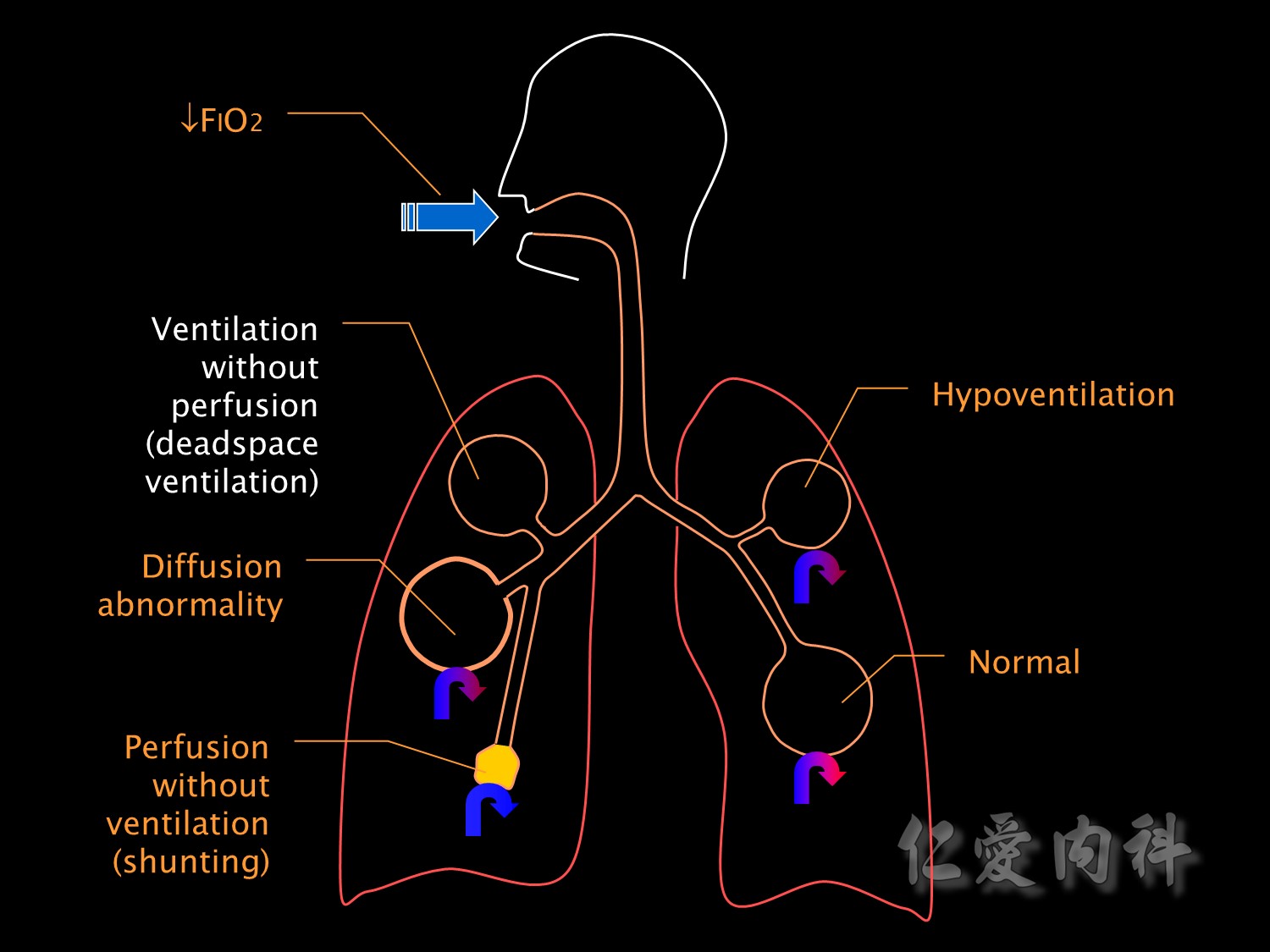
The opposite extreme of ventilation-perfusion mismatch is deadspace ventilation,也會造成低血氧。


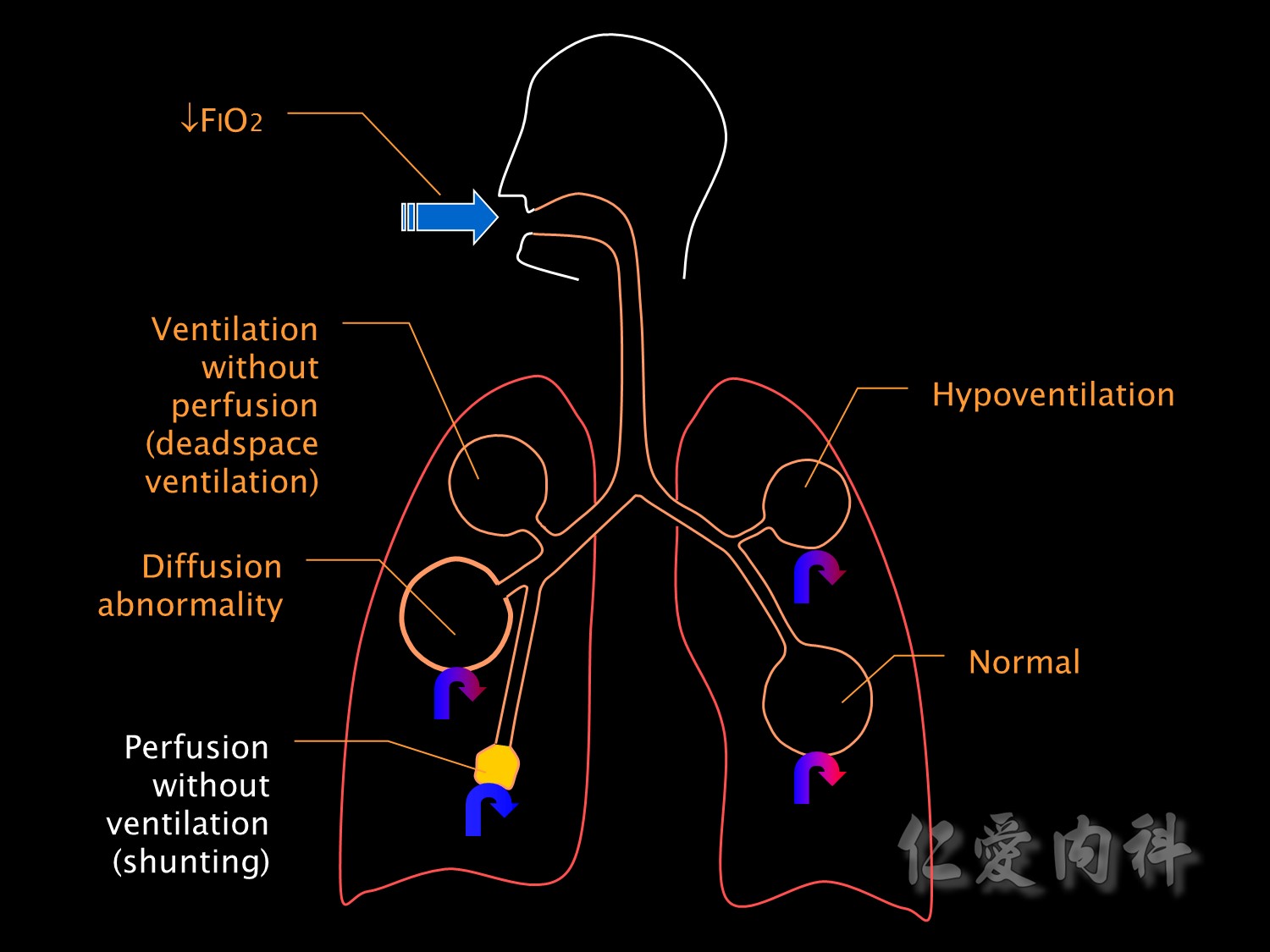
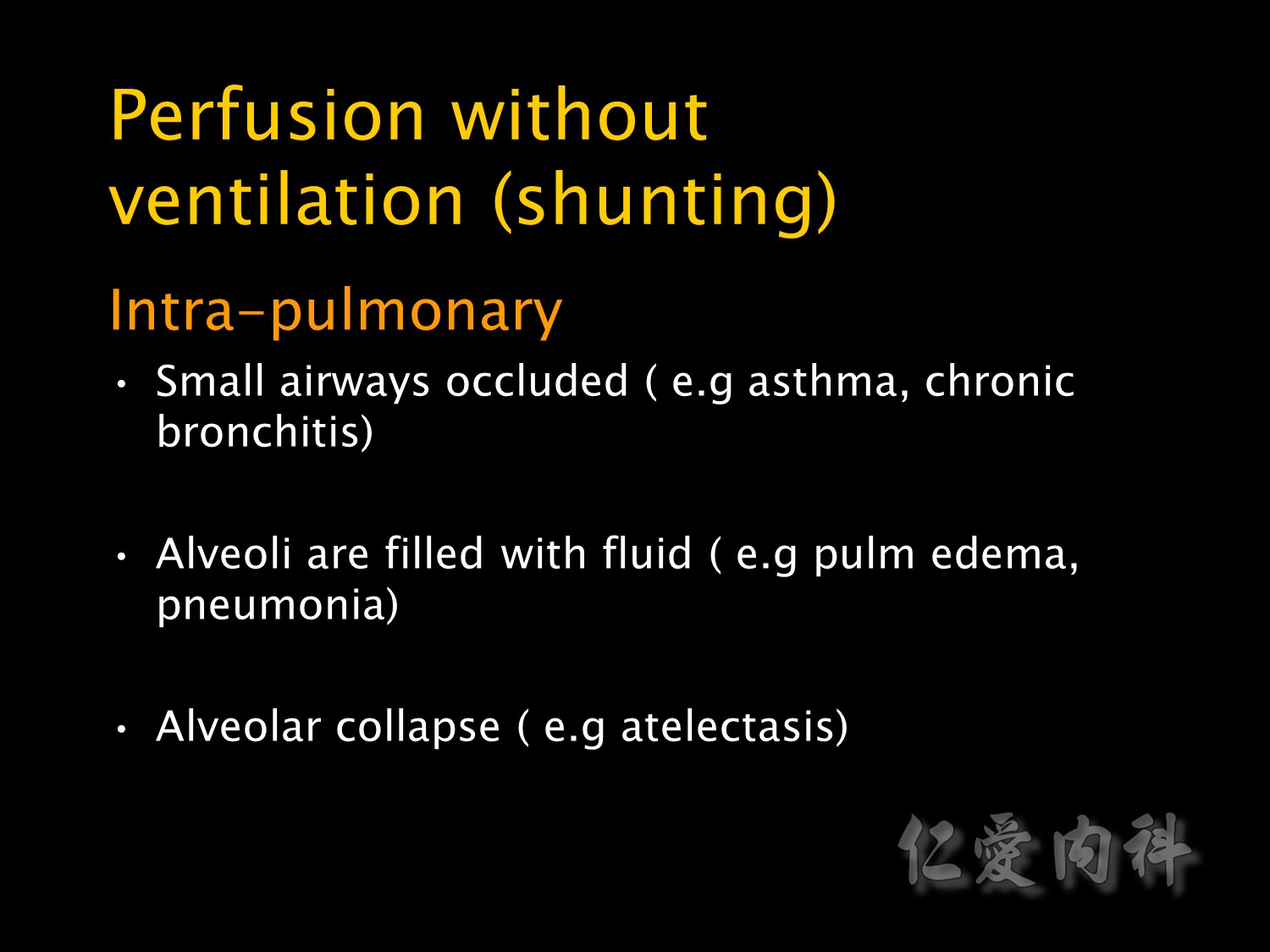
Shunting is the most common cause for hypoxaemic respiratory failure in ICU patients.
It is a form of ventilation-perfusion mismatch in which alveoli which are not ventilated (eg due to collapse or pus or oedema fluid) are still perfused.
Respiratory failure due to shunting is relatively resistant to oxygen therapy. Increasing the inspired oxygen concentration has little effect because it can not reach alveoli where shunting is occurring and blood leaving normal alveoli is already 100% saturated.
氣道阻塞(ex: pneumonia), 氧氣過不去,但血流正常,變成一種shunting,FiO2也因此下降。

Shunting can also occur at an intra-cardiac level but this is an unusual cause of hypoxaemia in the ICU. Causes of intrapulmonary shunting include pneumonia, pulmonary oedema, atelectasis, collapse and pulmonary haemorrhage or contusion.
Diffusion abnormalities
像是ILD(interstitial lung disease)會使肺泡間質變厚,會影響氣體交換。

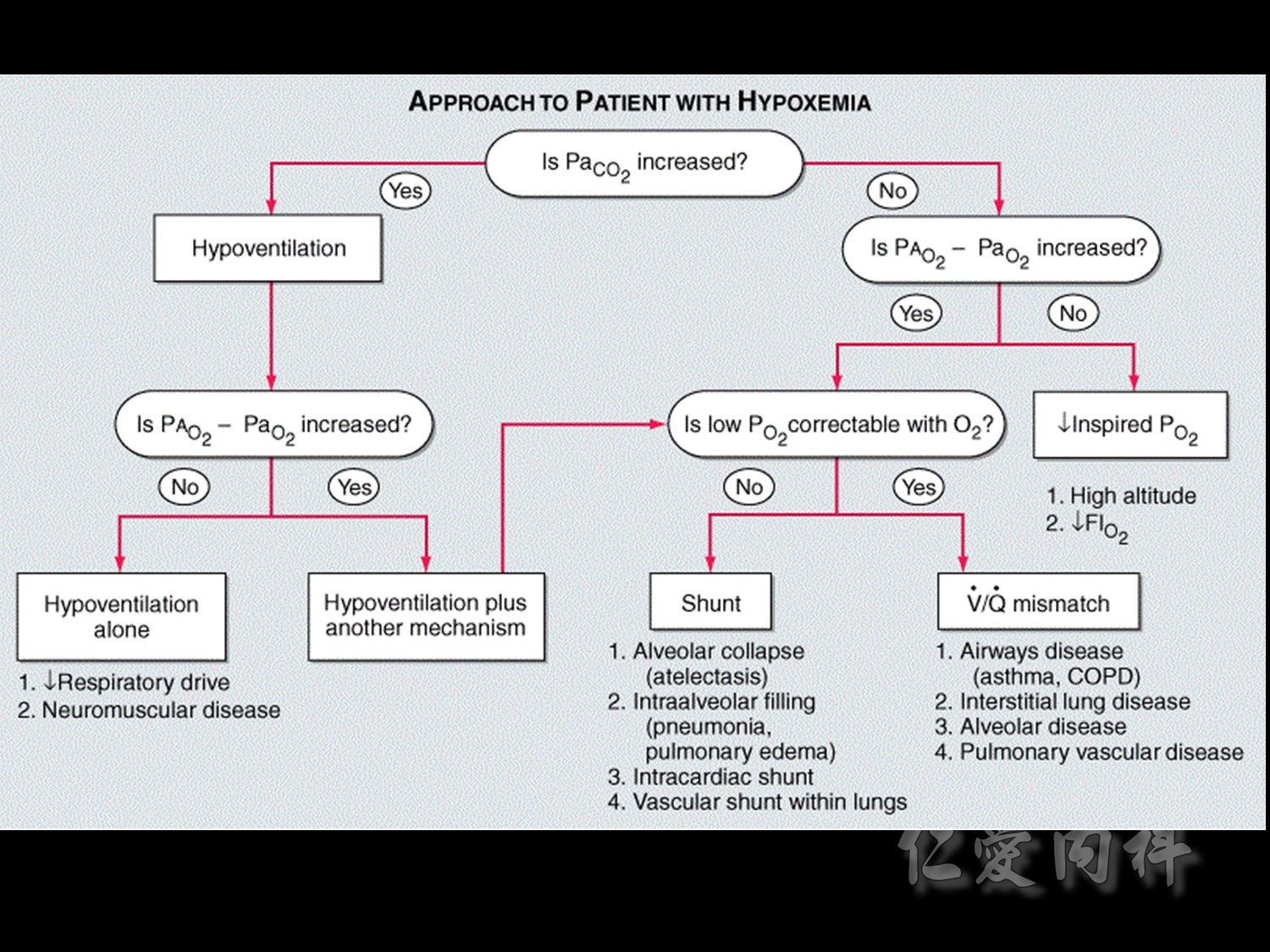
摘錄自harrison: 這是一張Hypoxemia的Flow chart。當Hypoxemia時,要先看病人的PaCO2來決定接下去的步驟。











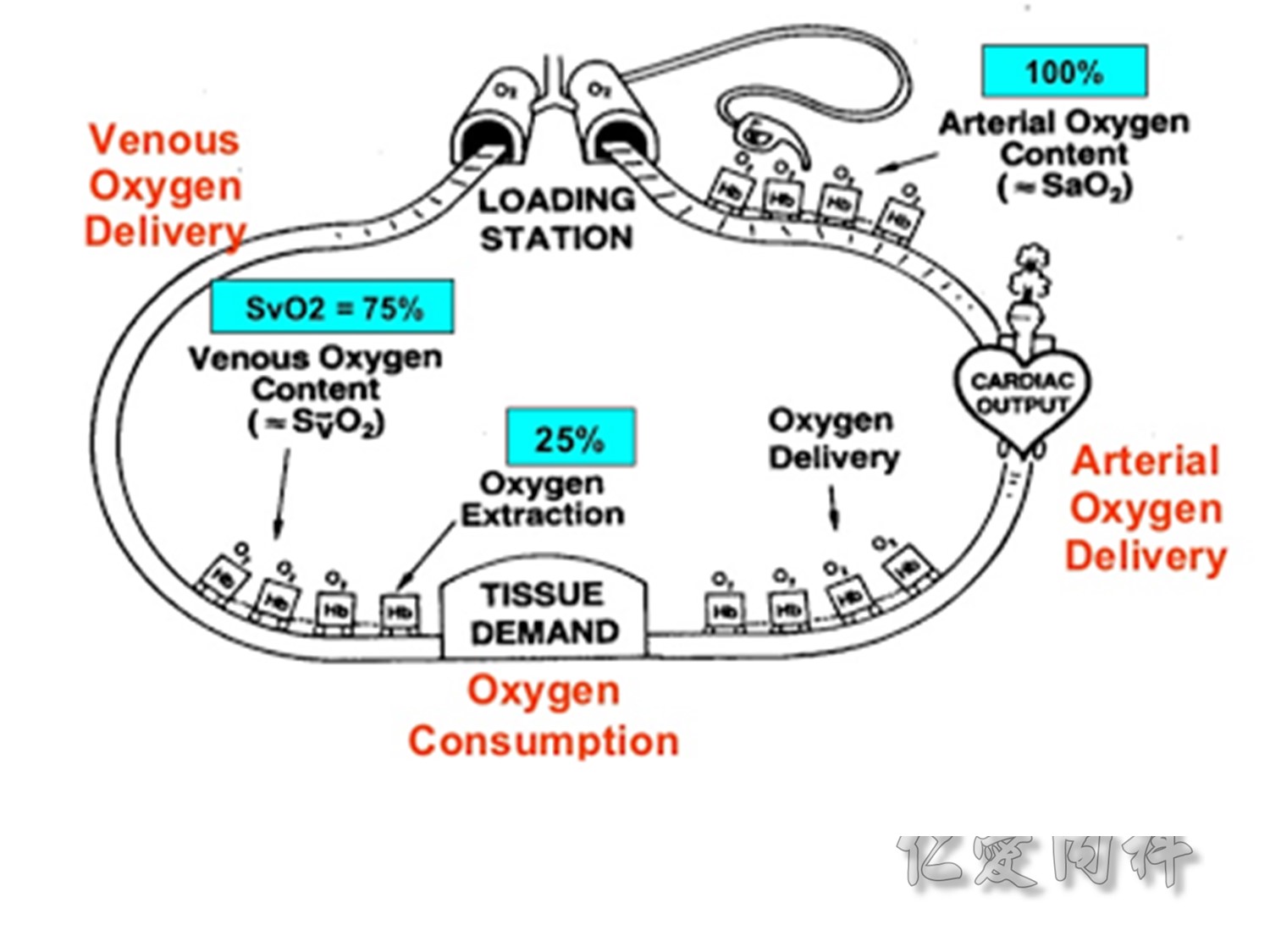
O2在血中與Hb結合,如果結合率不高,會影響SaO2。Cardio output也會影響arterial oxygen delivery。最後,當組織耗氧量大時(ex: infection……),會降低venous oxygen delivery的量。


CaO2 (動脈血含氧量)的公式為(1.34*Hb*SpO2) + (PaO2*0.003)。原因如上。
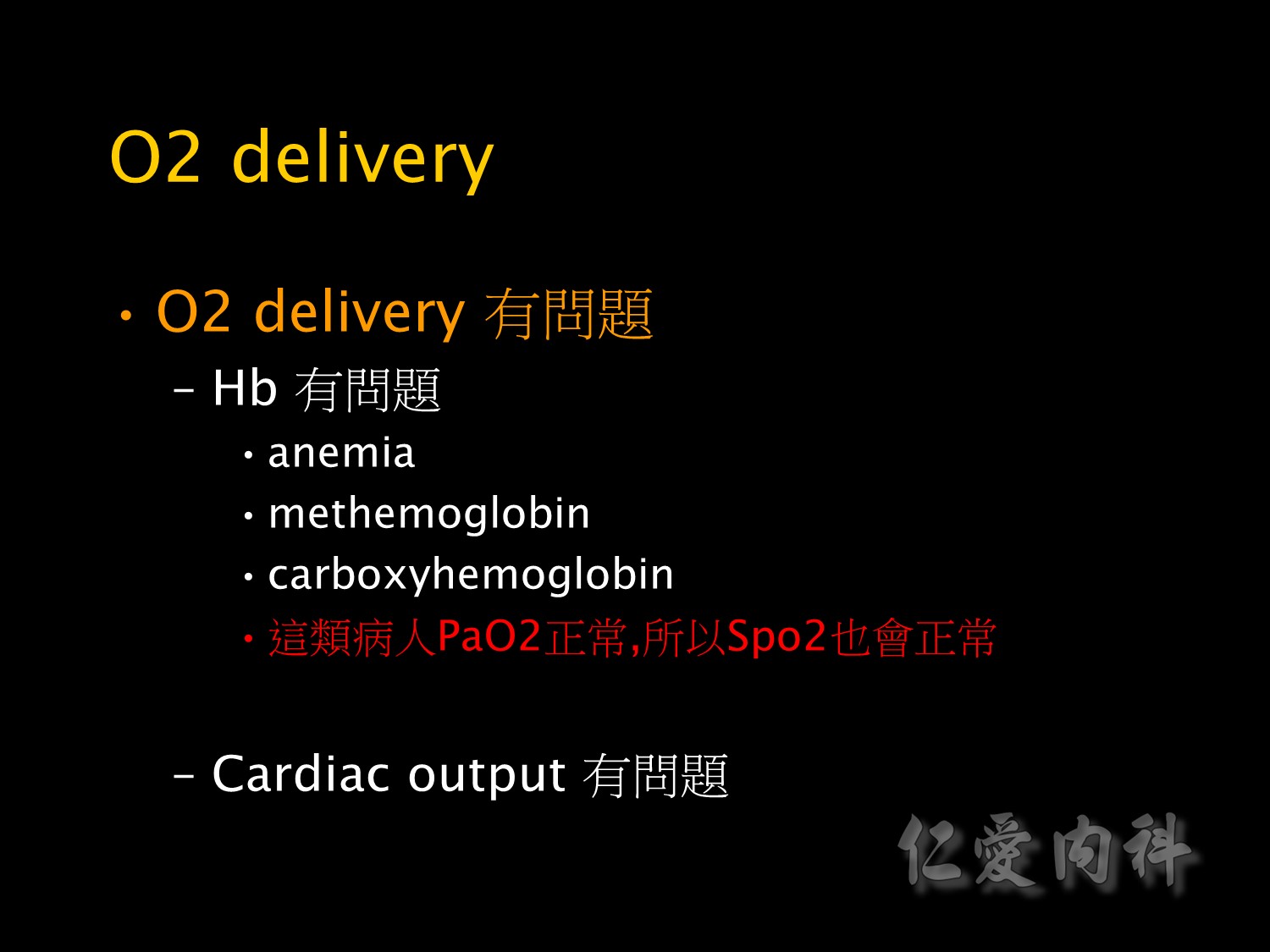
Methemoglobin:指的是變性的Hb無法結合O2。carboxyhemoglobin:指的是與CO結合的Hb。






接下來是病理性造成血中高二氧化碳的成因: 由呼吸的路徑依序開始想: brainstem->
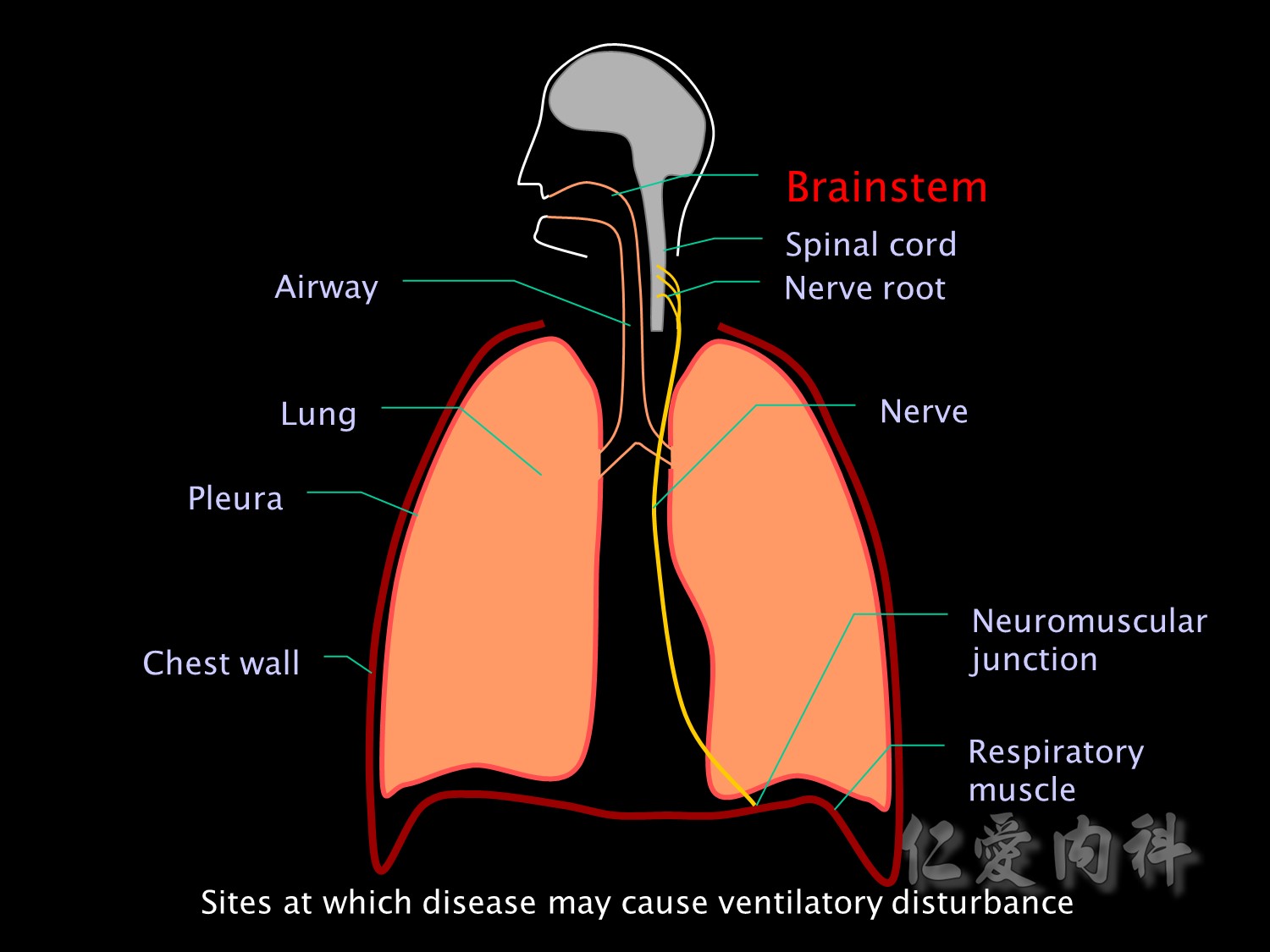
Hypoventilation can be caused by disease at any of the anatomical sites involved in ventilation. Brainstem injury or disease may result in impaired functioning of the respiratory centre, which may also be suppressed by depressant drugs.

brainstem異常的原因
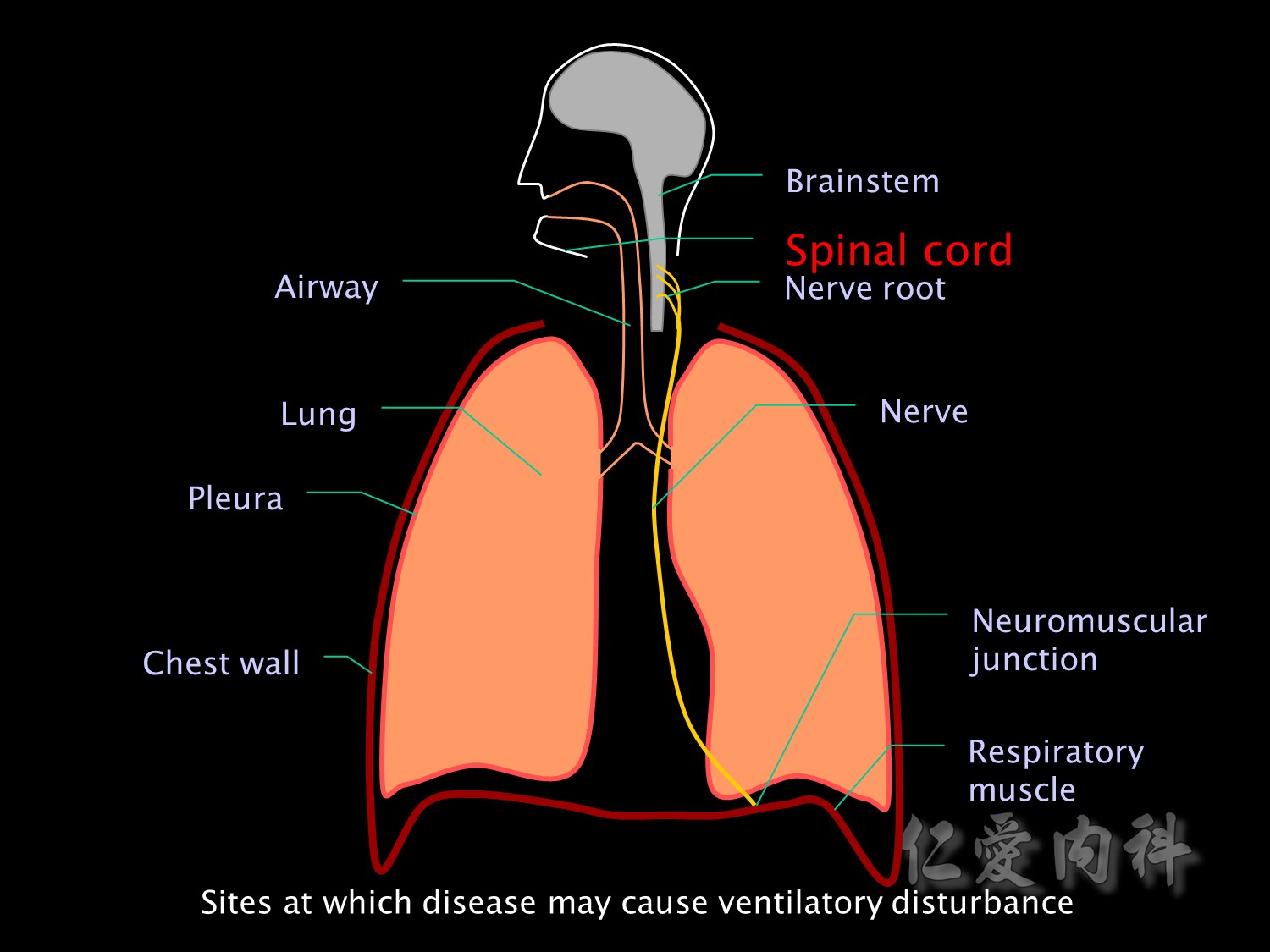
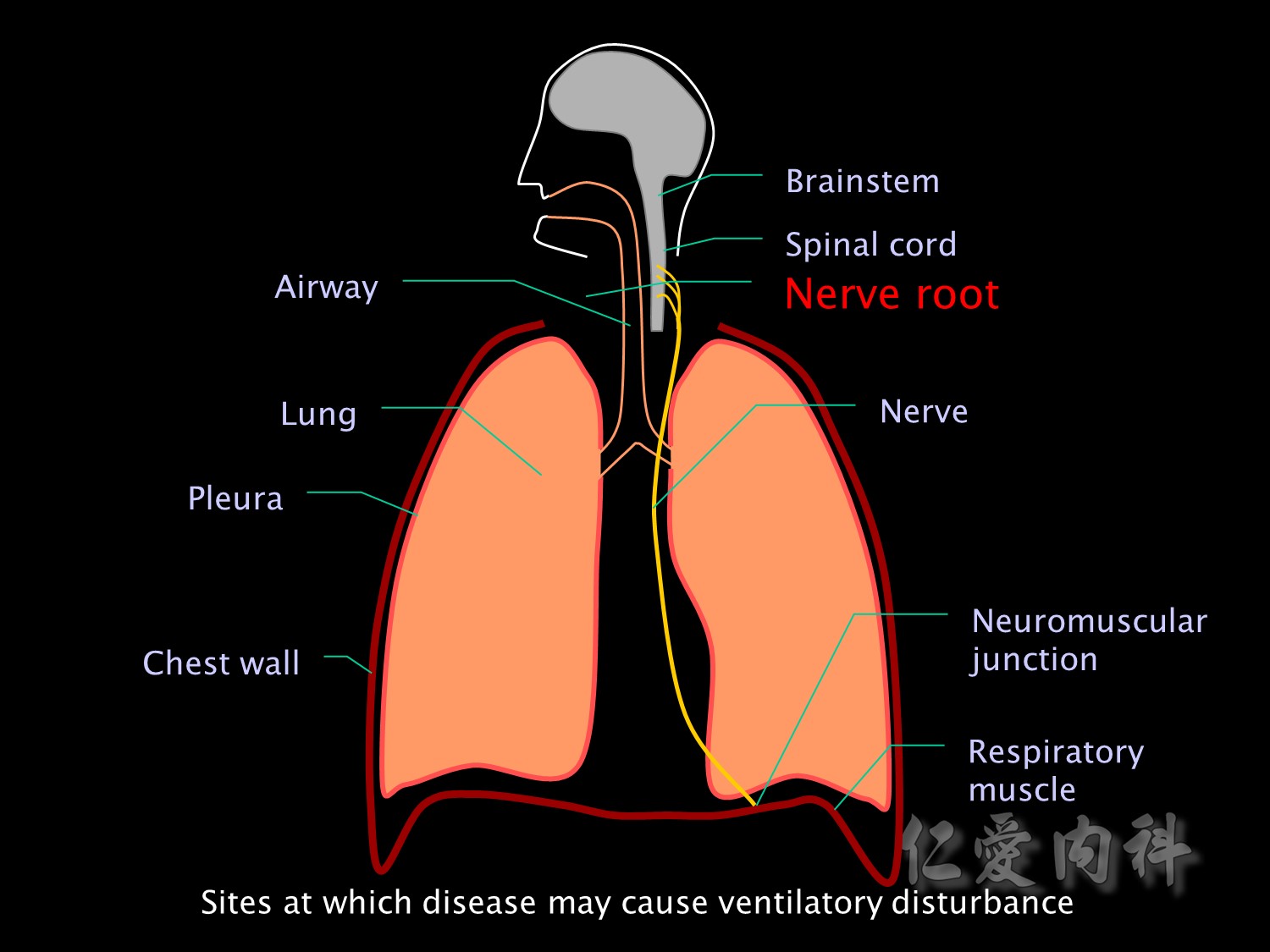
The nerve roots may be damaged by trauma or tumour.
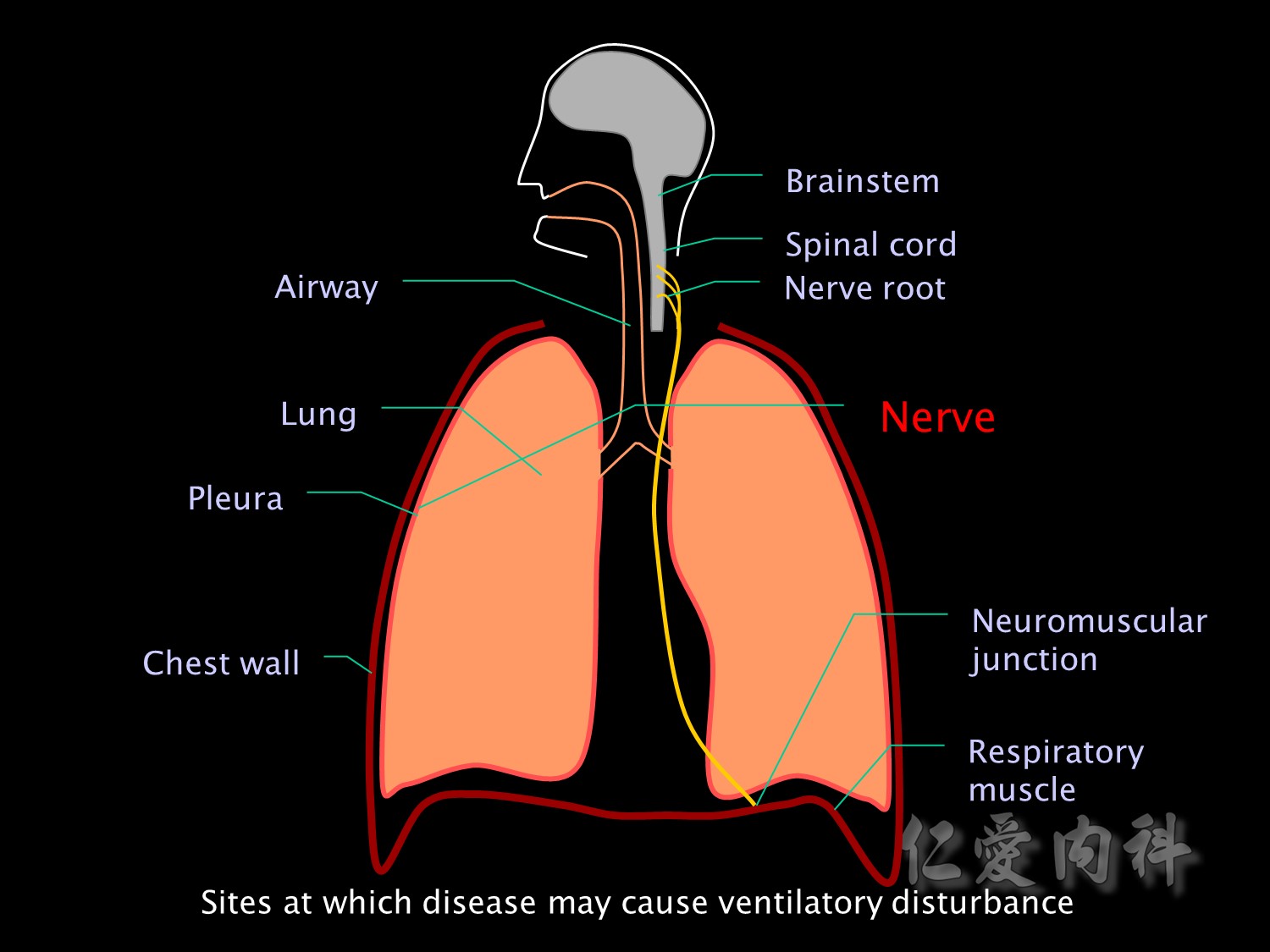
And nerve injuries and neuropathies such as Guillain Barre or critical illness neuropathy may affect motor neurons supplying respiratory muscles.

Nerve 異常的原因
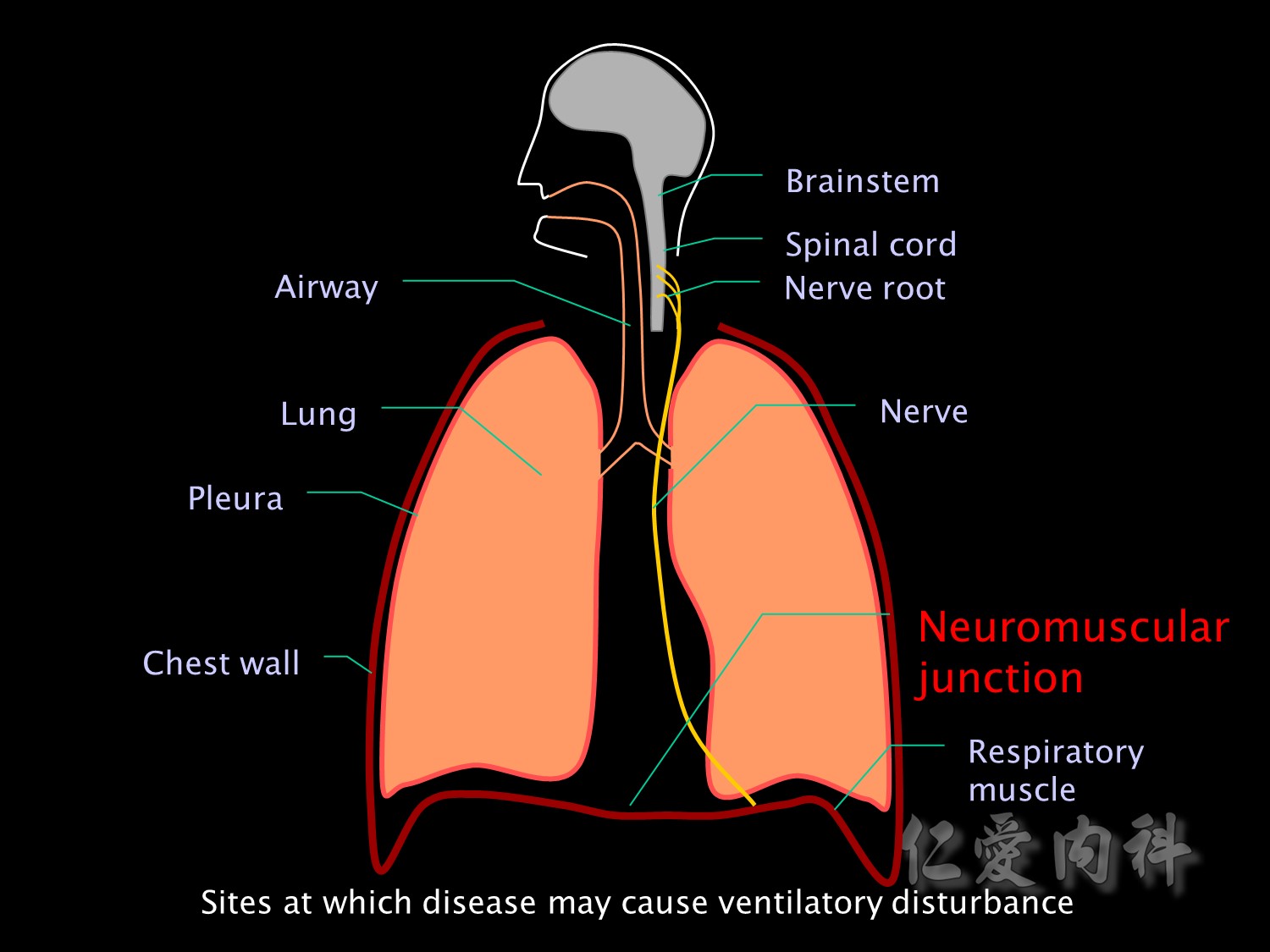
Neuromuscular blockers or disease of the neuromuscular junction (eg myasthenia gravis) may impair transmission of nerve impulses to respiratory muscles.

NMJ junction異常的原因.
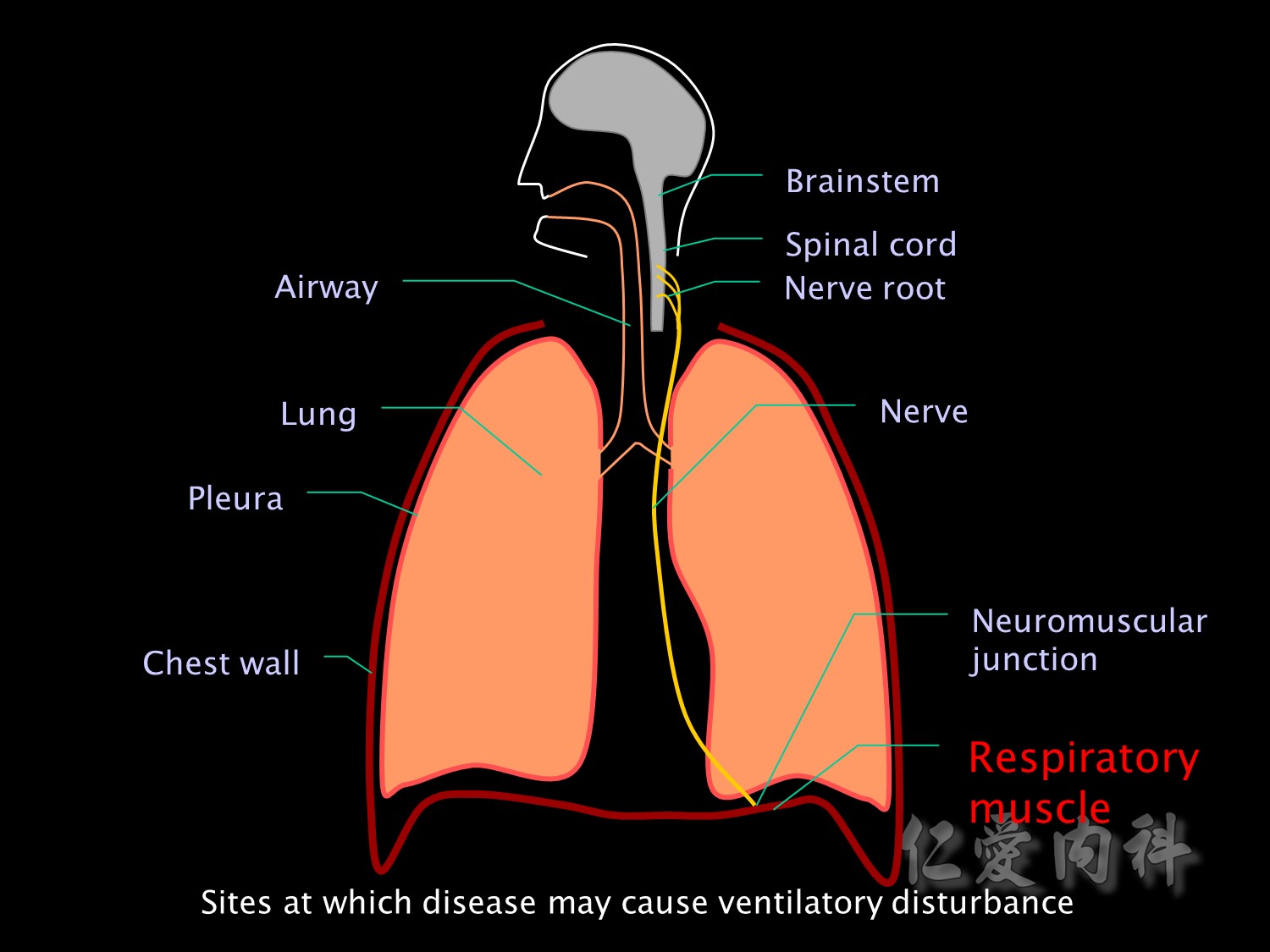
Or the problem may be in the muscle itself. Respiratory muscle fatigue, disuse atrophy and malnutrition are important causes of respiratory muscle failure in the ICU.
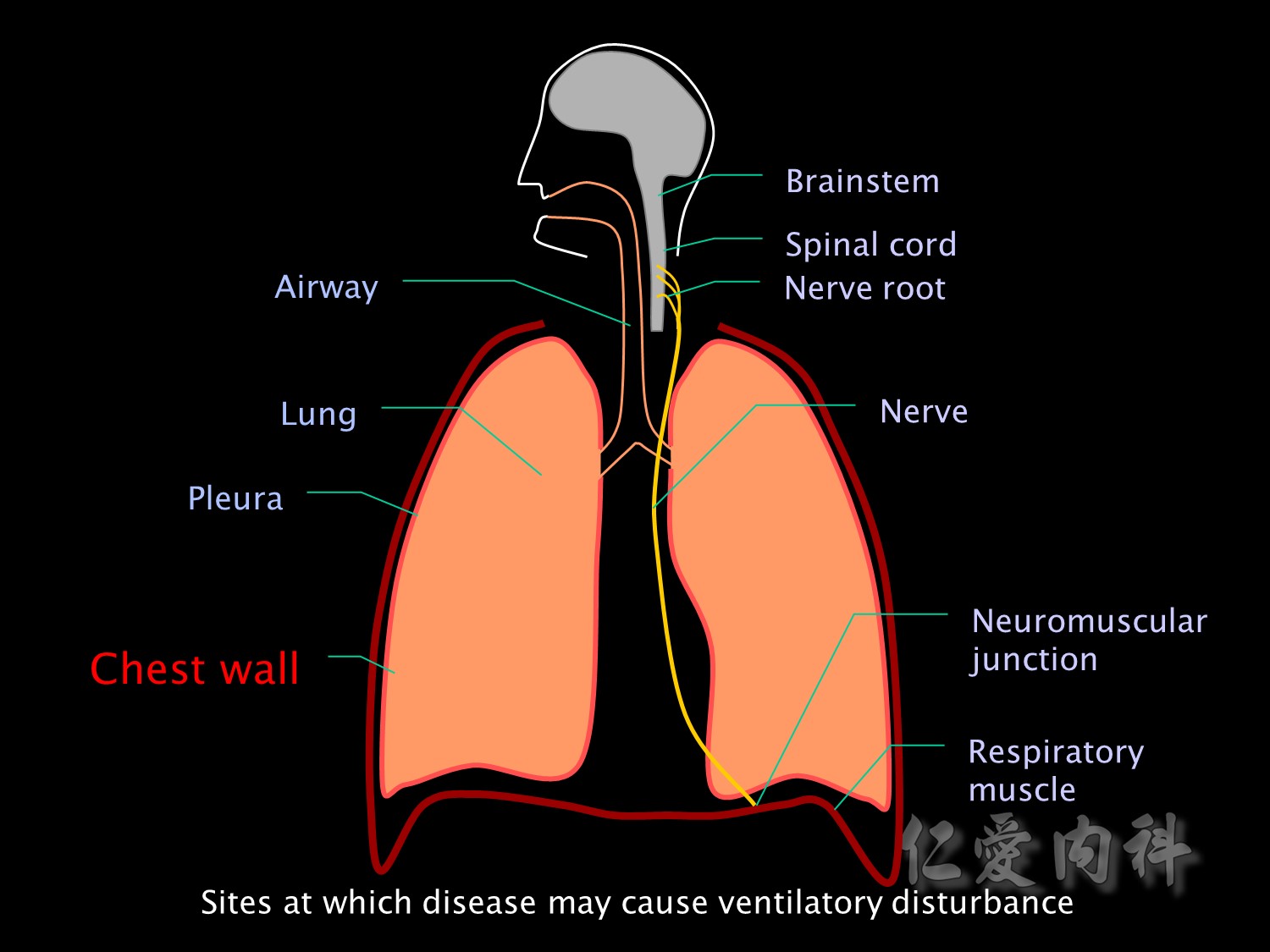
Or the problem may be decreased compliance of the lung itself, the pleura or the chest wall.

Chest wall異常的原因
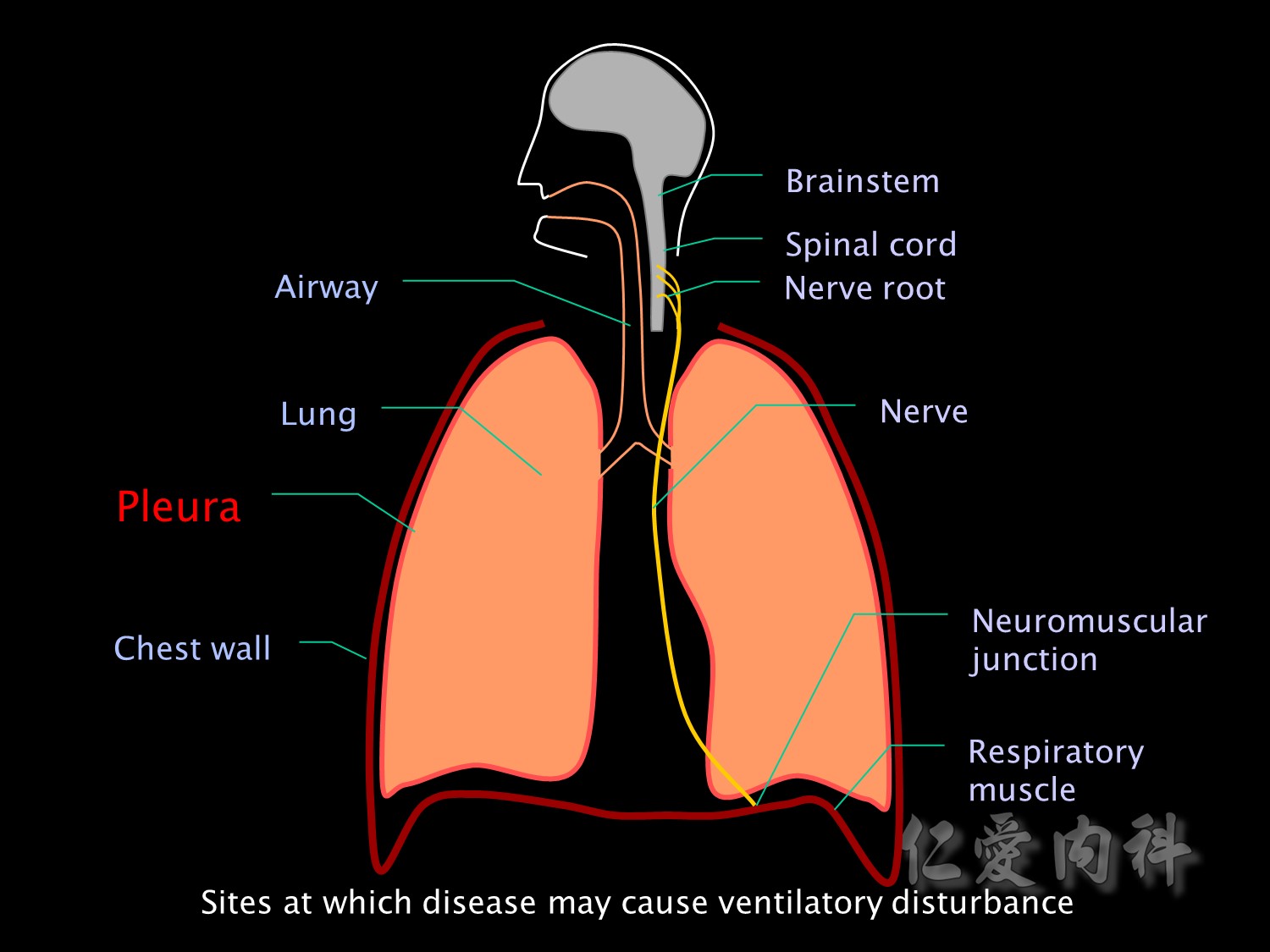
Or the problem may be decreased compliance of the lung itself, the pleura or the chest wall.
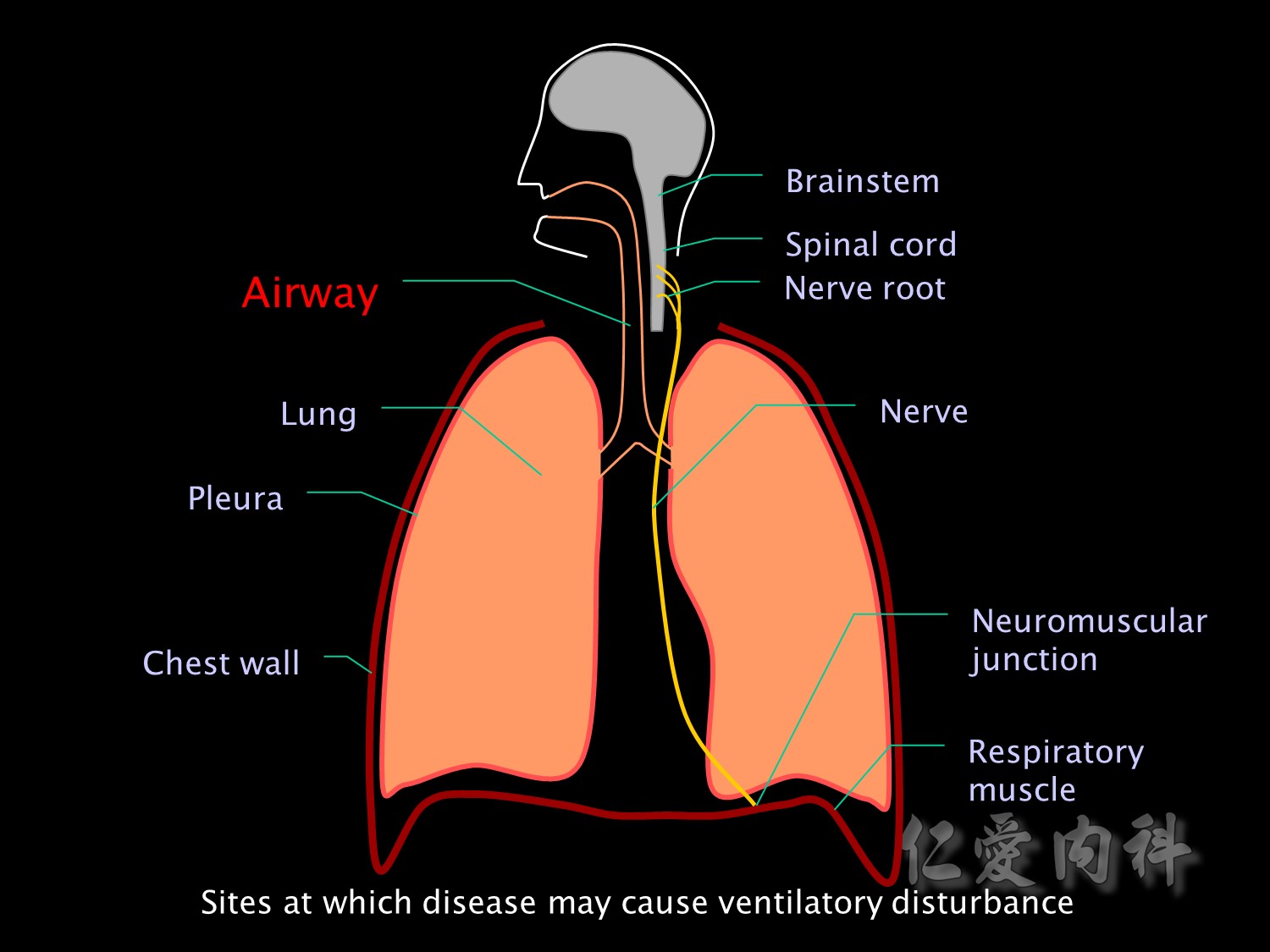
Alternatively the problem may be a problem of increased resistance to airflow. For example due to obstruction of the upper airway or bronchospasm.

airway異常的原因
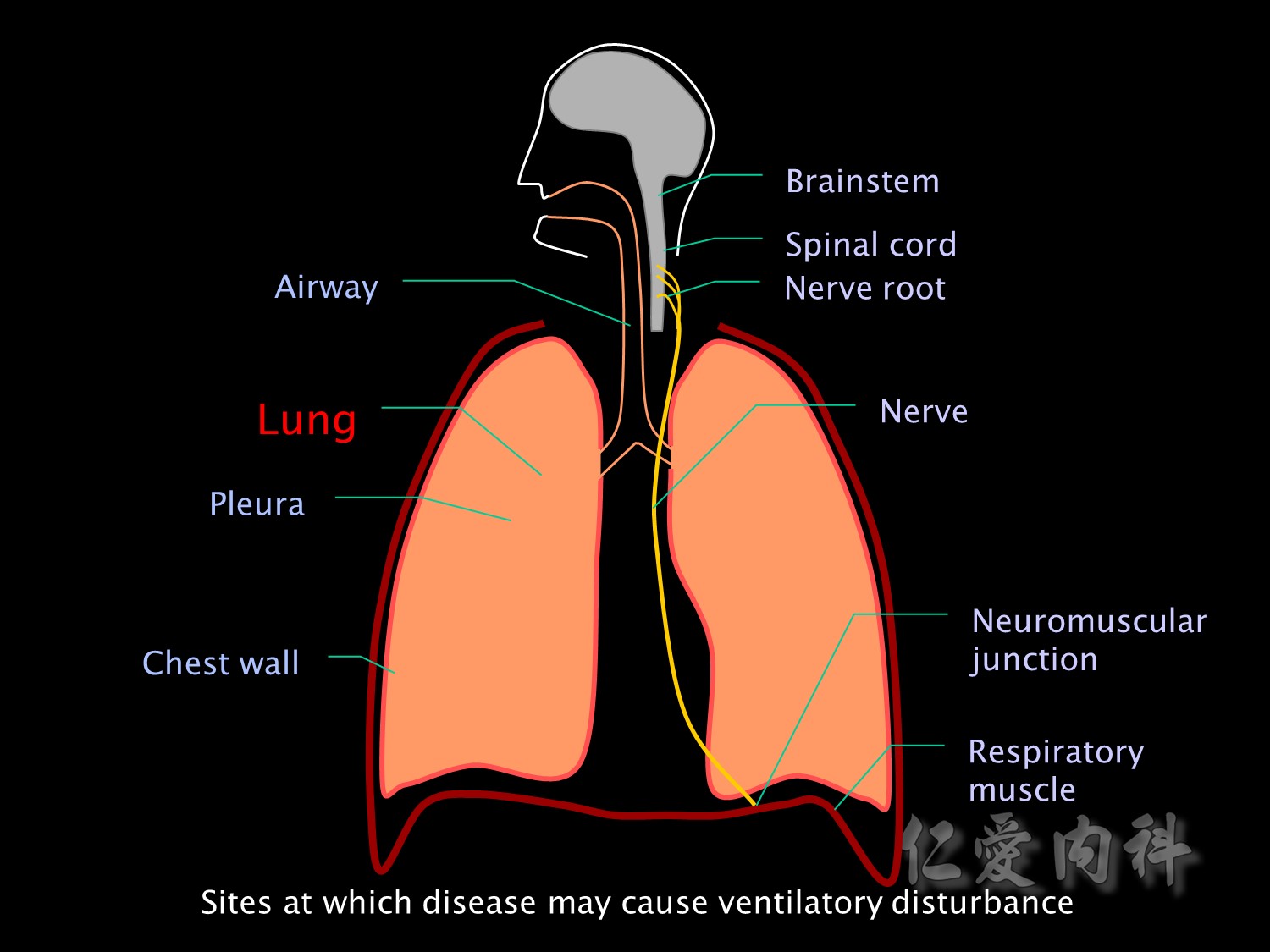
Or the problem may be decreased compliance of the lung itself, the pleura or the chest wall.

Respiratory Failure 的臨床表現

Respiratory Failure 的臨床表現
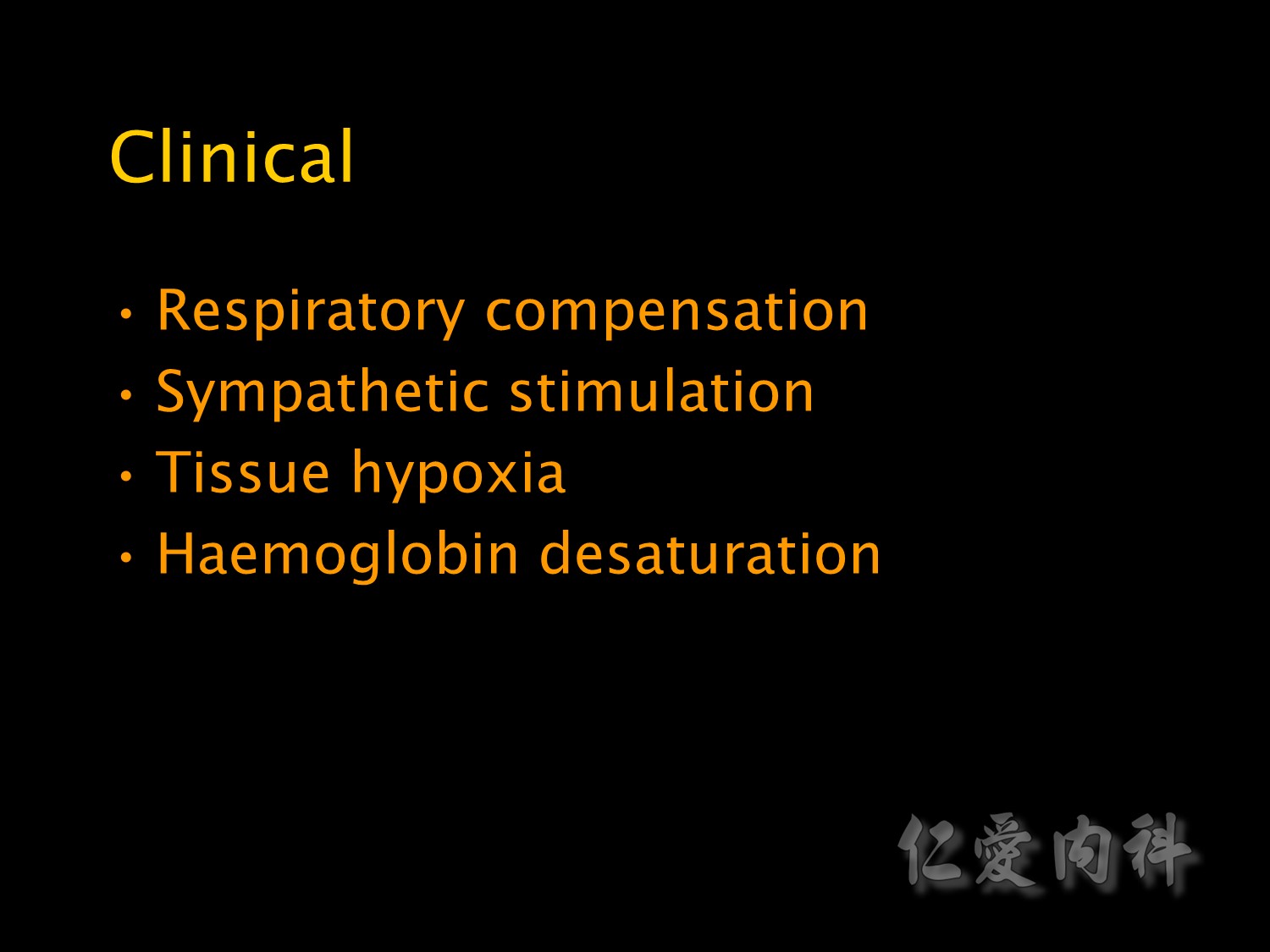
Clinical signs of respiratory failure can be divided into signs of respiratory compensation
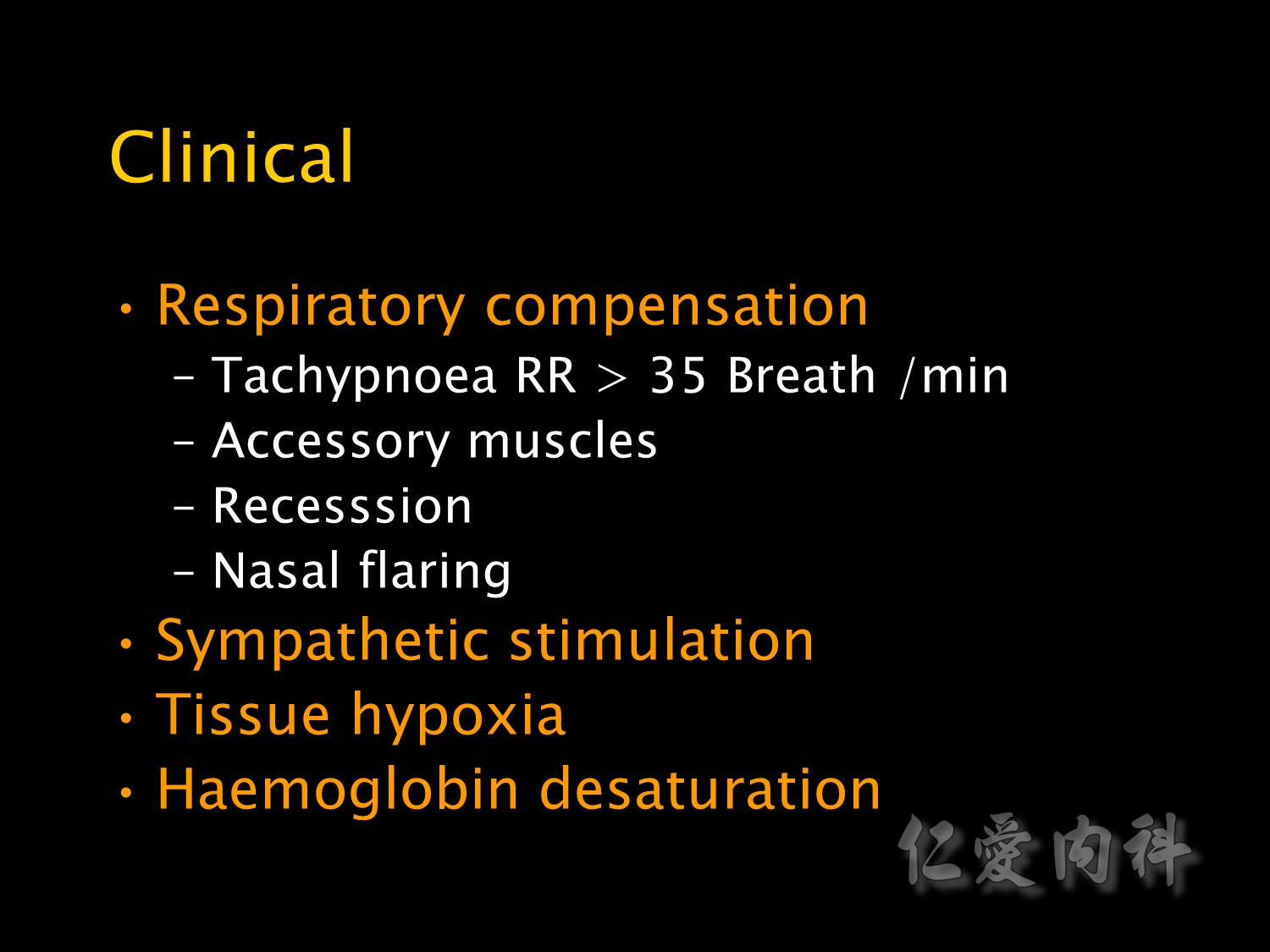
Such as tachypnoea, use of accessory muscles, recession and nasal flaring
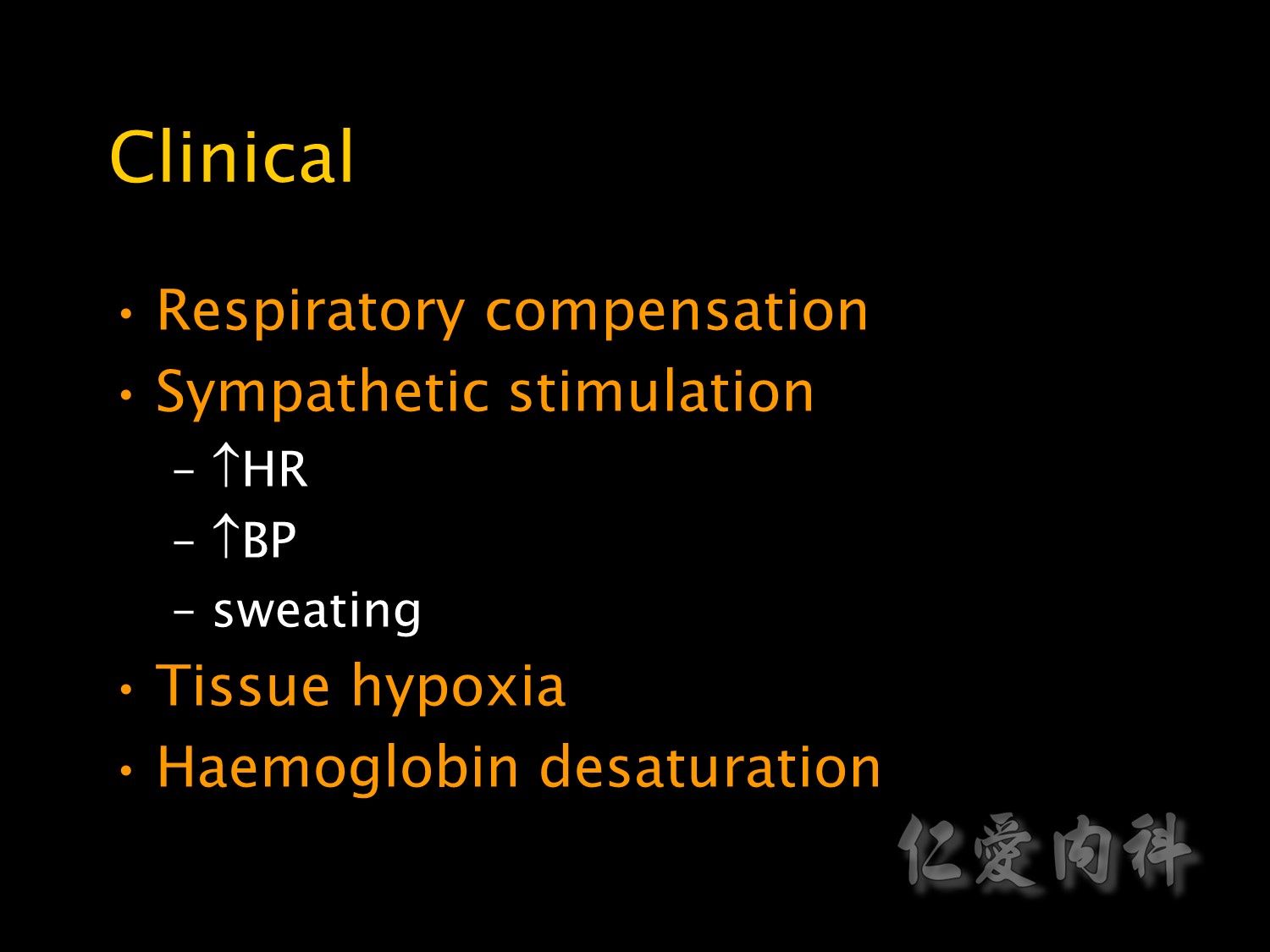
Signs of sympathetic stimulation such as tachycardia, hypertension and sweating
Signs of tissue hypoxia such as altered mental status and at a very late stage bradycardia and hypotension
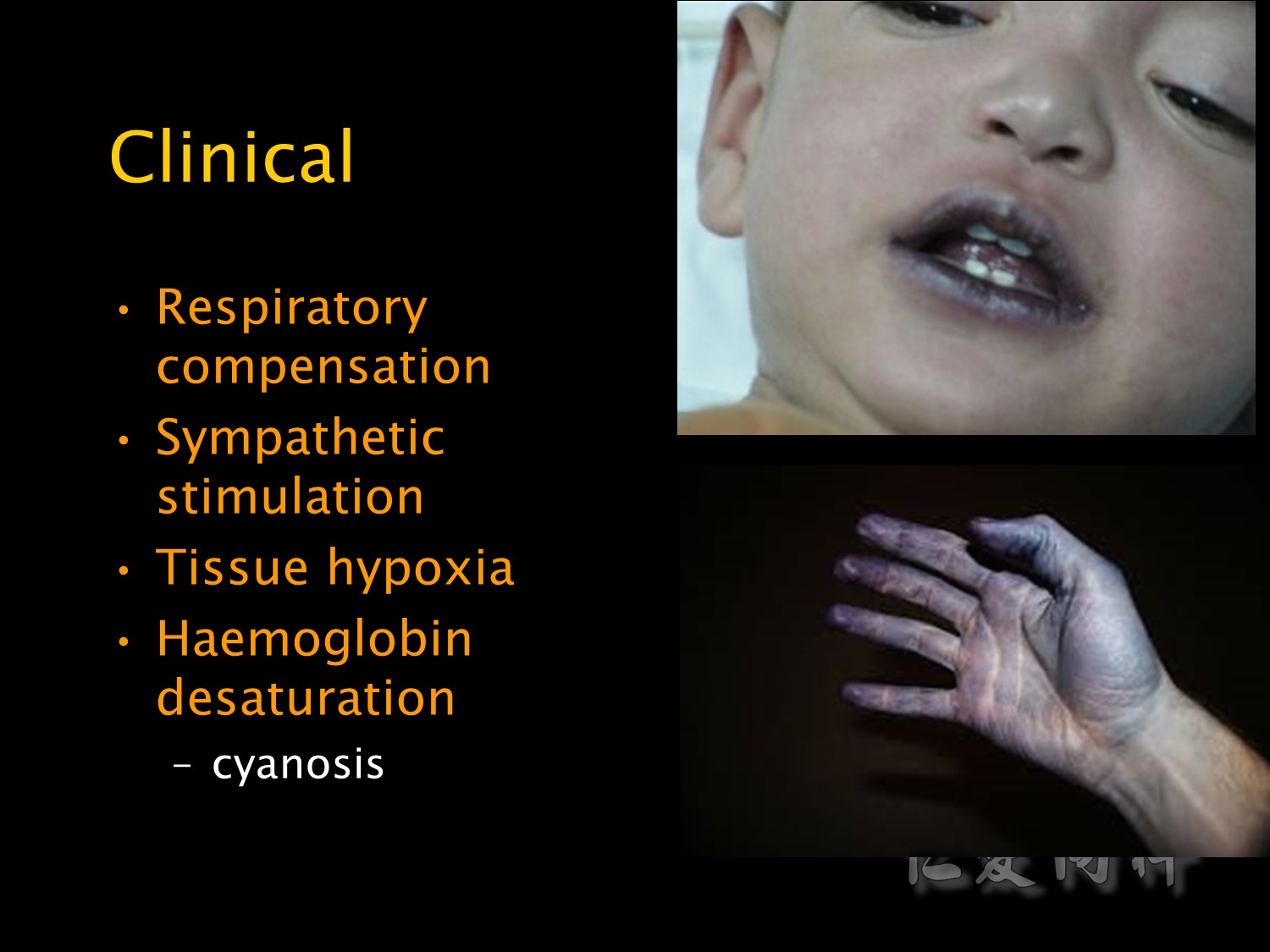
And signs of haemoglobin desaturation: Hb結合O2比率不高

