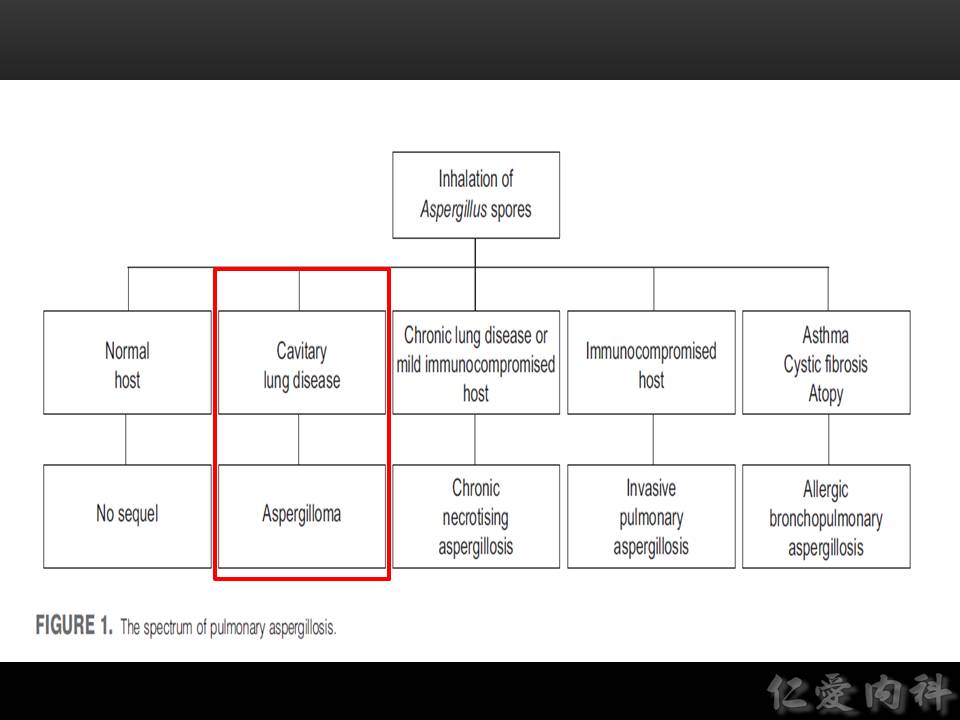
以下先介紹 Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis:

- Neutropenia < 500/mm3 超過 10 天,每多一天,被 Aspergillous 感染的機會每天增加 1%;超過 3 週時,每多一天,被 Aspergillous 感染的機會每天增加 4%。
- Bone marrow transplantation 的病人 (特別是 allotransplantation) 有兩個 timing 容易被 Aspergillous 感染:第一個時間點是剛移植的時候 (neutropenia),第二個時間點是78-112天 (GVHD)。
- 長期使用高劑量類固醇者也容易被 Aspergillous 感染。

- HIV 帶原者若同時發生 invasive aspergillosis,他們的 CD4 皆少於 100/mm3。
- 有 chronic granulomatous disease (eg, TB, sarcoidosis) 者也容易被 Aspergillous 感染。
- 嚴重 COPD (肺部結構不正常、營養差、使用類固醇) 與重症病人也容易被 Aspergillous 感染。


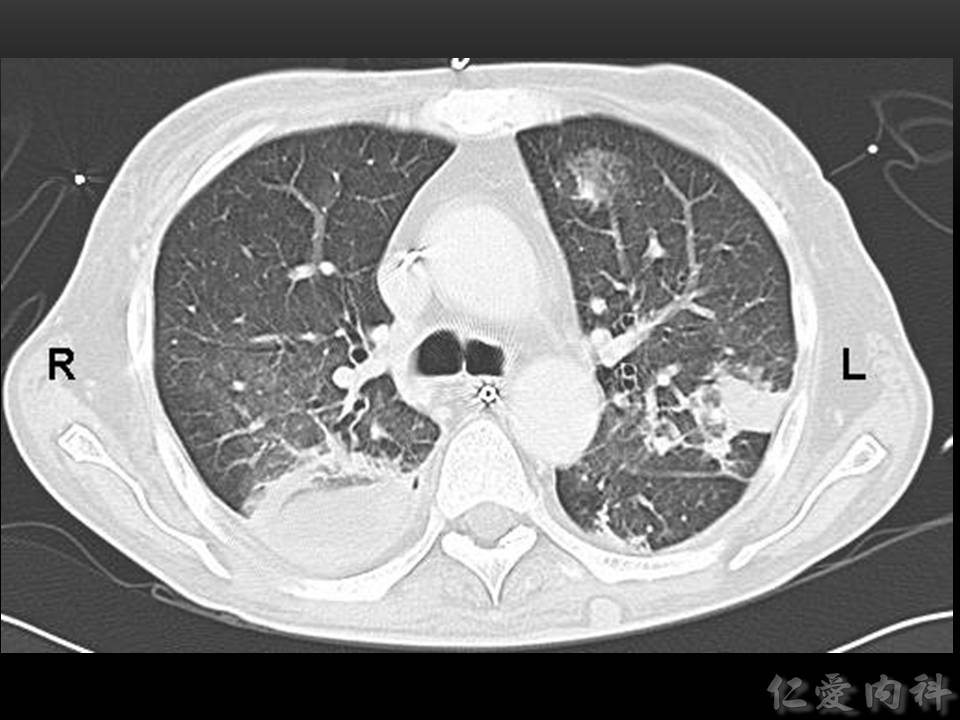
- Chest radiograph 的表現不具有特異性,可見到 rounded densities、consolidation、pleural-based infiltrates (pulmonary infarctions) 與 cavitations。

- CT 上可以發現 nodules (>90% cases),但 “halo sign” 的出現 depends on 病人接受 CT scan 的時間點。nodules 旁邊若是出現 necrosis,則可能見到 “air crescent sign”。
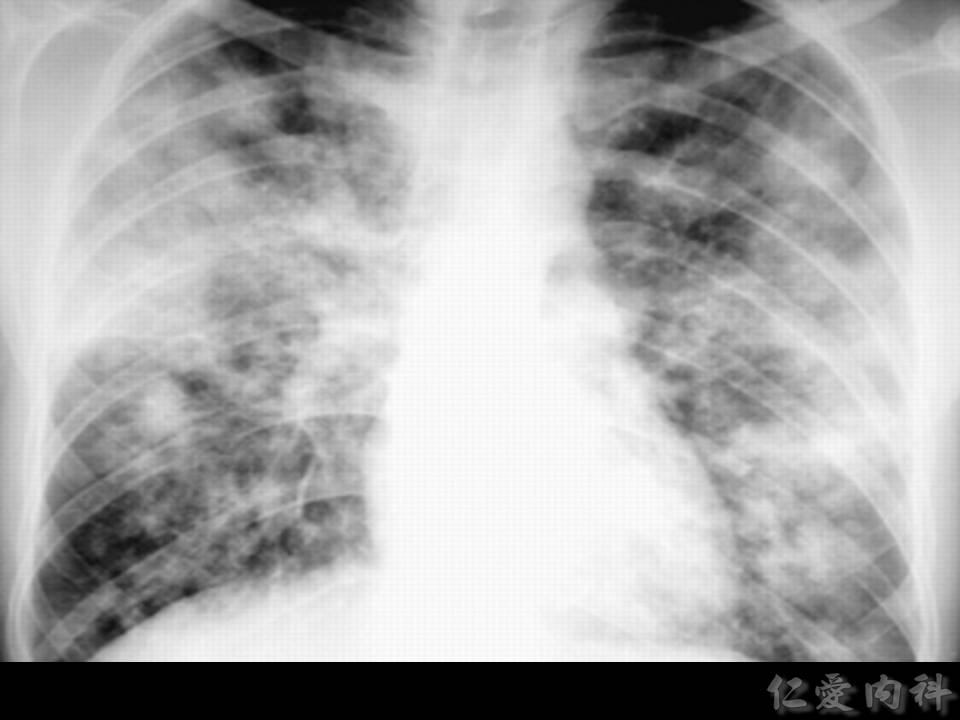
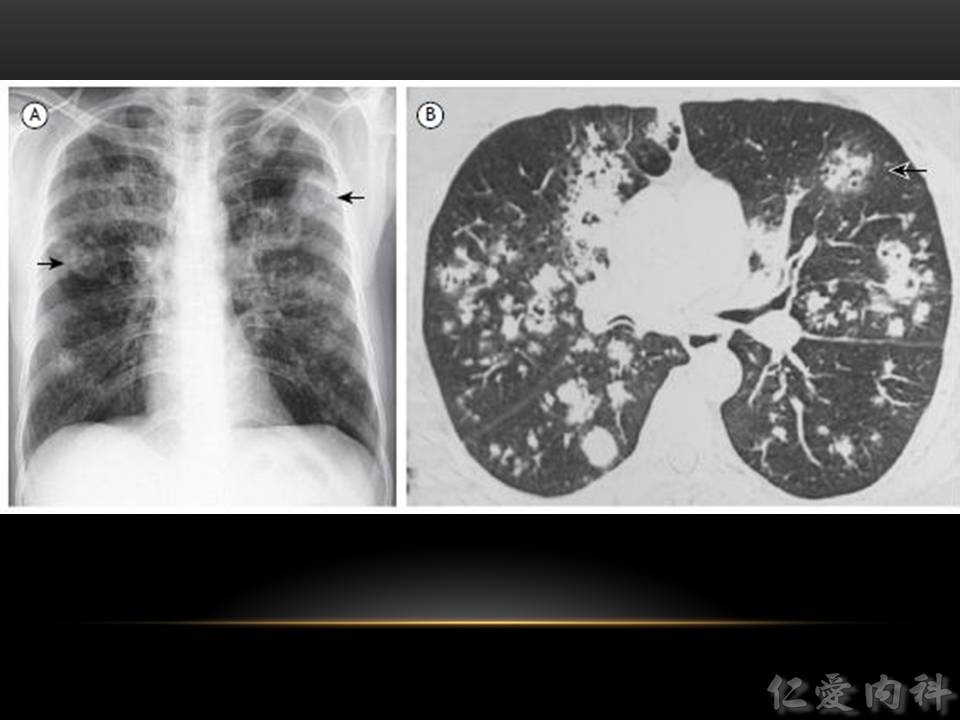
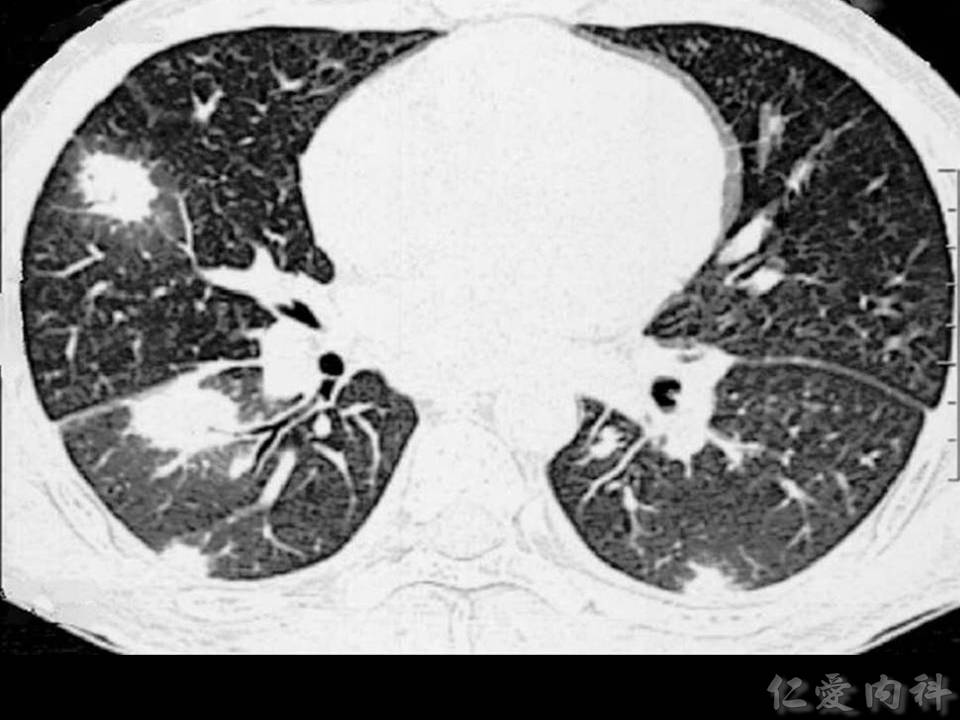
- “Halo sign”
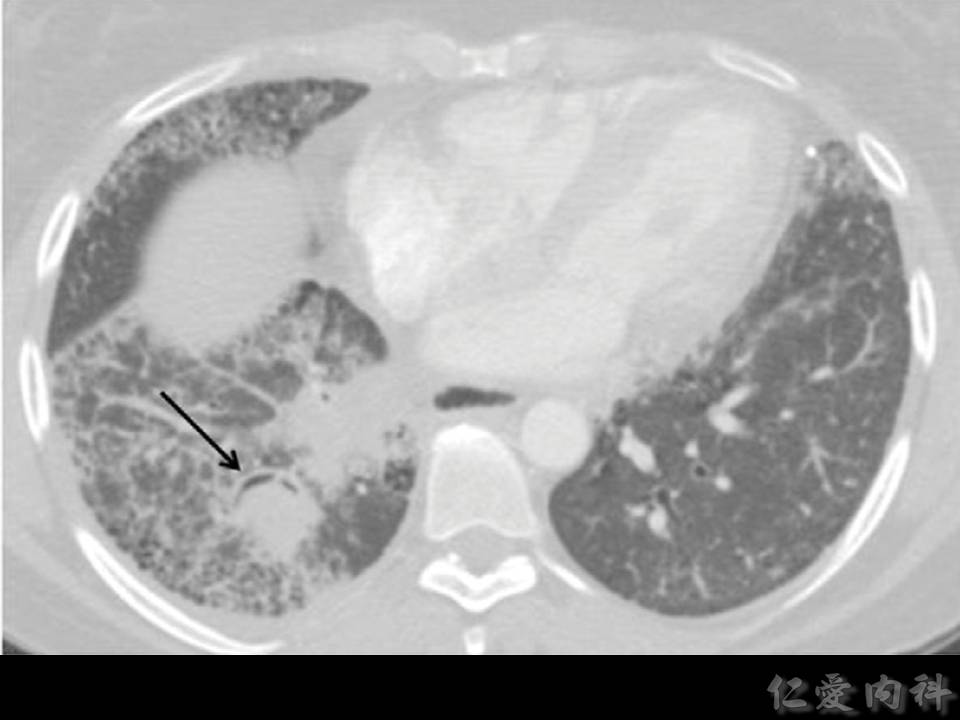
- “Air crescent sign”
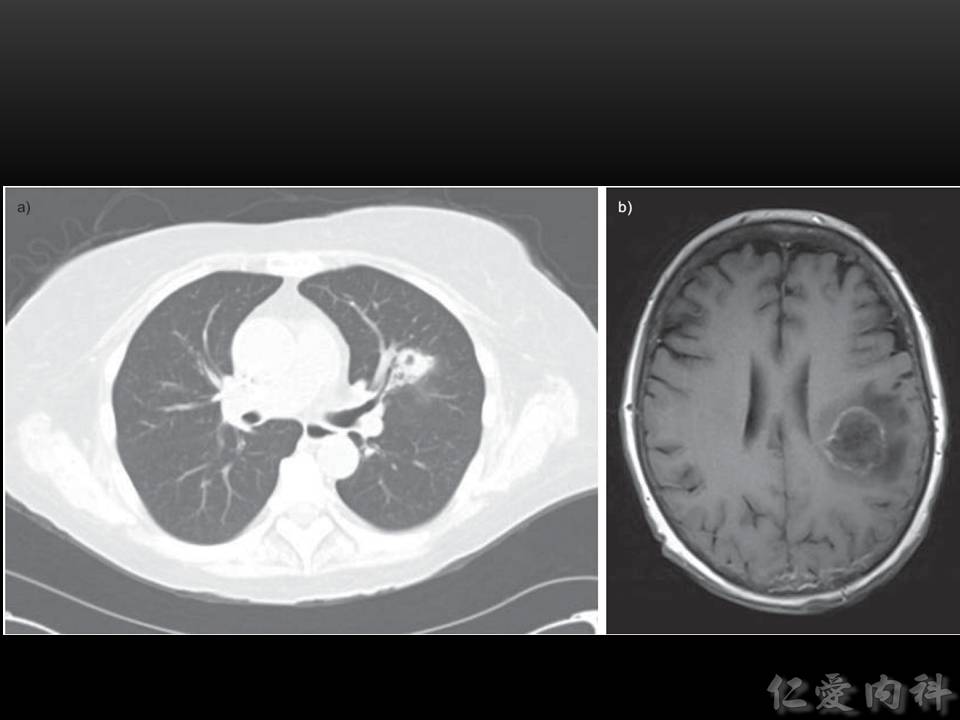
- 經由血行可以散佈至其他器官 (如 brain [cerebritis] 與 kidney)。
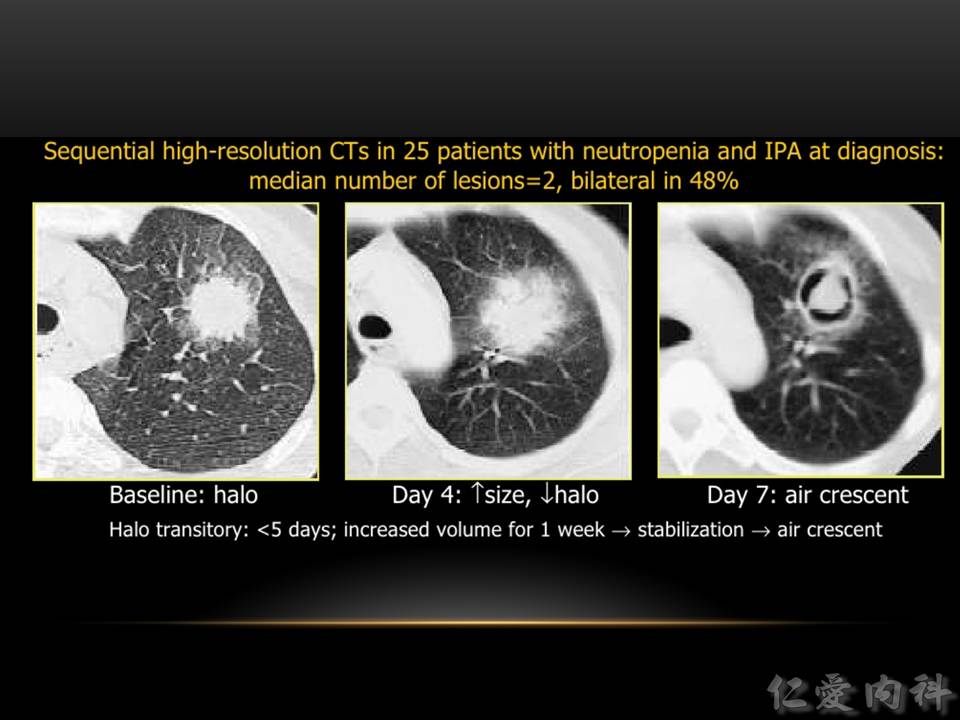
- Halo transitory:從 “halo sign” (< 5 days) 至 “air crescent sign” (after 7 days) 的一連串的變化。
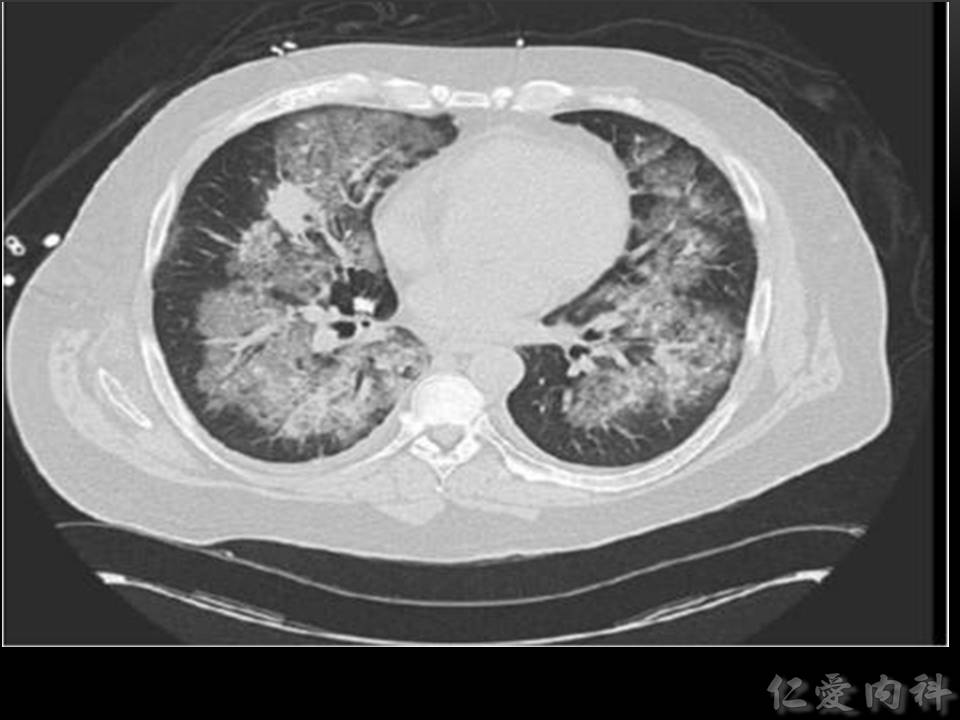
- 也可能之看到 ground glass opacities 與 consolidation,而沒有典型的 halo or air crescent signs。
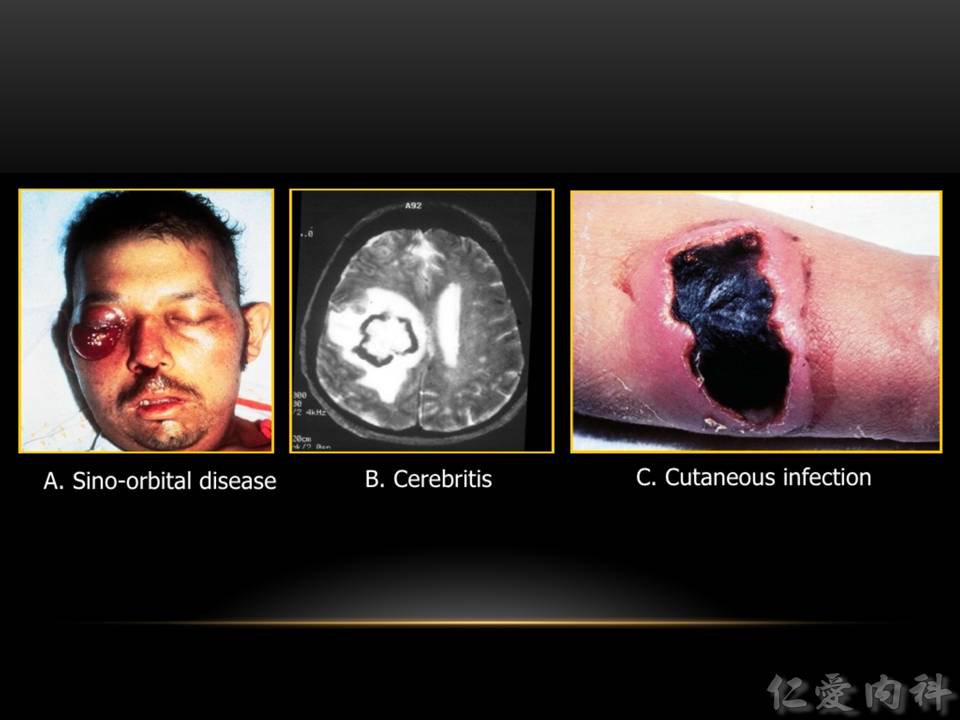
- IA 也可以表現為 sino-orbital disease, cerebritis, and/or cutaneous infection。

- 也有可能只侵犯氣管支氣管造成 Aspergillus tracheobronchitis。

- Aspergillus tracheobronchitis 分為 3 型 (obstructive, ulcerative, pseudomembraneous),其中以 pseudomembraneous aspergillus tracheobronchitis 最容易辨認。
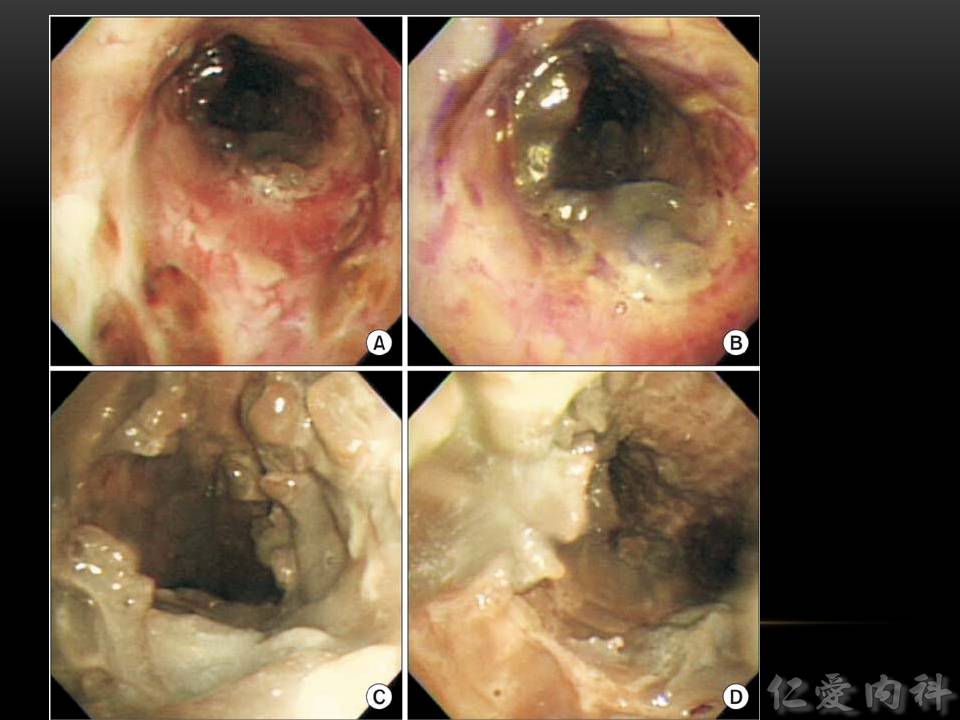
- Pseudomembraneous aspergillus tracheobronchitis 治療前。
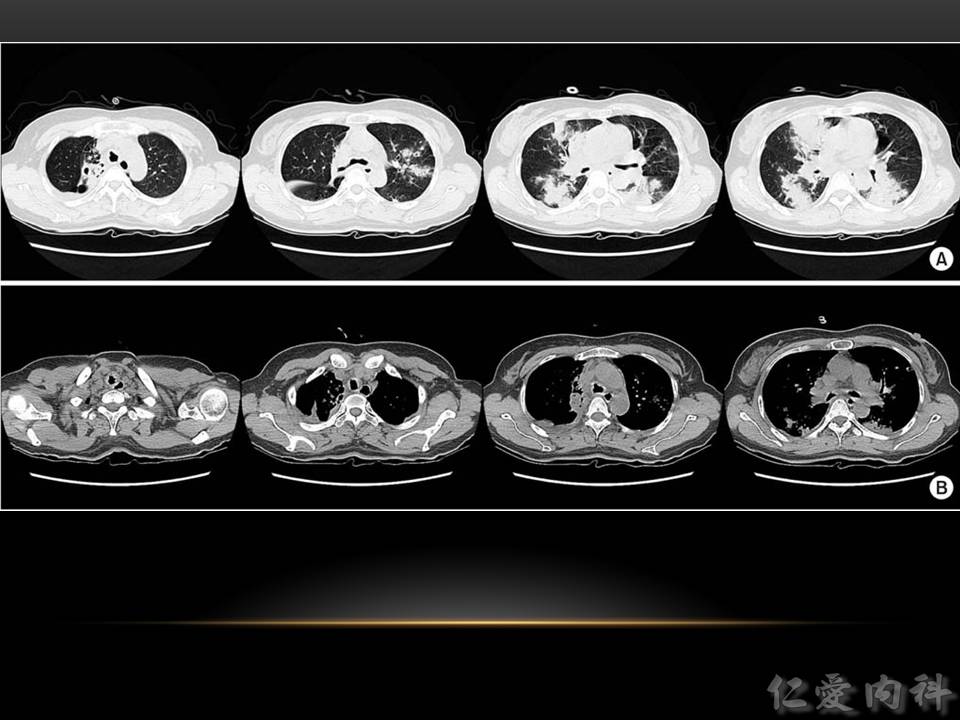
- CT scan 上可見 bronchial wall 增厚,airways 可能可以看到有 plugs 般的影像。
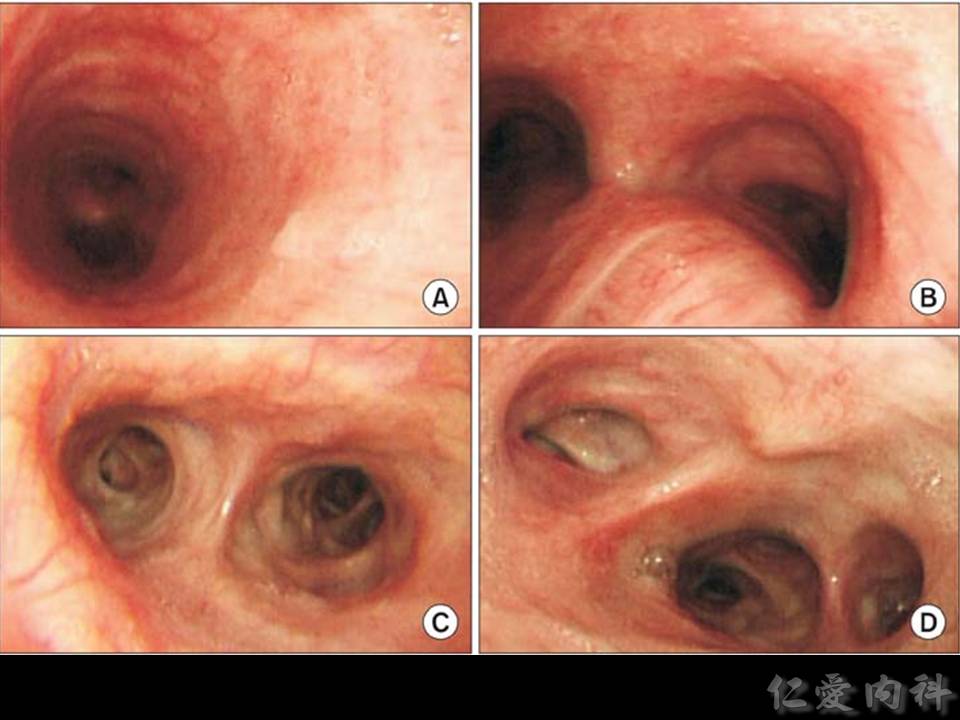
- Pseudomembrane 於治療後清除。
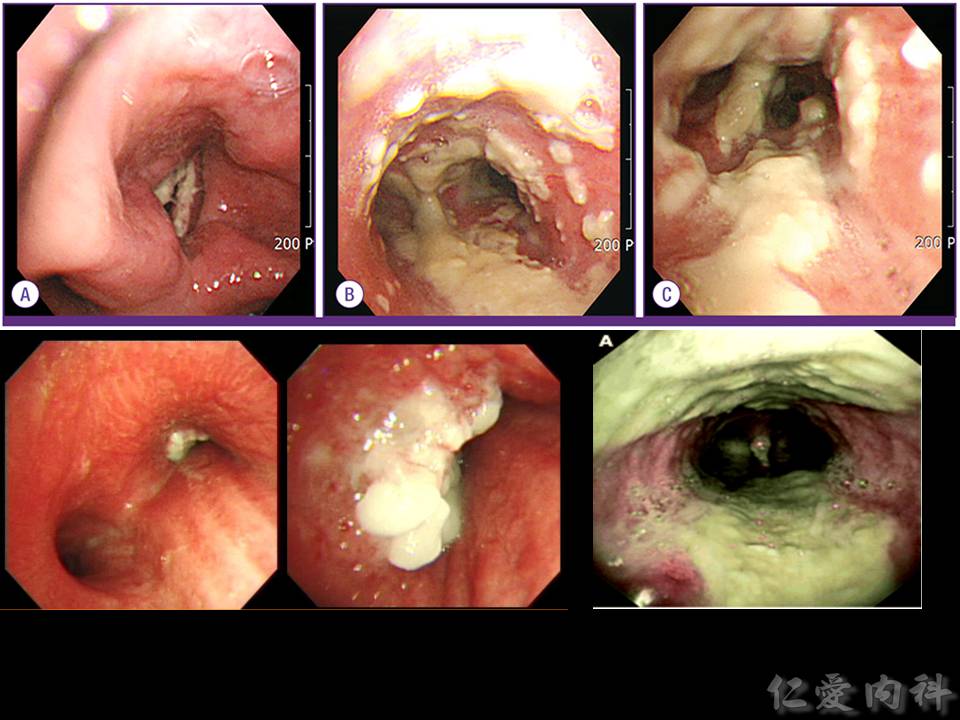
- Invasive aspergillosis 所造成的 airway 的 pseudomembrane 用 bronchoscopy 無法抽吸。

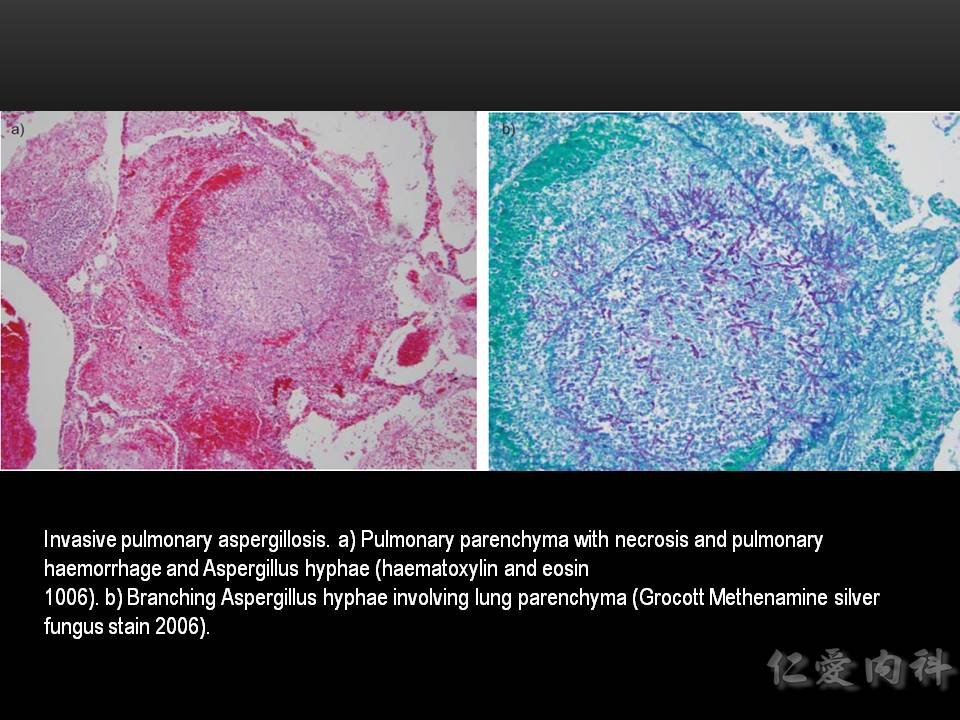
- 以 biospy 進行 histopathology 的檢查為 gold standard diagnostic method。
- 比較常應用的非侵襲性的血清學診斷工具為 galactomannan test;其他的診斷工具還有 beta-d-glucan assay (偵測黴菌細胞壁的成分, 不具專一性) 與 PCR。

- Galatomannan (Aspergillus 生長時所釋放出之 polysaccharide) 的檢查具有偵測 Aspergillus 的專一性。但由於 positive predictive value 不高,建議使用在高危險群的病人 (eg, haematological malignancy or allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [HSCT]) 以提高診斷之陽性預測率。
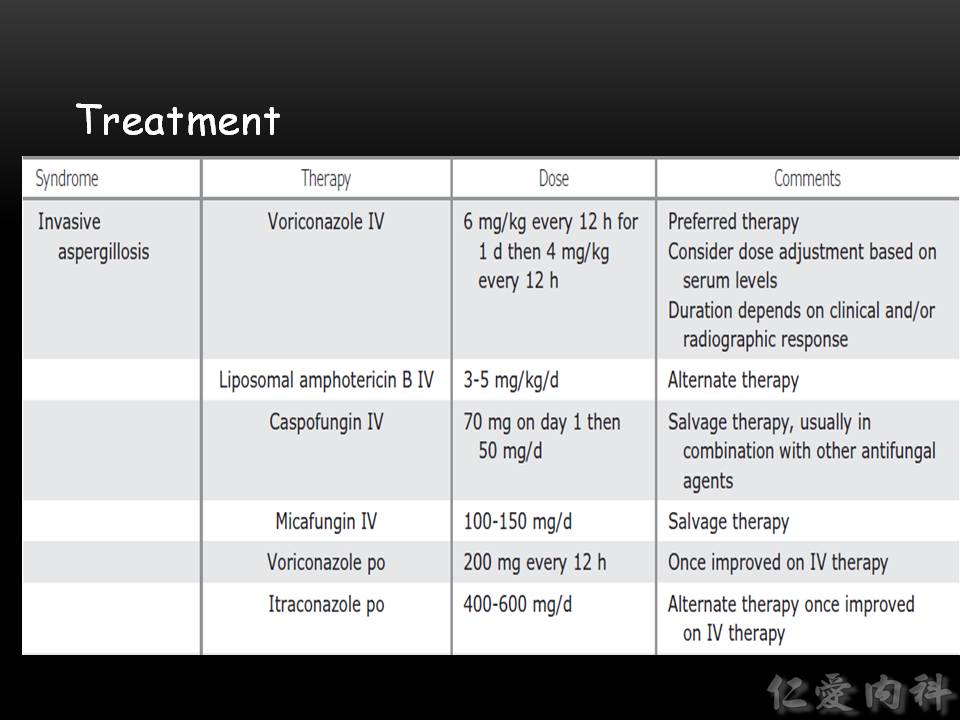
- Invasive aspergillosis 的治療首選是 intravenous voriconazole (one of the triazoles that work by disturbing the fungal cell membrane or the metabolism.);loading 劑量為 6 mg/kg q12h twice,之後改為 4 mg/kg q12h。
- Ian’s comment: Azole 類藥物可抑制黴菌透過自身的 cyp51A 基因所製造之的 lanosterol 14α-demethylase,進而抑制黴菌細胞膜上的麥角脂醇 (ergosterol) 的合成。Azole 類的使用上需要注意其肝毒性,若是 voriconazole 使用中發生肝毒性或是病人用藥前之肝功能不佳,可使用不具肝毒性的 isavuconazole。另外,臨床上不建議使用第一代的 azole 治療 aspergillosis,應使用第二代的 trizole 類藥物 (eg, voriconzole, posaconazole, isavuconazole 等)。
- Caspofungin interferes with fungal cell wall integrity by inhibiting the enzyme (1→3)-β-D-glucan synthase. 但是一般不會單獨使用 caspofungin 治療 aspergillosis。
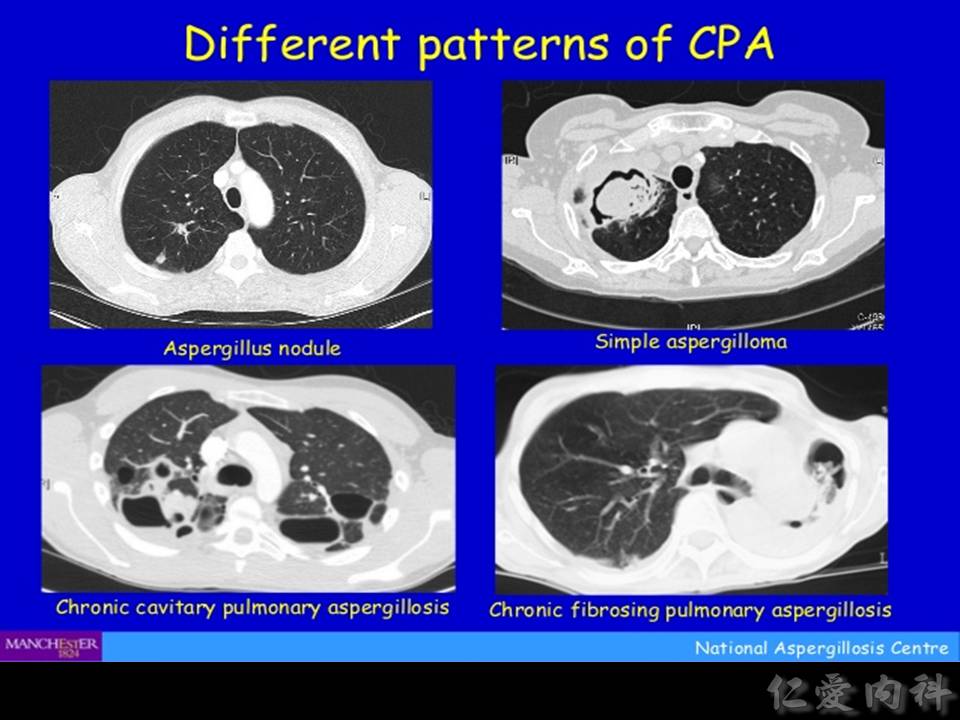
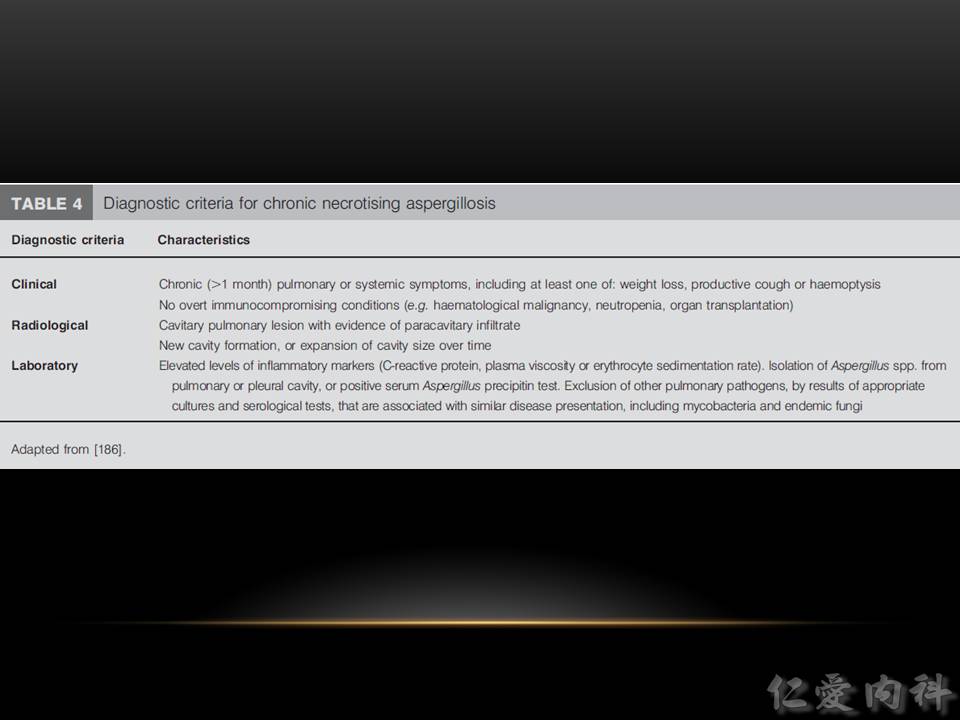
以下介紹 chronic necrotizing (cavitary) aspergillosis, 或稱為 subacute invasive aspergillosis:
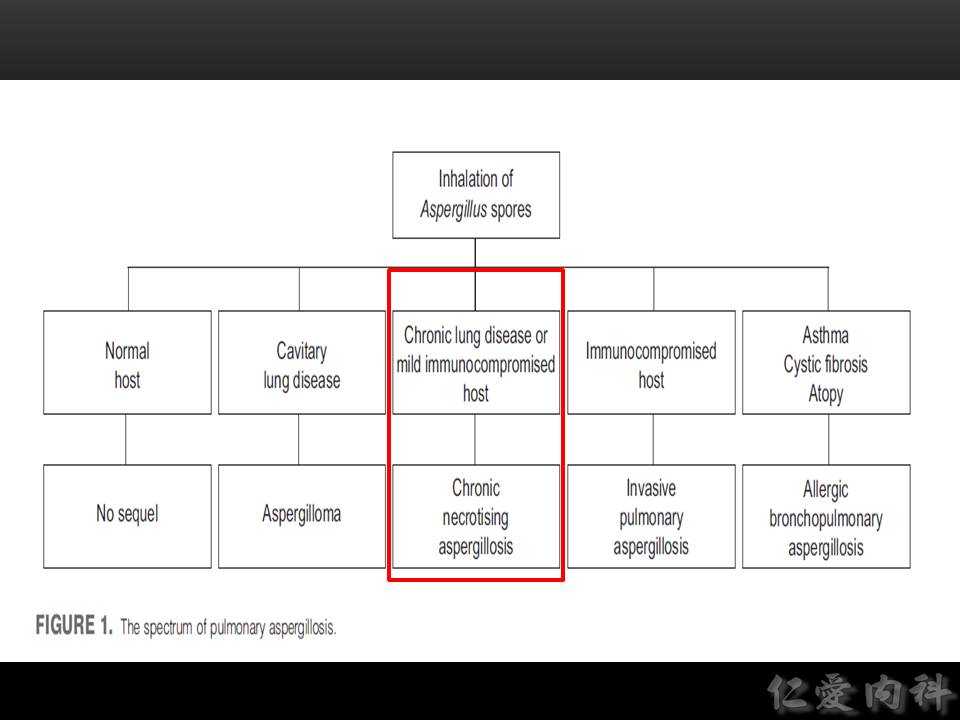


- Nonspecific、超過一個月的症狀。慢如 tuberculosis 般的表現。
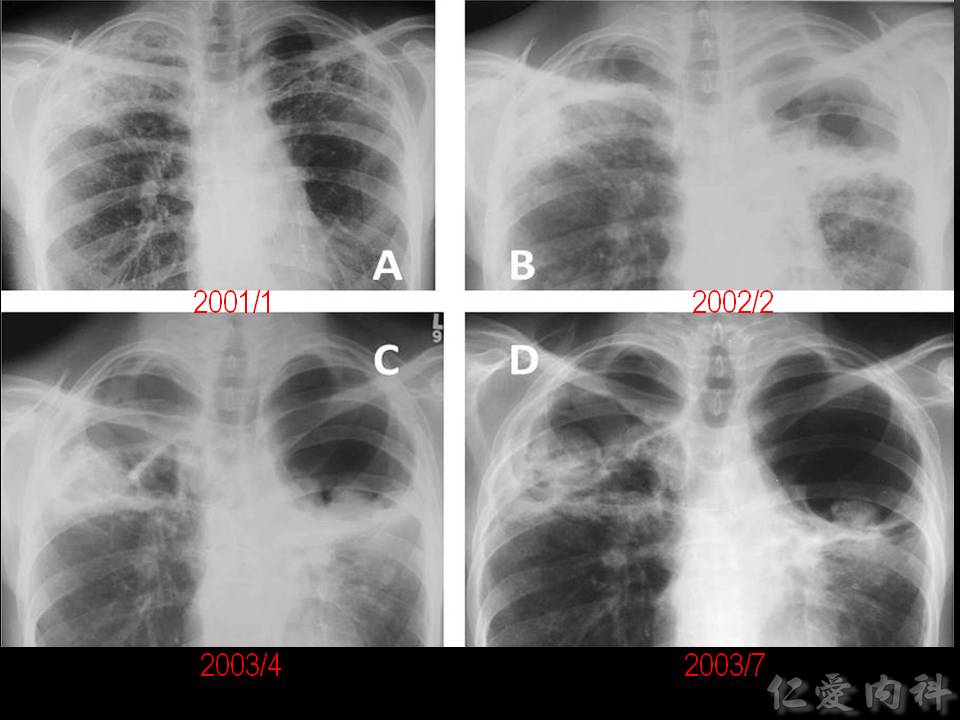
- 影像學為慢慢進展的開洞、洞中出現 mycetoma、與纖維化。
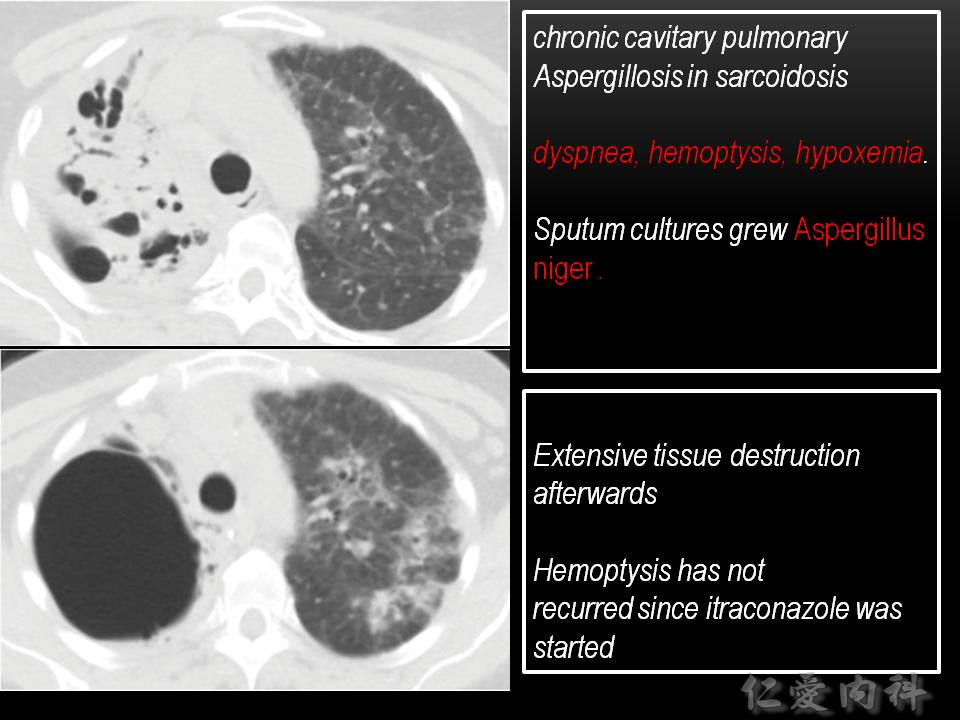
- 同一個病人的肺組織被破壞一段時間後留下的大空洞。
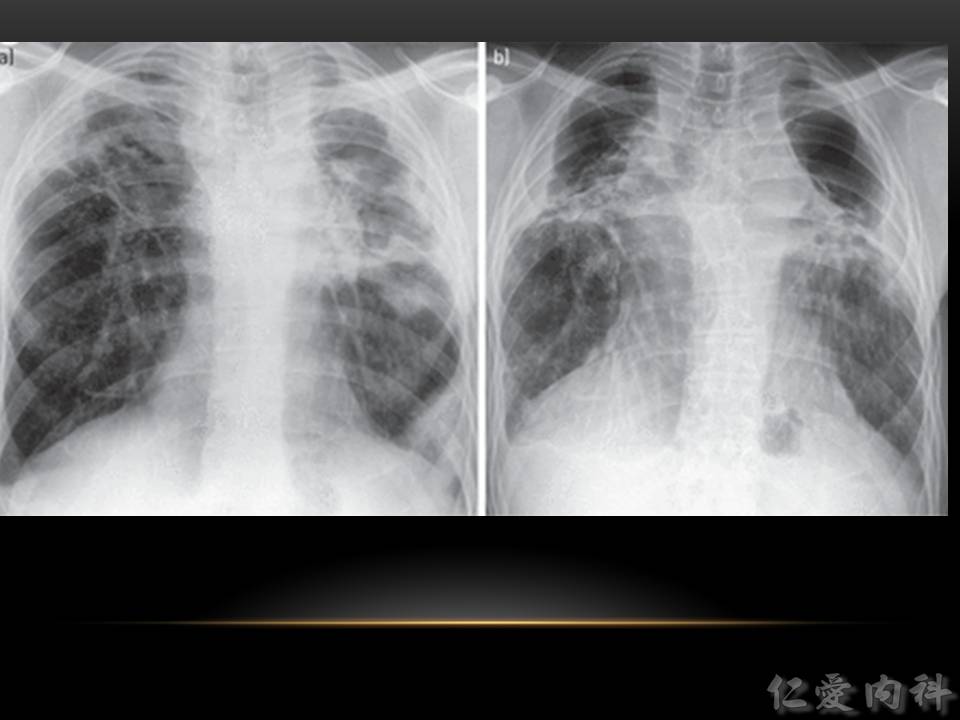
- 很像 TB 的 chest radiographic 表現。
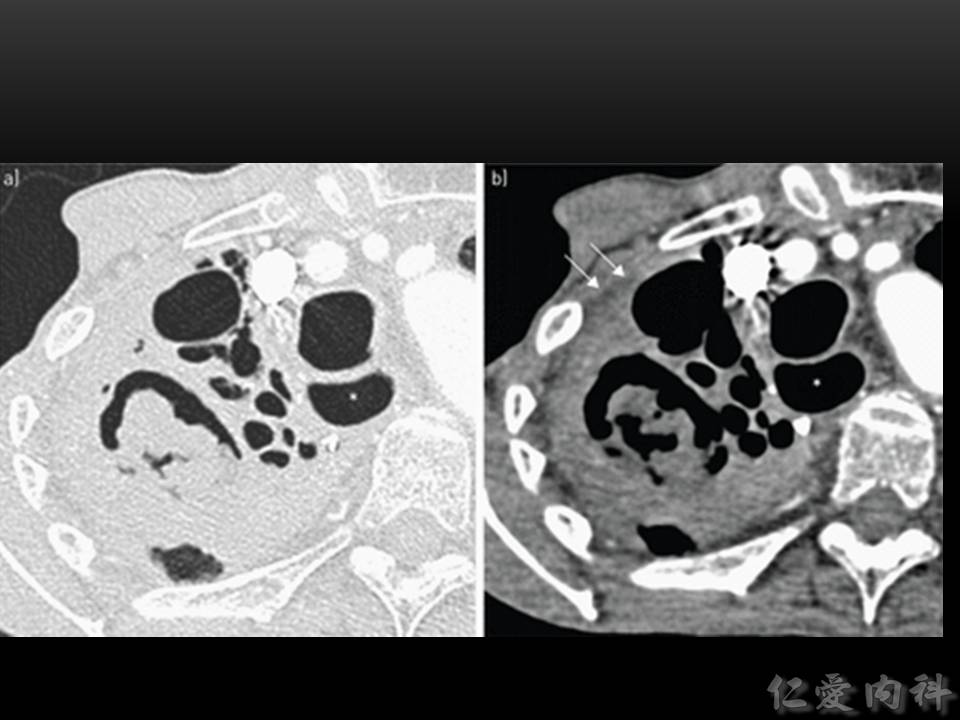
- Aspergilloma 的出現多是因為病人先前已有開洞性肺部病變 (such as pulmonary tuberculosis),之後受到 Aspergillus 感染所形成。
- Aspergilloma 乍看知會可能與之前介紹的 IA 所造成的 air-crescent sign 很像 (aspergilloma 也可以有 paracavitary infiltrate)。但與 IA 的即興表現不同, aspergilloma 的影像經常可發現一些慢性的肺部病灶。
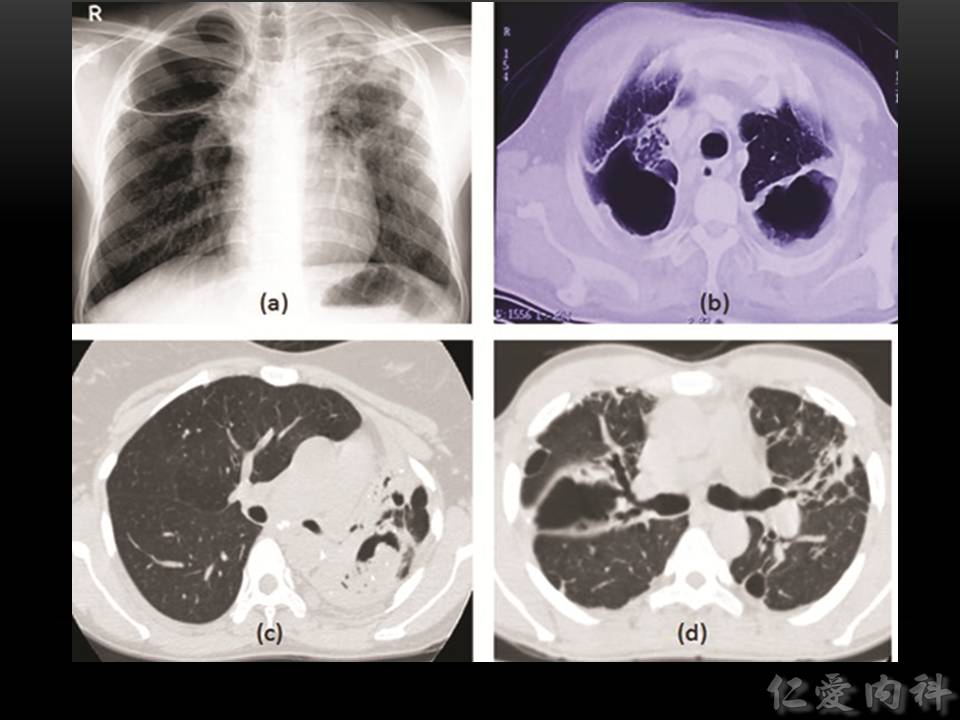

- IA 因為會侵犯血管,可以有一定的機會用血清學檢查其細胞成分 (eg, beta-d-glucan or galactomannan) 來輔助確診。但慢性的 aspergillosis 較不常侵犯血管,不是用此類診斷方式,一般是以偵測血中 IgG 的方式,或是 skin reactivity for Aspergillus antigens 來輔助診斷。
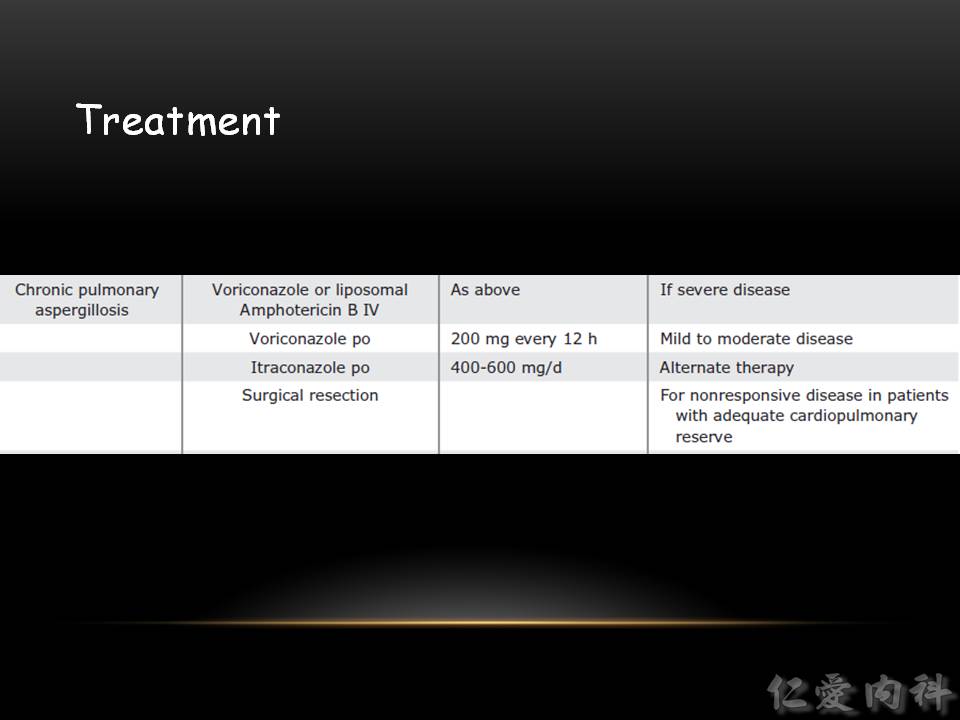
- Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis 的治療與 invasive aspergillosis 相似,但劑量可以依疾病嚴重度減少。
- 有時候病灶處對於藥物反應不佳,在適當狀況下 (eg, 病灶侷限於單一肺葉或更小的區域、有適當的 cardiopulmonary reserve),可採取手術切除。
以下介紹 aspergilloma:
這也是一種 aspergillosis 的慢性表現。


- Aspergilloma 很少侵犯 pulmonary parenchyma 造成症狀,最常見的症狀是咳血。

- 診斷當然是以影像學為主。影像學有懷疑時,可以抽血檢查 specific serum IgG antibodies against Aspergillus。
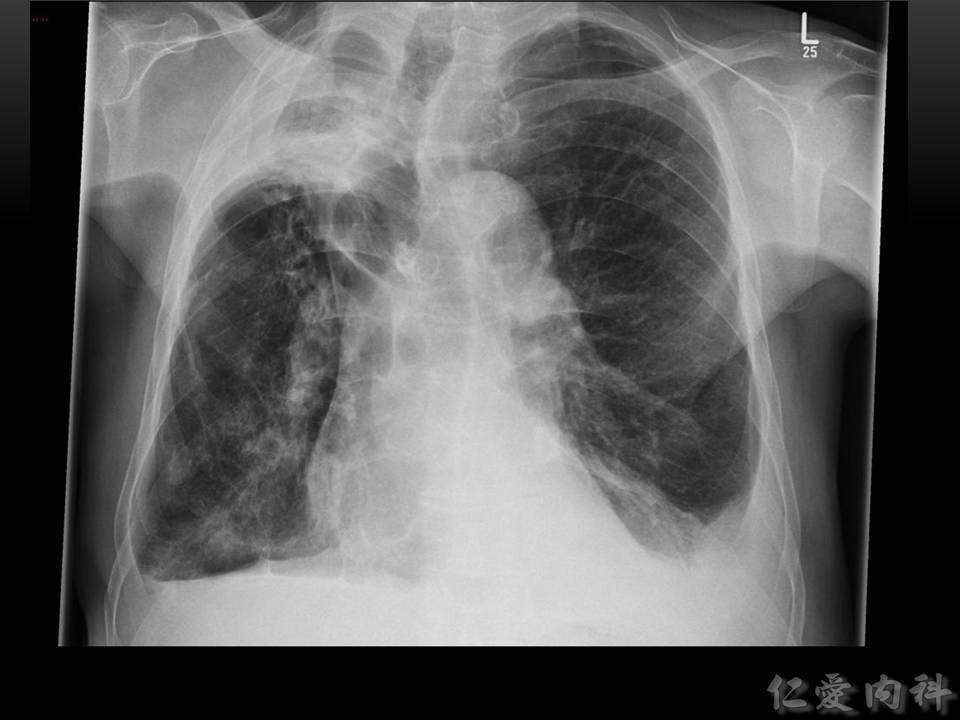
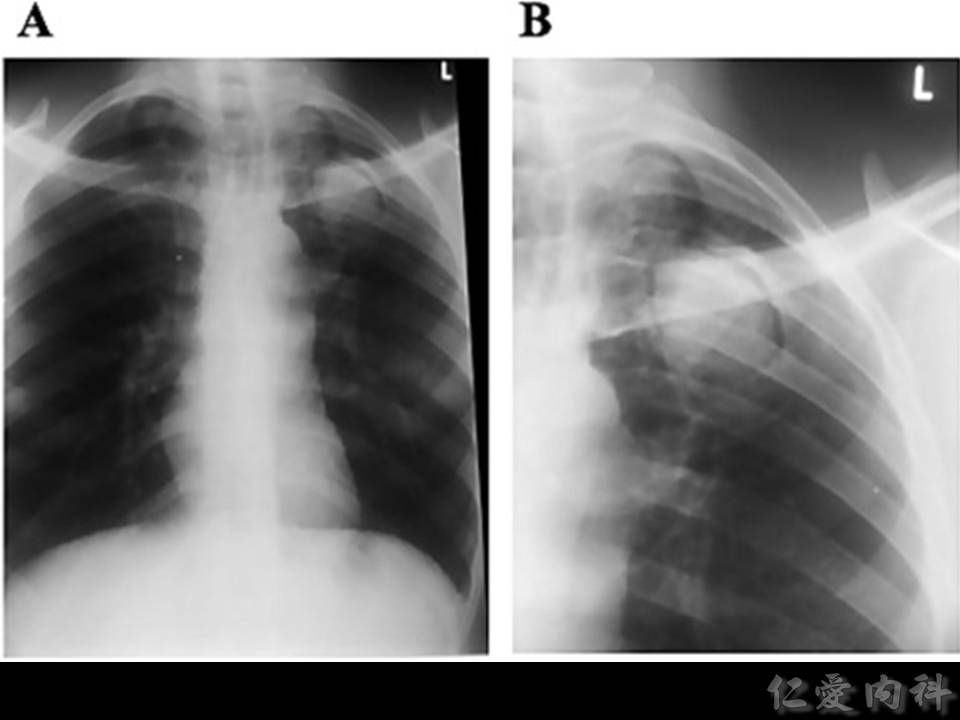
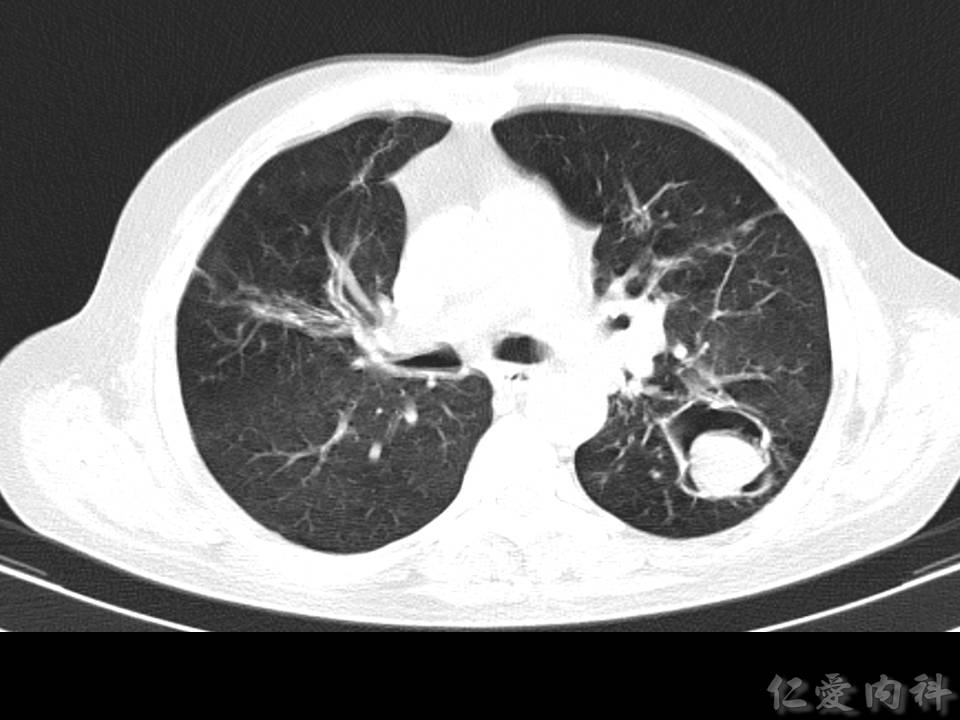
- 除了 fungal ball 的特徵之外,還有可能發現 bronchectasis 之類的慢性支氣管發炎的變化。

- 若只有看到 aspergilloma,沒有症狀,沒有其他 Aspergillus 散播之證據,一般不考慮治療。
- massive hemoptysis 時可採取 bronchial artery (來自主動脈) embolization (另一套血液供應為 pulmonary artery,通常不會提供足夠的條件造成 massive hemoptysis)。
- 醫院無法栓塞? –> surgical resection
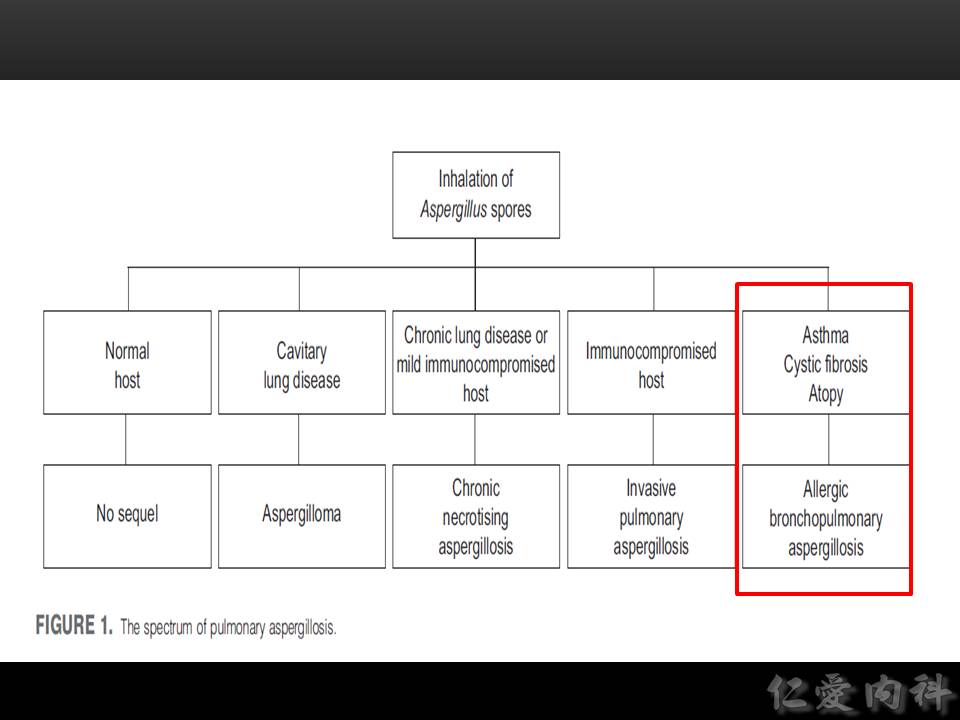
以下介紹 allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA):
Ian’s comment: ABPA is more appropriately called allergic bronchopulmonary mycosis because the offending organism is not always Aspergillus.
- 大部分是發生在 asthma, cystic fibrosis, atopy 的病人身上。
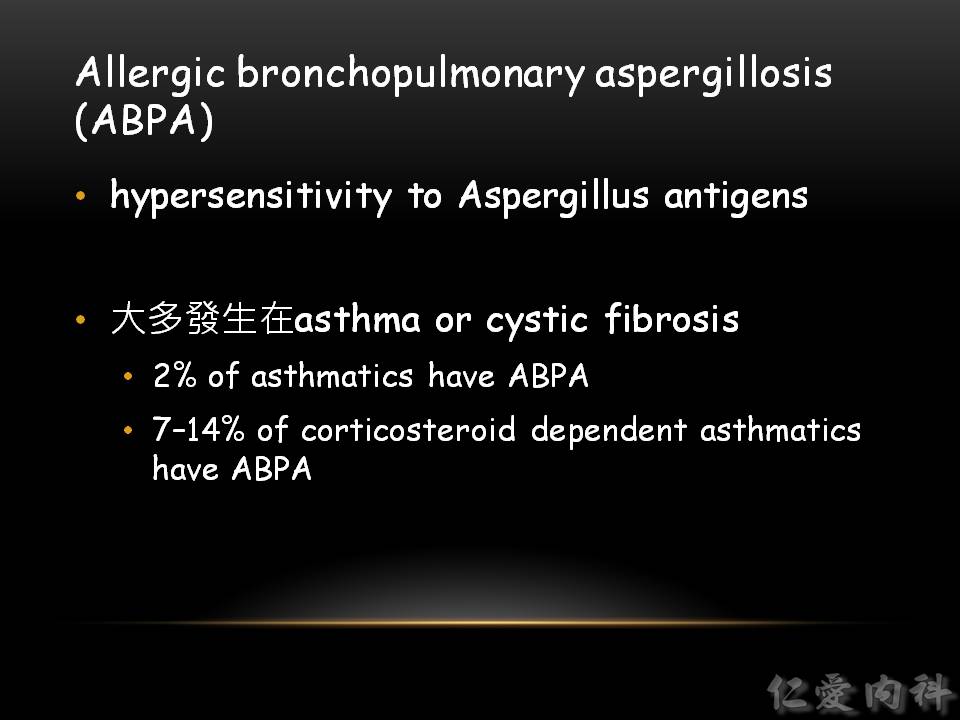
- 有研究顯示,約有 2% 的 asthma 病人有 ABPA。若病人必須依賴類固醇,有高達 7-14% 的 asthma 病人會有 ABPA。
- 如果 asthma 治療效果不佳要考慮 ABPA、Samter’s syndrome (aspirin-sensitive asthma + nasal polyps)、Churg-Strauss (asthma + eosinophilia + granulomatous vasculitis)。

- 除了 asthma 的症狀,還會有 fever、brown-plug-containing sputum、pleuritic chest pain。
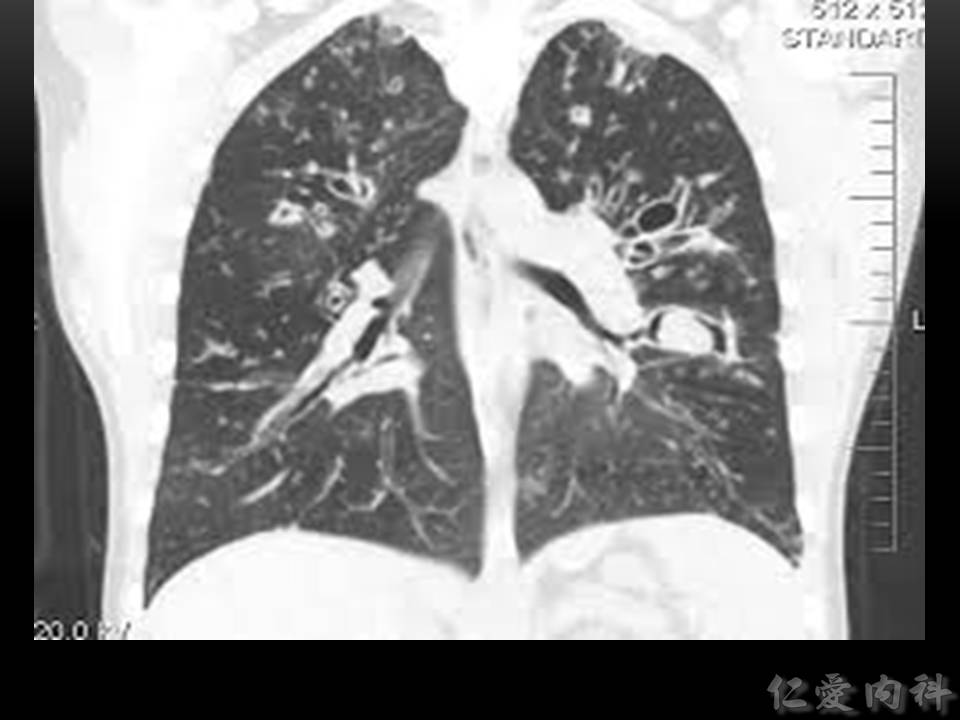
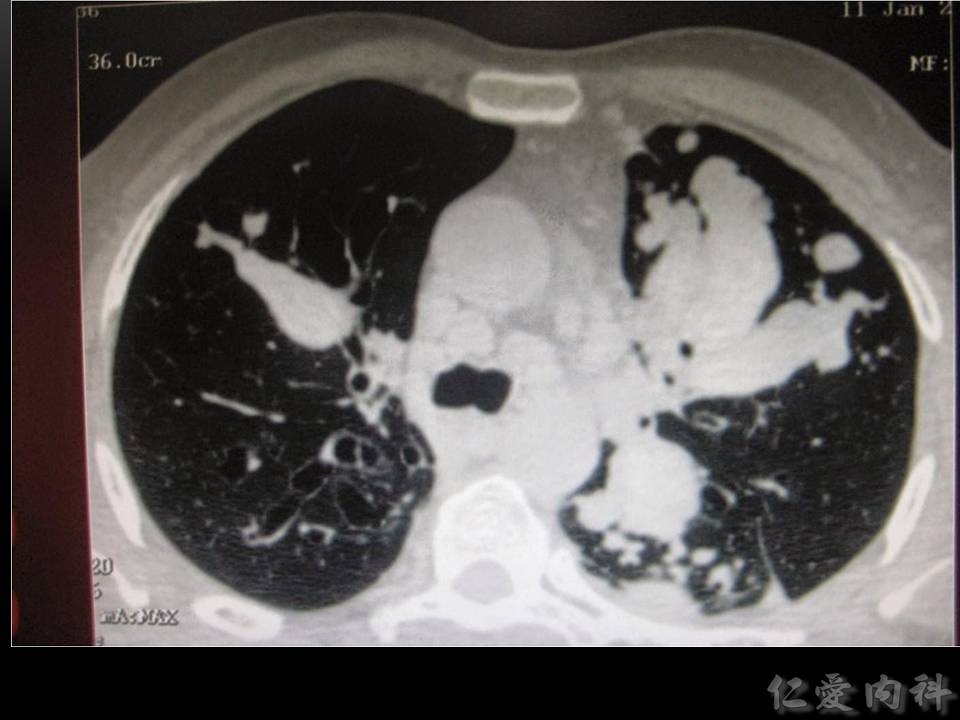
- 影像學常考的特徵為 mucoid impaction 所造成特殊的 “gloved finger appearance”。但是早期可能只有 upper and central infiltration。
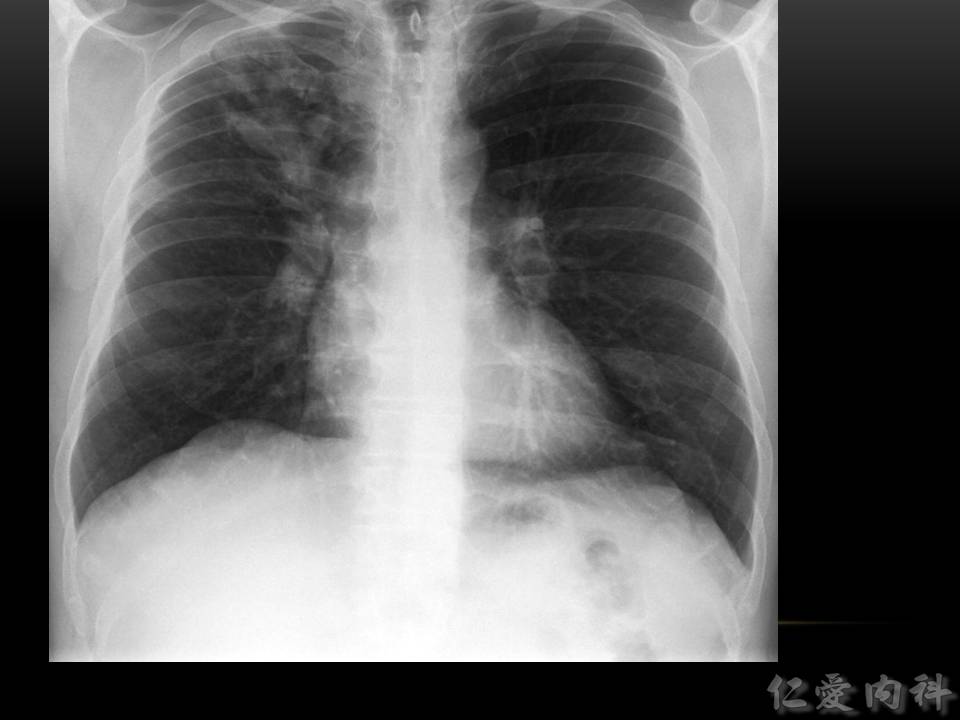
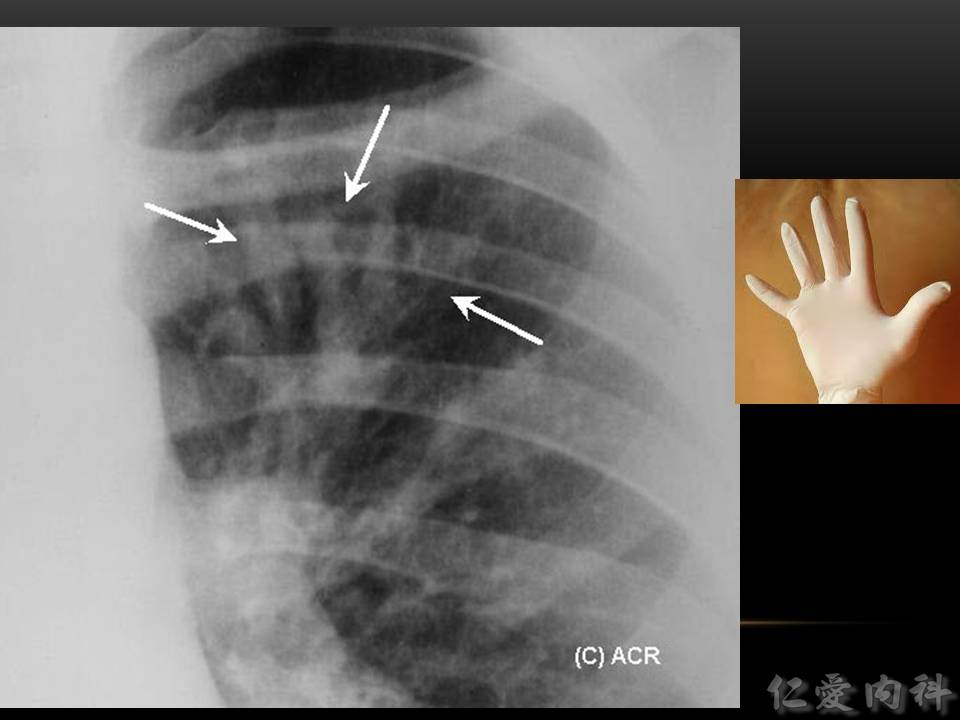
- 擴張的支氣管裡面塞了痰–> “gloved finger appearance”。
- 你的手套就是擴張的支氣管,你的手就是……痰。
- Ian’s comment: “Finger in glove”sign can be seen in obstructive (eg, bronchogenic carcinoma, bronchial hamartoma, bronchial lipoma, bronchial carcinoid) or non-obstructive causes (eg, asthma, ABPA, cystic fibrosis)
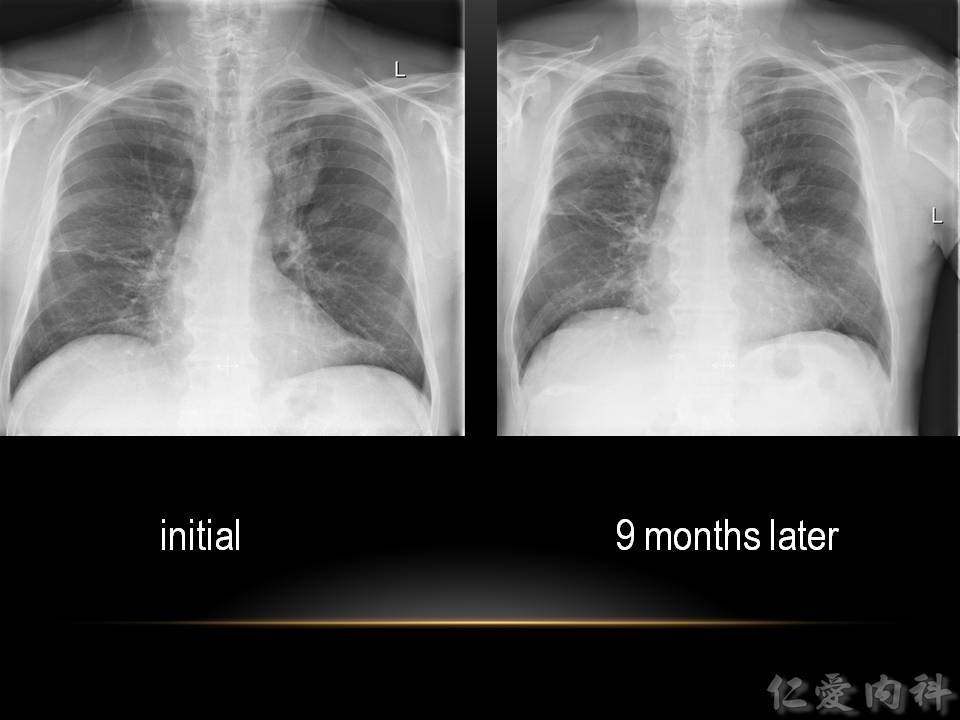
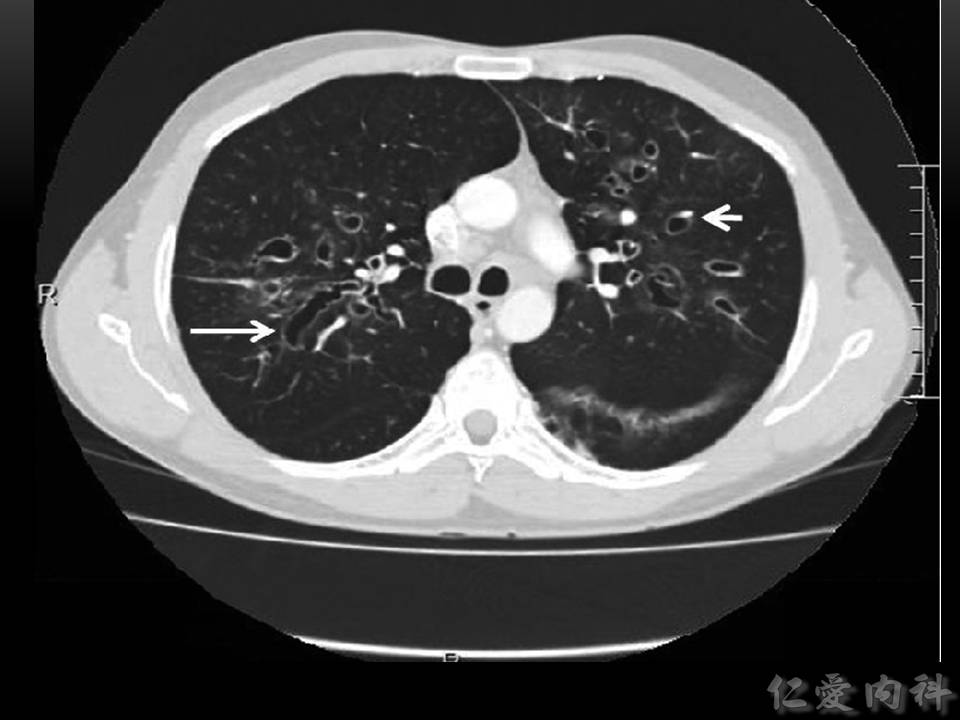
- bronchoectasis (可見 tram-track appearance、signet ring sign、甚至出現 cysts) 。
- 傳統的支氣管擴張會在出現在下肺野,ABPA 造成的 bronchiestasis 則是出現在 upper and central regoins。
- Ian’s comment: CT 上可見的到的特徵有 (1) mucus plugging (which may be of high attenuation), (2) central bronchiectasis, (3) tree-in-bud and ground-glass opacities, (4) mosaic attenuation due to air trapping (大部分是因為 bronchocentric granulomatosis), (5) 慢性發炎可導致 fibrosis.
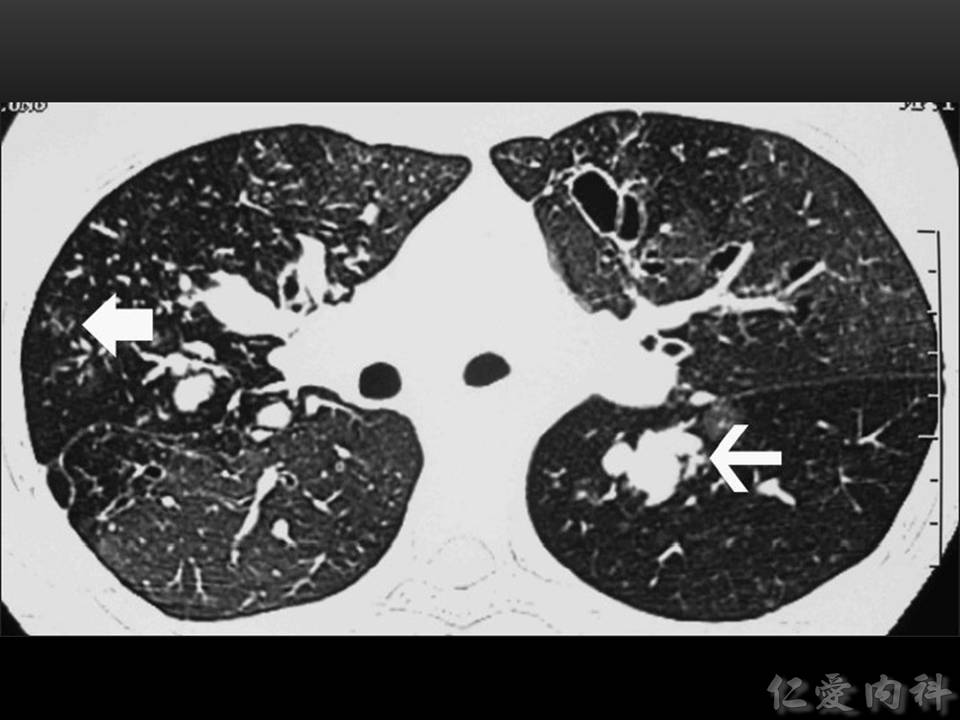
- 週邊 (right lung) 還出現一些 centrilobular nodules。

- Ian’s Comment:從 1952 年有第一篇 case series 開始,diagnostic criteria for ABPA 其實沒有明確之共識 (版本眾多),大人小孩的免疫反應也不同,發病時的 IgE level 與 eosinophils level 也不盡相同。須注意,符合的 criteria 越多,越有可能是 ABPA;但是不符合任一個 criterion (例如 peripheral eosinophilia < 1000 cells/mm3) 也不能因此排除其可能性。
-
Rosenberg-Patterson criteria
-
Major criteria (mnemonic ARTEPICS)A AsthmaR Roentgenographic fleeting pulmonary opacitiesT Skin test positive for Aspergillus (type I reaction, immediate cutaneous hyperreactivity)E EosinophiliaP Precipitating antibodies (IgG) in serumI IgE in serum elevated (1,000 IU/mL)C Central bronchiectasisS Serums A fumigatus-specific IgG and IgE (more than twice the value of pooled serum samples from patients with asthma who have Aspergillus hypersensitivity)
-
Minor criteriaPresence of Aspergillus in sputumExpectoration of brownish black mucus plugsDelayed skin reaction to Aspergillus antigen (type III reaction)The presence of six of eight major criteria makes the diagnosis almost certain; the disease is further classified as ABPA-S (seropositive) orABPA-CB (central bronchiectasis) on the absence or presence of central bronchiectasis, respectively
-
Minimal diagnostic criteria for ABPA
-
Minimal ABPA-CBAsthmaImmediate cutaneous hyperreactivity to Aspergillus antigensCentral bronchiectasisElevated IgERaised A fumigatus-specific IgG and IgE
-
Minimal ABPA-SAsthmaImmediate cutaneous hyperreactivity to Aspergillus antigensTransient pulmonary infiltrates on chest radiographElevated IgERaised A fumigatus-specific IgG and IgE
-
-
Ref: Chest. 2009 Mar;135(3):805-826
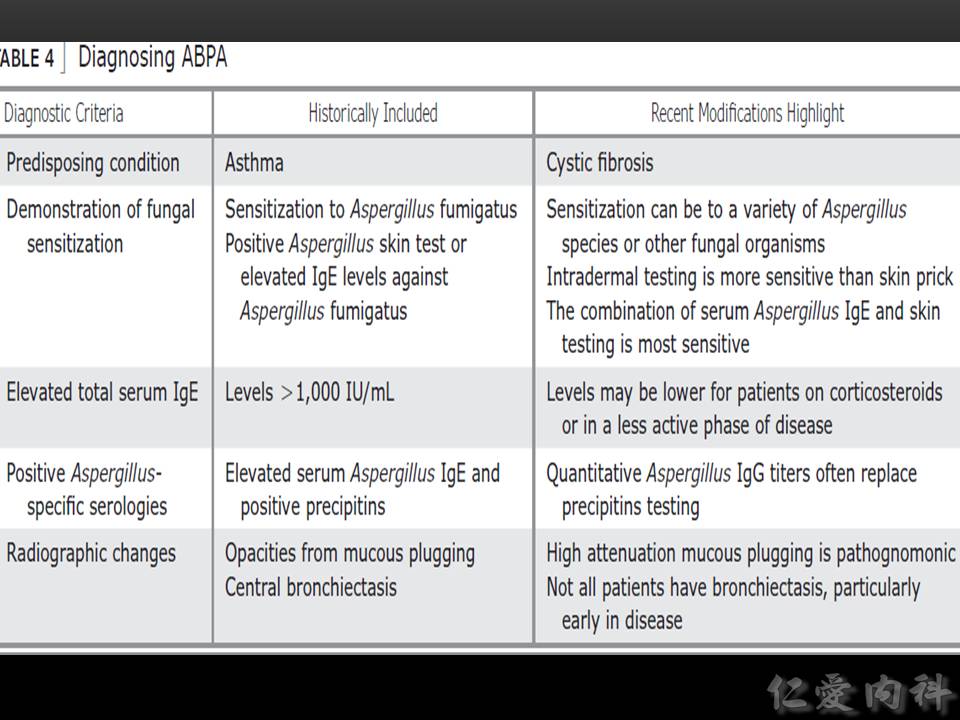
Ian’s comment: 診斷不需要 bronchoscopic findings,也不仰賴 biopsy。如果有進行這兩項檢查,則有可能在 airways 見到 fungal hyphea 但很少見到 invasion into tissue。

- 治療需以類固醇為主。
- Ian’s comment: corticosteroids with a prolonged taper; 可考慮 16 weeks of antifungal therapy; 也可使用 omalizumab 治療 refractory asthma in ABPA (IgE elevation); 50% reduction in IgE levels 表示對治療有反應。
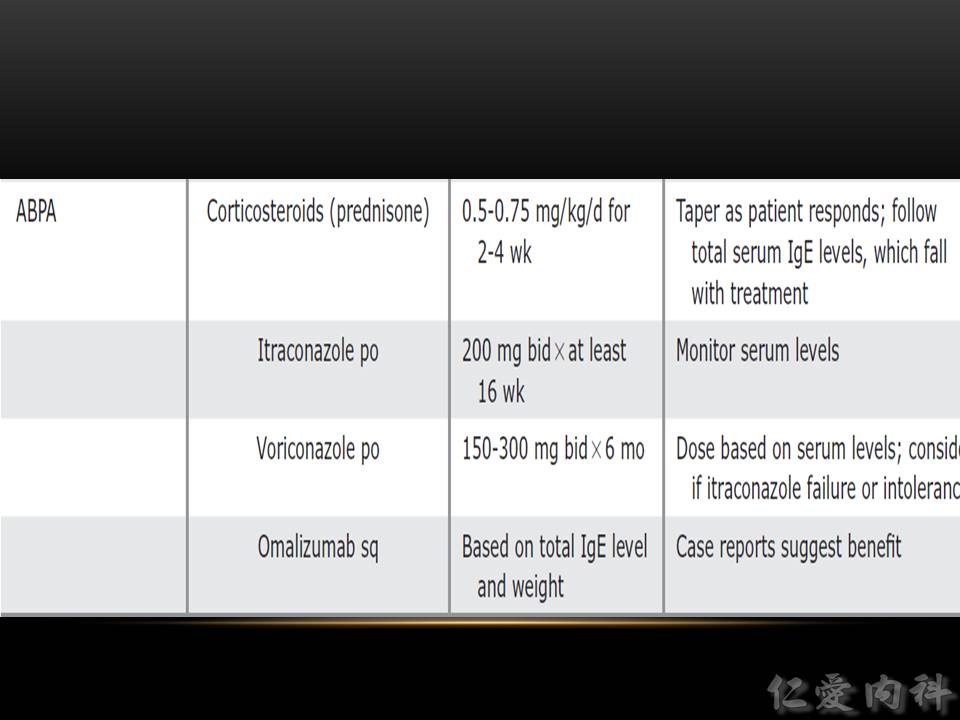
- 加上抗黴菌藥可以縮短類固醇使用時間。



Ian’s question: 一個規則使用氣喘藥物卻長期控制不佳的氣喘病人,因為在小醫院發現 eosinophilia 與胸部 X 光片異常,尋求轉診至貴院進一步 survey,你覺得該患者最有可能患有哪兩個疾病? 你如何從 history taking 與 physical examination 區別這兩個疾病?
Answer:
This patient may have ABPA or eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (formerly, Churg-Strauss syndrome). Both conditions are with eosinophilia, asthma, and abnormal imaging. But patients with Churg-Strauss syndrome tend to have some components of vasculitis and extrapulmonic involvement, such as mononeuritis multiplex and the radiographic findings are more often nonspecific ground-glass or tree-in-bud opacities.
